
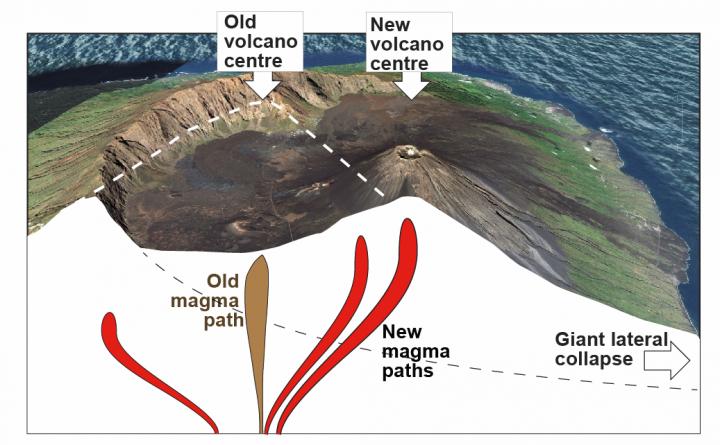
Giant lateral volcano collapses affects the deep paths of magma. This process can be seen at Fogo Volcano, Cabo Verde.
Credit: Fig. GFZ/Walter
Giant lateral collapses may change the style of volcanism and the chemistry of magma, and as a new study by GFZ scientists reveals, also affects and diverges the deep paths of magmas.
New volcano centres may form at other places, which the scientists explain by studying the stress field changes associated with the lateral collapse.
In the study entitled “The effect of giant lateral collapses on magma pathways and the location of volcanism”, authored by F. Maccaferri, N. Richter and T. Walter, all working at GFZ, in section 2.1 (Physics of earthquakes and volcanoes), the propagation path of magmatic intrusions underneath a volcanic edifice has been simulated by means of a mathematical model.
Computer simulations revealed that the mechanical effect on the earth crust resulting from a large lateral collapse, can promote the deflection of deep magmatic intrusions, favouring the formation of a new eruptive centre within the collapse embayment.
This result has been quantitatively validated against observations at Fogo Volcano, Cabo Verde.
A broader view to other regions reveals that this shift of volcanism associated with giant lateral collapses is rather common, as observed at several of the Canary Islands, Hawaii, Stromboli and elsewhere.
This study may have implications particularly for our understanding of the long term evolution of intraplate volcanic ocean islands and sheds lights on the interacting processes occurring during growth and collapse of volcanic edifices.












