Osaka, Japan – A research team at the University of Osaka has introduced a groundbreaking approach to generating ultrahigh magnetic fields using a technique known as bladed microtube implosion (BMI). By leveraging laser-driven implosions of specially structured microtubes, the team has demonstrated the potential to reach magnetic field strengths nearing one megatesla—a remarkable leap in compact plasma science. These extreme fields, theoretically comparable to those observed near highly magnetized neutron stars and astrophysical jets, are created using a compact experimental…

New theory shows that high performance needn’t mean high risk.
For man-made systems such as machines and markets, catastrophe lurks somewhere between high risk and high performance. US physicists may have found a way to strike the optimal balance 1 .
This trade-off is familiar to the financial world. Brokers develop investment portfolios to provide the best returns within a specified level of risk. Mark Newman and co-workers at the Santa Fe Institute in New M

Community and Member Feedback Shapes New Royalty-Free Draft
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) today published a revised Patent Policy Working Draft which is based on strong, explicit commitments to producing Royalty-Free (RF) specifications. To achieve the goal of producing Royalty-Free specifications, the draft requires all who participate in the development of W3C Recommendations to make any essential patents they hold available for free.
The option which would have permi

Chase a fast-moving comet, land on it and ’ride’ it while it speeds up towards the Sun: not the script of a science-fiction movie, but the very real task of ESA’s Rosetta spacecraft.
New observations with the European Southern Observatory’s (ESO) Very Large Telescope (VLT) provide vital information about Comet Wirtanen – Rosetta’s target – to help ESA reduce uncertainties in the mission, one of the most difficult ever to be performed.
Every 5.5 years Comet Wirtanen completes an o

The Sagittarius dwarf galaxy is our nearest neighbor. Yet it has been discovered only recently, in 1994, being hidden by the stars and dust in our own Galaxy, the Milky Way. It is however possible today to better know this companion galaxy, thanks to variable stars, the RR Lyrae, in which Sgr-dw is particularly rich. In a recent paper, Patrick Cseresnjes, from Paris Observatory, shows for the first time that Sgr-dw is not typical of other satellites of the Milky Way, but reveals instead striking simi

During the night of 28 February/1 March, Envisat, ESA’s most powerful and sophisticated Earth observation satellite, will be launched by an Ariane 5 rocket from Europe’s spaceport in Kourou at 22:07 hrs Kourou time (02:07 hrs CET).
Built by a consortium of 50 companies led by Astrium, Envisat is the successor to ESA’s ERS satellites. With an array of ten instruments to monitor land, oceans, atmosphere and ice caps, it will provide the most complete set of observations ever achieved, to hel

“Nuclear fusion” is the melting of light nuclei into heavier ones, a process that according to the laws of physics releases enormous amounts of energy. For the past 50 years many scientists have sought ways of harnessing this fusion reaction under controlled reactor conditions as a safe, clean and practically inexhaustible source of energy. Siegbert Kuhn and his team at the Institute of Theoretical Physics at Innsbruck University are making a major contribution to these efforts and positioning Austri
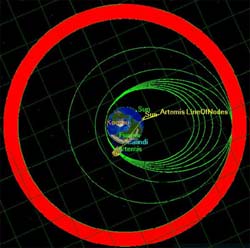
Thanks to ion propulsion, the Artemis mission is turning near-defeat into a success story. Nominal operations could start this summer, with ESA’s satellite, manufactured by Alenia Spazio as prime contractor (I), playing a significant role in the pursuit of high technology and advanced telecommunications.
On 12 July 2001, 30 minutes after lift-off from Europe’s spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana, it became apparent that the Ariane 5 launcher had propelled the Artemis satellite into a transf

Proceedings of the Royal Society Series A Vol. 458, No. 2019 Cover Date 8 March 2002
Christiaan Huygens` observations in 1665 of anti-phase synchronisation in two pendulum clocks were the subject of some of the earliest deliberations of The Royal Society but have remained a scientific puzzle. Huygens` acute observations are often quoted but have never been adequately explained – until today. The forthcoming issue of Proceedings A, a Royal Society journal, offers a simple and compelli

Researchers from the Technology Foundation STW and the University of Twente, in cooperation with Smit Transformatoren and Smit Draad, have developed a prototype coil for a superconducting transformer which is not only light and compact but also energy-efficient. A keen interest has already been expressed by several companies.
The coil is made from superconducting wires, insulated using a newly patented method. Furthermore, together with Smit Transformatoren the researchers have developed a m

In the powerful, fast-fading realm of gamma-ray bursts, scientists say they have detected for the first time a lingering afterglow of the shortest types of bursts, which themselves disappear within a second.
This afterglow, radiating in X rays, may provide crucial insight into what triggers the mysterious bursts, the most energetic explosions in the Universe, second only to the big bang in total power. Previously, scientists had only detected the afterglow of longer bursts, which can last fr

Interstellar travellers should be “motivated, tolerant and nice”.
One hundred and sixty fertile, motivated, English speakers could make it to distant stars, researchers have worked out. But generations down the line, returning voyagers may speak an alien tongue.
Travel to planets orbiting other stars will soon be technically possible, the meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Sciences in Boston heard last week. But the 200-year odyssey will require a cer

Markus Landgraf of the European Space Agency and colleagues (*) have found the first direct evidence that a bright disc of dust surrounds our Solar System, starting beyond the orbit of Saturn.
Remarkably, their discovery gives astronomers a way to determine which other stars in the Galaxy are most likely to harbour planets and allows mission planners to draw up a ’short-list’ of stars to be observed by ESA’s future planet-search missions, Eddington and Darwin.
The discovery of th

Light-sensitive ’plastic’ magnets could replace your hard drive.
A ’plastic’ magnet that responds to light could lead to new ways of storing and reading large amounts of computer data. Light would be used to store information in cheap, fast and high-capacity ’magneto-optic’ memories.
The light-switchable magnet is the first to be made from organic (carbon-based) molecules. This means its discoverers, Arthur Epstein of Ohio State University in Columbus and Joel Miller of the

After nearly 12 years of incredible scientific discoveries, the ESA/NASA Hubble Space Telescope orbiting Earth is about to have another service visit. The purpose is to upgrade Hubble system and to install newer and more powerful instruments that will astoundingly increase Hubble’s discovery capabilities and extend the longevity of the observatory.
As a unique collaboration between the European Space Agency (ESA), and NASA, Hubble has had a phenomenal scientific impact. The unsurpassed sha

A team of physicists in the United States has made an important step towards making quantum computing a reality. Research into a new type of noiseless quantum information bit, or qubit, is published today in the joint Institute of Physics and German Physical Society journal, New Journal of Physics.
At a sub-atomic scale the laws of quantum physics lead to strange new properties of matter. For several years physicists have been trying to exploit this quantum weirdness to build a new type of `

Joint work with IETF produces XML-based solution for digital signatures, foundation for Secure Web services
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) has issued XML-Signature Syntax and Processing (XML Signature) as a W3C Recommendation, representing cross-industry agreement on an XML-based language for digital signatures. A W3C Recommendation indicates that a specification is stable, contributes to Web interoperability, and has been reviewed by the W3C Membership, who favor its widespread