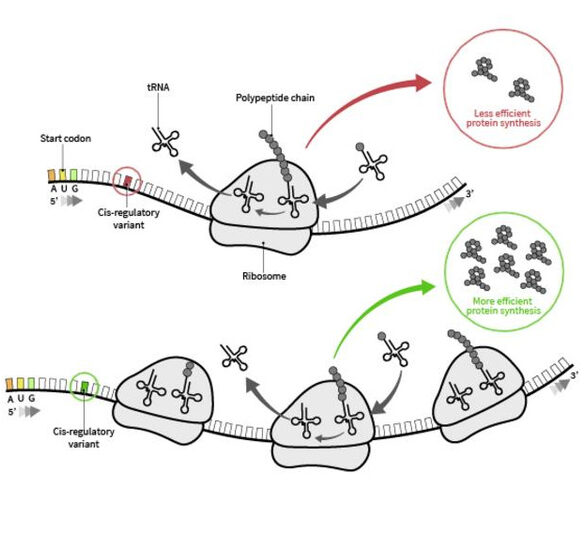
An innovative artificial intelligence approach enhances medication and vaccine discovery by forecasting the efficacy of certain mRNA sequences in protein synthesis across different cell types. The recent advancement, created through a collaboration between The University of Texas at Austin and Sanofi, facilitates the prediction of protein production in cells, thereby reducing the necessity for trial-and-error research and expediting the development of the next generation of mRNA treatments. Messenger RNA (mRNA) encodes directives for protein synthesis, facilitating bodily growth and the…
Psychological and philosophical research has consistently demonstrated that an individual’s subjective moods and emotions profoundly influence their perception of life’s significance. Philosopher Matthew Ratcliffe noted that an individual’s mood significantly influences perception and is crucial in shaping their understanding of life’s meaning. Empirical studies in psychology have examined the influence of mood on the perception of life’s purpose. Phenomenology has demonstrated that the embodied, first-person experience significantly shapes our perception of the world. In related disciplines, the notions of affordance,…
Synopsis A research team led by Professor Akihiko Nakamura from the Research Institute of Green Science and Technology at Shizuoka University, in collaboration with Researchers Takashi Matsuzaki and Toshiyuki Saeki from Kirin Holdings Co., Ltd., Professor Ryota Iino from the Institute for Molecular Science, and Professor Nobuyasu Koga from the Institute for Protein Research at Osaka University, has successfully engineered a novel PET hydrolase enzyme, PET2-21M, significantly enhancing the biodegradation of bottle-grade polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastics. Significant activity was also…
Recent research elucidates how our brains are inherently attracted to and recognise faces in many contexts. Experiencing the phenomena of face pareidolia occurs when one perceives faces or human-like expressions in ordinary items. A recent study conducted by the University of Surrey has examined how this phenomena captures our attention, perhaps offering insights for advertising in the promotion of future items. The research, published in i-Perception, examined the distinctions between attention directed by averted gazes—when an individual looks away from…

Study reveals new information about how to prevent chronic inflammation from zombie-like cells that accumulate with age In humans and other multicellular organisms, cells multiply. This defining feature allows embryos to grow into adulthood, and enables the healing of the many bumps, bruises and scrapes along the way. Certain factors can cause cells to abandon this characteristic and enter a zombie-like state known as senescence where they persist but no longer divide to make new cells. Our bodies can remove…

University of Arizona neuroscientists studying the brains of songbirds have found that aging alters the gene expressions that control the birds’ song. The finding could lead to earlier diagnoses and better treatments for human neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease, which are known to hinder vocal production in their early stages. The study, published in the journal Neurobiology of Aging, found that networks of interacting genes, in a region of the bird’s brain involved with singing, dramatically…

A new type of antibody which stimulates the immune system to target cancer cells slows tumor growth, according to new research Antibody treatment which activates the patient’s own immune system against cancer, known as immunotherapy, is increasingly being investigated as an alternative for chemotherapy and radiotherapy. This is because it specifically targets the cancer cells, which reduces the side effects seen with more conventional therapies. Tumours, such as some breast and ovarian cancers, can express the marker HER2. HER2 is…

