Could black holes help explain high-energy cosmic radiation? The universe is full of different types of radiation and particles that can be observed here on Earth. This includes photons across the entire range of the electromagnetic spectrum, from the lowest radio frequencies all the way to the highest-energy gamma rays. It also includes other particles such as neutrinos and cosmic rays, which race through the universe at close to the speed of light. Curiously, “cosmic rays” are not actually rays…

Researchers at Heriot-Watt University have made a ground-breaking discovery paving the way for a transformative era in photonic technology. For decades, scientists have theorised the possibility of manipulating the optical properties of light by adding a new dimension—time. This once-elusive concept has now become a reality thanks to nanophotonics experts from the School of Engineering and Physical Sciences in Edinburgh, Scotland. The team’s breakthrough emerged from experiments with nanomaterials known as transparent conducting oxides (TCOs) – a special glass capable…

A team of researchers from the University of Ottawa has made significant strides in understanding the ionization of atoms and molecules, a fundamental process in physics that has implications for various fields including x-ray generation and plasma physics. Think about atoms – the building blocks of everything around us. Sometimes, they lose their electrons and become charged particles (that’s ionization). It happens in lightning, in plasma TVs, and even in the northern lights. Until now, scientists thought they could only…

We all know someone who seems to defy aging—people who look younger than their peers despite being the same age. What’s their secret? Scientists at Osaka University (Japan) may have found a way to quantify this difference. By incorporating hormone (steroid) metabolism pathways into an AI-driven model, they have developed a new system to estimate a person’s biological age a measure of how well their body has aged, rather than just counting the years since birth. Using just five drops…
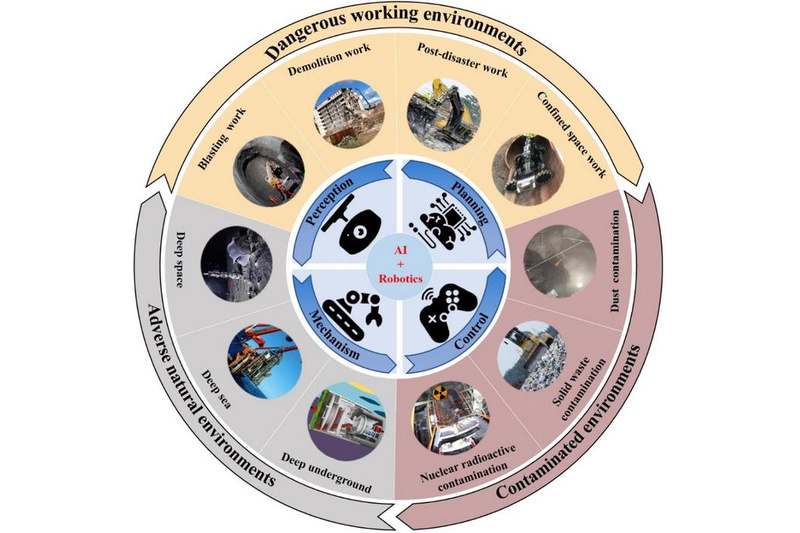
As the new wave of technological revolution and industrial transformation progresses, scientific research is expanding towards the macroscopic, delving into the microscopic, and advancing into extreme conditions, which becoming the developmental trends at the forefront of global science and technology. With the implementation of national strategies such as the high-quality development of green and low-carbon, China faces a series of new scientific and technological challenges in the field of construction under extreme environments. Among these, construction robotics in extreme environments,…

As the planet warms, Antarctica’s ice sheet is melting and contributing to sea-level rise around the globe. Antarctica holds enough frozen water to raise global sea levels by 190 feet, so precisely predicting how it will move and melt now and in the future is vital for protecting coastal areas. But most climate models struggle to accurately simulate the movement of Antarctic ice due to sparse data and the complexity of interactions between the ocean, atmosphere, and frozen surface. In…

Lunar Magnetotelluric Sounder to characterize Moon’s mantle Just hours after touching down on the surface of the Moon on March 2 aboard Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost 1 lander, the Southwest Research Institute-led Lunar Magnetotelluric Sounder (LMS) was activated and deployed its five sensors to study the Moon’s interior by measuring electric and magnetic fields. The LMS instrument is the first extraterrestrial application of magnetotellurics. “For more than 50 years, scientists have used magnetotellurics on Earth for a wide variety of…

Advancing the search for weird life on weird planets Scientists have identified a promising new way to detect life on faraway planets, hinging on worlds that look nothing like Earth and gases rarely considered in the search for extraterrestrials. In a new Astrophysical Journal Letters paper, researchers from the University of California, Riverside, describe these gases, which could be detected in the atmospheres of exoplanets — planets outside our solar system — with the James Webb Space Telescope, or JWST….

