
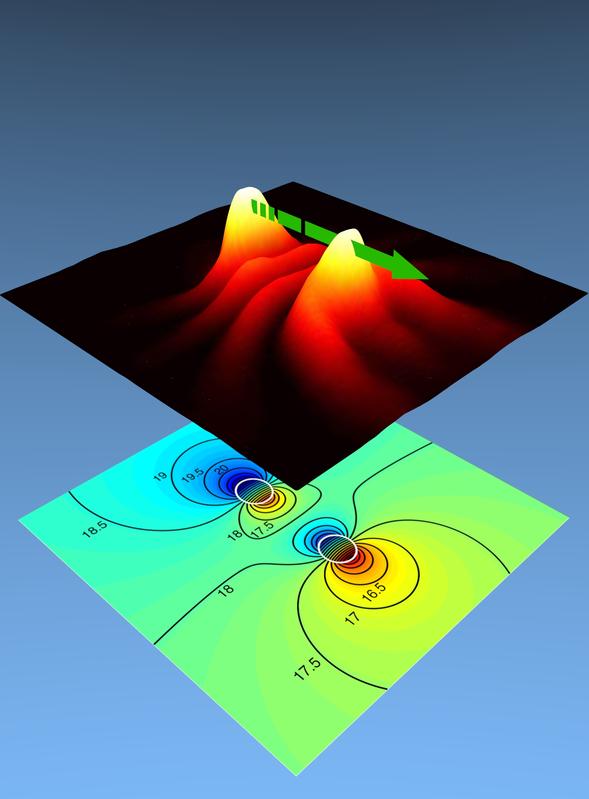
focused spin wave beams
University of Gothenburg
Unfortunately, such nanoscale microwave oscillators suffer from an unbearably low power and high phase noise. It is generally accepted that one of the most attractive ways to solve this issue is to synchronize a large number of these nanoscopic oscillators in order to limit the detrimental influence of thermal energy.
The synchronization of two such oscillators was first published in 2005. However, by 2013 the number of synchronized oscillators had only increased to four low-frequency oscillators and three microwave-frequency oscillators. Furthermore, the coupling was difficult to control in a reproducible manner.
PhD student Afshin Houshang and his supervisor Dr. Randy Dumas in Professor Johan Åkerman's team have now succeeded in demonstrating that it is possible to create and utilize focused beams of spin waves to (i) synchronize oscillators over much larger distances than shown previously and (ii) robustly synchronize a record number of oscillators.
In their article, published in Nature Nanotechnology, they synchronize five oscillators and demonstrate the resulting improvement in the oscillator quality.
Because we now know how to control the spin wave propagation, there is really no limit to how many oscillators we can now synchronize, said Randy Dumas, who sees great potential in several research areas.
Since the direction of the spin wave beam can also be tailored via electrical current through the oscillator and via an external magnetic field, the results will also have a major impact in the burgeoning field of spin wave based electronics, termed magnonics. By changing the direction of the beam, one can choose which oscillators synchronize and thereby control the flow of information in magnonic circuits in a way that was not possible before.
The results also open up new opportunities for fundamental studies of networks of strongly nonlinear oscillators where an array of perhaps a hundred such oscillators in different geometric architectures can be externally controlled and studied in detail.
We hope to use these and similar components for extremely fast neuromorphic calculations based on oscillator networks explains Randy.
Contacts:
Johan Åkerman, Professor at the University of Gothenburg, Physics Department.
+46 70-710 4360, johan.akerman@physics.gu.se
http://science.gu.se/english/News/News_detail/?languageId=100001&contentId=1…












