Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
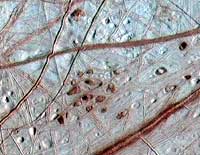
Colorado U. space team studying water, ice and potential life on Jupiter moon, Europa
The oozing of glacial material in the floating ice shell on Jupiter’s moon Europa has important implications for future exploration of the enigmatic moon and prospects of life in its ice-covered ocean, according to a University of Colorado at Boulder professor.
Robert Pappalardo, an assistant professor in the astrophysical and planetary sciences department and one of the world’s foremost Europa experts, said the icy moon is believed to contain an ocean some 13 miles under its icy

Through a light, darkly
A British physicist has come up with a way to reveal the shifting and shining colours that form in the dark spots where light waves interfere with each other. The patterns await experimental demonstration but computer-generated images are already illuminating new aspects of light that had until now remained in the shadows.
When two waves meet their peaks and troughs interfere. If the peaks are in phase you get a higher peak as the energies of each wave add together, two troughs take away from eac

Galaxy Merger Leaves Behind Telltale Blue Arc
Astronomers have identified the vivid scar of a cosmic catastrophe: a blue arc thousands of light years long produced when a galaxy pulled in a smaller satellite galaxy and tore it apart.
The streak is composed of clusters of young blue stars that formed as the larger galaxy, Centaurus A, absorbed the smaller galaxy about 200 million to 400 million years ago. Researchers will report in the December Astronomical Journal that their discovery suggests absorption of smaller galaxies may be a sig

Zooming star points to supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way
Supermassive black holes – the name given to black holes whose mass is more than 1,000,000 times the mass of the sun – can be found at the center of many galaxies. Scientists from the Weizmann Institute of Science, the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics, and several institutions in France have succeeded in tracking a star racing around a dark mass at the center of our galaxy. This achievement offers more support for the widely held view that the dark mass is a supermassive black hole.

Surfing a Black Hole
An international team of astronomers [2], lead by researchers at the Max-Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics (MPE), has directly observed an otherwise normal star orbiting the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way Galaxy.
Ten years of painstaking measurements have been crowned by a series of unique images obtained by the Adaptive Optics (AO) NAOS-CONICA (NACO) instrument [3] on the 8.2-m VLT YEPUN telescope at the ESO Paranal Observatory. It turns out that earli

Exploding star takes astronomers by surprise
A partially exploding star, known as a nova, has recovered more quickly than expected, say scientists who have analysed new data from the ESA`s XMM-Newton X-ray satellite.
Nova explosions are not completely destructive phenomena. In fact, after an explosion occurs, the star recovers and starts shining again. Until now, astronomers have not known how long this process takes. In this case, however, the exploding star recovered in less than three years. This is surprising, given the fact that t