Gemini North’s MAROON-X instrument finds evidence for four mini-Earth exoplanets around our famous cosmic neighbor Barnard’s Star For a century, astronomers have been studying Barnard’s Star in the hope of finding planets around it. First discovered by E. E. Barnard at Yerkes Observatory in 1916, it is the nearest single star system to Earth [1]. Barnard’s Star is classified as a red dwarf — low-mass stars that often host closely-packed planetary systems, often with multiple rocky planets. Red dwarfs are extremely numerous in the Universe, so scientists…

University of Arizona astronomers have learned more about a surprisingly mature galaxy that existed when the universe was just less than 300 million years old – just 2% of its current age. What Does the James Webb Telescope Tell Us About the Universe? Ever since the launch of the James Webb Telescope, it has sailed across the starry universe, discovering galaxies formed around thirteen billion years ago—almost the inception of time itself! It possesses advanced infrared capabilities, much more evolved…

CAM is proposed to highlight the class-related activation regions for an image classification network, where feature positions related to the specific object class are activated and have higher scores while other regions are suppressed and have lower scores. For specific visual tasks, CAM can be used to infer the object bounding boxes in weakly-supervised object location(WSOL) and generate pseudo-masks of training images in weakly-supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS). Therefore, obtaining the high-quality CAM is very important to improve the recognition performance…

Computer simulations reveal how water separates into high-density and low-density liquids Water is unique. It is one of the only substances that can exist in nature as a solid, liquid and gas at the same time under ambient conditions (think of solid ice over a pond, which is liquid underneath while storm clouds float overhead). It is also one of the only substances whose solid form is less dense than its liquid — this is why ice floats. Now scientists…

Cutting-edge observations of Centaurus Cluster shine new light on evolving universe The XRISM collaboration have discovered flows of hot gas in the core of the Centaurus Cluster. By comparing state-of-the-art X-ray measurements from the XRISM satellite with numerical simulations, they showed this is evidence for collisions between galaxy clusters, causing gas inside to “slosh”. This solves the longstanding mystery of how cluster cores stay hot, and sheds light on how our universe continues to evolve. Astronomers have long envisioned how…
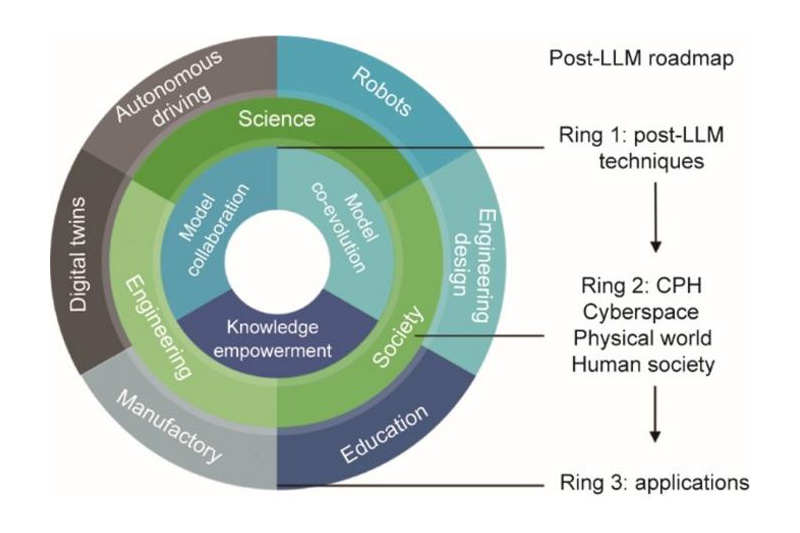
A recent paper published in the journal Engineering delves into the future of artificial intelligence (AI) beyond large language models (LLMs). LLMs have made remarkable progress in multimodal tasks, yet they face limitations such as outdated information, hallucinations, inefficiency, and a lack of interpretability. To address these issues, researchers explore three key directions: knowledge empowerment, model collaboration, and model co-evolution. Knowledge empowerment aims to integrate external knowledge into LLMs. This can be achieved through various methods, including integrating knowledge into training objectives,…

EP’s cutting-edge instruments and international collaboration drive new discoveries in transient and multi-messenger astronomy The Science White Paper for the Einstein Probe (EP) mission has been published in Science China: Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy. This mission, spearheaded by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) in collaboration with the European Space Agency (ESA), the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics (MPE), and the French National Centre for Space Studies (CNES), is poised to advance the field of time-domain and X-ray astronomy…

Hyperspectral imaging and AI can identify individuals using blood vessels in palms Hyperspectral imaging is a technology that detects slight differences in color to pinpoint the characteristics and conditions of an object. While a normal camera creates images using red, green, and blue, a hyperspectral camera can obtain over 100 images in the visible to near-infrared light range in a single shot. As a result, hyperspectral imaging can obtain information that the human eye cannot see. Specially Appointed Associate Professor…

New method to detect life makes Mars sample return protocols rock solid Within the next decade, space agencies plan to bring samples of rock from Mars to Earth for study. Of concern is the possibility these samples contain life, which could have unforeseen consequences. Therefore, researchers in this field strive to create methods to detect life. For the first time, researchers, including those from the University of Tokyo and NASA, successfully demonstrated a method to detect life in ancient rocks…