Gemini North’s MAROON-X instrument finds evidence for four mini-Earth exoplanets around our famous cosmic neighbor Barnard’s Star For a century, astronomers have been studying Barnard’s Star in the hope of finding planets around it. First discovered by E. E. Barnard at Yerkes Observatory in 1916, it is the nearest single star system to Earth [1]. Barnard’s Star is classified as a red dwarf — low-mass stars that often host closely-packed planetary systems, often with multiple rocky planets. Red dwarfs are extremely numerous in the Universe, so scientists…

Study links genetics, vision and neural processing to mating behavior in Heliconius butterflies A simple neural change alters mating preferences in male butterflies, aiding rapid behavioral evolution, Nicholas VanKuren and Nathan Buerkle at the University of Chicago, US, and colleagues, report March 11th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology. Heliconius are a group of tropical butterflies known for their wide variety of wing patterns and colors, which act as a warning to predators. Because wing coloration is crucial for their…

Understanding children’s subjective experiences through color As a child, did it ever occur to you that your perception of color differed from that of others? It’s quite common to have this thought, but it turns out that the human color experience may be more universal than we previously believed. In psychology and neuroscience, the relationship between subjective experience, such as how we perceive color, and physical brain activity has remained an unresolved problem. Furthermore, due to their limited language abilities,…

University of Arizona astronomers have learned more about a surprisingly mature galaxy that existed when the universe was just less than 300 million years old – just 2% of its current age. What Does the James Webb Telescope Tell Us About the Universe? Ever since the launch of the James Webb Telescope, it has sailed across the starry universe, discovering galaxies formed around thirteen billion years ago—almost the inception of time itself! It possesses advanced infrared capabilities, much more evolved…

Physics professor J. Ping Liu helps boost nation’s energy security and advance toward a world-class magnet research hub University of Texas at Arlington physics Professor J. Ping Liu has won the 2025 Hill Prize in Physical Sciences for pioneering new ways to design magnets that power high-tech devices. Awarded by the Texas Academy of Medicine, Engineering, Science and Technology (TAMEST) and Lyda Hill Philanthropies, the prize recognizes groundbreaking innovations with the potential for real-world impact. Dr. Liu shares the award as co-principal…
The scientific team led by Dr. Miloslav Polášek at IOCB Prague has come up with a technique to separate and purify rare earth elements (lanthanides). These are critical to industries ranging from electronics and medicine to automotive and defense. This novel method enables the extraction of metals like neodymium and dysprosium from used neodymium magnets. It is an important component in electric vehicles and wind turbines. Eco-Friendly and Solvent-Free Process Unlike conventional methods that rely on harsh chemicals and generate…

Research from Carnegie Mellon’s School of Computer Science suggests prompt engineering could be as important as coding Today’s generative artificial intelligence models can create everything from images to computer applications, but the quality of their output depends largely on the prompt a human user provides. Carnegie Mellon University researchers have proposed a new approach for teaching everyday users how to create these prompts and improving their interactions with generative artificial intelligence models. The method, called Requirement-Oriented Prompt Engineering (ROPE), shifts…

A new quantum random number generator is almost 1000 times faster than other generators and much smaller, promising to change data management and cybersecurity in several industries including health, finance, and defense A joint team of researchers led by scientists at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) and King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (KACST) has reported the fastest quantum random number generator (QRNG) to date based on international benchmarks. The QRNG, which passed the required randomness…

Very secure and highly efficient: encryption and decryption with luminescent perovskites To guarantee high data security, encryption must be unbreakable while the data remains rapidly and easily readable. A novel strategy for optical encryption/decryption of information has now been introduced in the journal Angewandte Chemie by a Chinese research team. It is based on compounds with carefully modulated luminescent properties that change in response to external stimuli. The compounds are hybrid two-dimensional organic-inorganic metal-halide perovskites, whose structure consists of inorganic…

Researchers at the University of Utah’s Department of Psychiatry and Huntsman Mental Health Institute today published a paper introducing RiskPath, an open source software toolkit that uses Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) to predict whether individuals will develop progressive and chronic diseases years before symptoms appear, potentially transforming how preventive healthcare is delivered. XAI is an artificial intelligence system that can explain complex decisions in ways humans can understand. The new technology represents a significant advancement in disease prediction and prevention…
Bedtime procrastination in young adults is associated with negative emotions DARIEN, IL – A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2025 annual meeting found that bedtime procrastination in young adults is associated with specific personality traits, including depressive tendencies. Results show that bedtime procrastination was associated with higher neuroticism and lower conscientiousness and extraversion. These results remained significant after statistically adjusting for chronotype. “Our study demonstrated that individuals who habitually procrastinate their bedtime were actually less likely to…

Astronomers may have caught a young planet in the process of forming, sculpting its surroundings within a disc of gas and dust encircling its host star. Using the European Southern Observatory’s (ESO) Very Large Telescope (VLT), researchers observed striking spiral arms in a protoplanetary disc — and for the first time, found evidence of a planet candidate nestled within such a spiral. “We will never witness the formation of Earth, but here, around a young star 440 light-years away, we…

Osaka, Japan – A research team at the University of Osaka has introduced a groundbreaking approach to generating ultrahigh magnetic fields using a technique known as bladed microtube implosion (BMI). By leveraging laser-driven implosions of specially structured microtubes, the team has demonstrated the potential to reach magnetic field strengths nearing one megatesla—a remarkable leap in compact plasma science. These extreme fields, theoretically comparable to those observed near highly magnetized neutron stars and astrophysical jets, are created using a compact experimental…

Astronomers have identified a colossal exoplanet, measuring between three and ten times the size of Jupiter, concealed behind the swirling disc of gas and dust encircling a nascent star. Previous investigations of the star MP Mus indicated that it existed in isolation, devoid of any orbiting planets, encircled by a uniform cloud of gas and dust. However, a further analysis of MP Mus using a combination of data from the European Space Agency’s Gaia mission and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter…

The NSF-DOE Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile has unveiled the very first “mega” images of the cosmos obtained thanks to the extraordinary features and wide-field view of its LSST camera—the largest in the world. The camera took nearly two decades to build and involved hundreds of scientists across the globe, including a number of CNRS teams. The world-wide First Look unveiling event is held on 23 June at the National Academy of Sciences in Washington, D.C. The impressive, car-sized…

COLUMBUS, Ohio – Chemists have unveiled a groundbreaking method to generate a wide range of highly useful chemical building blocks using metal carbenes, according to new research. Carbenes—short-lived, highly reactive carbon atoms—are crucial in chemical reactions involved in drug synthesis and materials science. However, creating carbenes in the lab has traditionally been a challenge due to the hazardous and limited methods available. A team at The Ohio State University has now discovered a significantly easier way to produce metal carbenes.“Our…

A recent study published in the Annals of the Entomological Society of America provides the most comprehensive insight to date into the development of this atypical fly and its live birth—a uncommon occurrence among flies. Undergraduate student Parker Henderson ‘22 from St. Olaf College spearheaded the project, which unveiled significant findings regarding the reproductive biology of Ormia ochracea, a parasitic fly renowned for its hyperacute directional hearing that enables it to locate chirping crickets. The scientists utilised dissection, fluorescence labelling,…

Researchers at Osaka Metropolitan University have elucidated a longstanding enigma in sonochemistry: the reason chemical reactions decelerate when ultrasonic power is very high. Their discoveries facilitate more intelligent use of ultrasound in scientific and industrial contexts, including environmental remediation and the synthesis of beneficial nanoparticles. Science Behind Ultrasound and Chemical Reactions Despite being imperceptible to the human ear, ultrasonography significantly influences sonochemistry. Ultrasonic waves applied to a liquid produce small bubbles that swiftly expand and disintegrate, a phenomenon known as…

Quantum computers encounter a significant obstacle in their pursuit of practical applications: their constrained capacity to rectify emerging computational mistakes. To create genuinely dependable quantum computers, researchers must replicate quantum calculations on classical computers to validate their accuracy – an essential yet exceptionally challenging endeavour. Researchers from Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden, the University of Milan, the University of Granada, and the University of Tokyo have introduced a pioneering method for simulating particular forms of error-corrected quantum computations, marking…

Synopsis A research team led by Professor Akihiko Nakamura from the Research Institute of Green Science and Technology at Shizuoka University, in collaboration with Researchers Takashi Matsuzaki and Toshiyuki Saeki from Kirin Holdings Co., Ltd., Professor Ryota Iino from the Institute for Molecular Science, and Professor Nobuyasu Koga from the Institute for Protein Research at Osaka University, has successfully engineered a novel PET hydrolase enzyme, PET2-21M, significantly enhancing the biodegradation of bottle-grade polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastics. Significant activity was also…
![[1] Key Research Findings on Transfer-Printed Alumina–Gold Dual-layer Protective Coating](https://www.innovations-report.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/Transfer_printing_technology_for_lithium_protectiv_1753252750-e1753252940671-362x245.jpg)
A research team in South Korea has created an innovative transfer printing process that applies protective thin layers to lithium metal surfaces, addressing the persistent dendrite problem affecting next-generation lithium-metal batteries. Dr. Jungdon Suk’s team at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT) has successfully applied hybrid protective layers made of solid polymers and ceramics onto lithium metal through a solvent-free method. This process allows for uniform coating over extensive regions without compromising the reactive lithium surface, representing a…

MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (07/18/2025) — Researchers at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities have uncovered a promising path to make computer memory faster and far more energy-efficient through the use of a novel material, according to a recent study published in Advanced Materials. The university team has also filed a patent for this technology. As technology evolves, the need for more efficient memory continues to grow. Scientists are actively exploring advanced materials that can support higher performance with lower…

Coordination nanosheets—two-dimensional materials made by linking metal ions with organic ligands—have captured attention in recent years due to their remarkable conductivity, redox activity, and catalytic performance. They are especially useful in areas such as energy storage, sensors, and electronics. However, producing these nanosheets, particularly heterometallic ones (which contain two or more metal ions), has traditionally relied on a complex two-phase interfacial reaction and lacked precise structural control. Addressing this challenge, a team led by Professor Hiroshi Nishihara from the Research…

At the onset of the millennium, a consortium of distinguished scientists commenced the compilation of a list of risks they deemed most probable to affect the world’s rocky shorelines in the ensuing twenty-five years. Published in 2002, it contained predictions that, among other aspects, pollution from oil spills would diminish, the prevalence of invasive species worldwide would increase, genetically-modified organisms would adversely affect the ocean, and the repercussions of global climate change would intensify. After 25 years, the original academics,…

People’s intuitive assessments of biodiversity based on visual and auditory stimuli are very accurate and closely match science assessments of biodiversity. Based on a new study from the British Ecological Society that came out in the magazine People and Nature. Researchers from the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv), the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ), and Friedrich Schiller University Jena recently did a study where people who had never studied ecology had to sort pictures and sounds of…

The forecast is bright for future, long-term multiband monitoring of planets Imaging data from Japan’s Himawari-8 and -9 meteorological satellites have been successfully used to monitor temporal changes in Venus’ cloud-top temperature, revealing unseen patterns in the temperature structure of various waves. A team led by the University of Tokyo collated infrared images from 2015–25 to estimate brightness temperatures on day to year scales. The results demonstrate that meteorological satellites can serve as additional eyes to access the Venusian atmosphere…

Chipmunk and vole skulls from over 125 years reflect changes in diet and noise exposure In general, evolution is a long, slow process of tiny changes passed down over generations, resulting in new adaptations and even new species over thousands or millions of years. But when living things are faced with dramatic shifts in the world around them, they sometimes rapidly adapt to better survive. Scientists recently found an example of evolution in real time, tucked away in the collection…