
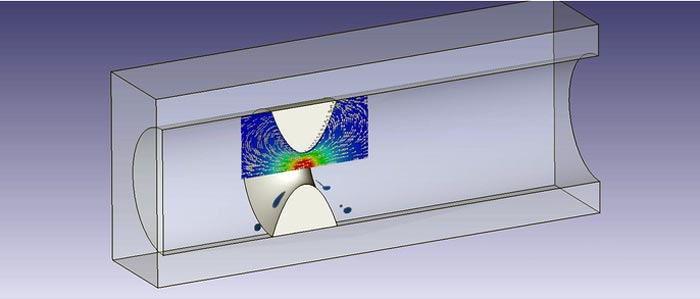
Illustration depicts the flow field and the drop breakup around antral contraction waves.
Credit: Damien Dufour
Droplet breakup shows how lower stomach contraction waves classify foods.
In efforts to fight obesity and enhance drug absorption, scientists have extensively studied how gastric juices in the stomach break down ingested food and other substances. However, less is known about how the complex flow patterns and mechanical stresses produced in the stomach contribute to digestion.
Researchers from France, Michigan, and Switzerland built a prototype of an artificial antrum, or lower stomach, to present a deeper understanding of how physical forces influence food digestion based on fluid dynamics. In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, they reveal a classifying effect based on the breakup of liquid drops combined with transport phenomena derived from complementary computer simulations.
The relevant parts of the stomach are the corpus, where food is stored; the antrum, where food is ground; and the pylorus, or pyloric sphincter, the tissue valve that connects to the small intestine. Slow-wave muscle contractions begin in the corpus, with wave speed and amplitude increasing to form the antral contraction waves (ACWs) as they propagate toward the pylorus.
The researchers’ antrum device consists of a cylinder, capped at one end to imitate a closed pylorus, and a hollow piston that moves inside the cylinder to replicate ACWs. As verified through computer simulations and experimental measurements, the protype produces the characteristics of retropulsive jet flow that exist in the antrum.
Food disintegration is quantified by determining the breakup of liquid drops in flow fields produced by ACWs. The researchers studied different model fluid systems with various viscosity to account for the broad physical properties of digested food. The drop size and other parameters resemble conditions in a real stomach.
Drop breakup occurred near the surface of the hollow piston, where the flow field exhibited slower velocities but higher strain rates, thus exposing the drop to higher shear stresses during a longer period of time. No breakup occurred for drops near the center of the piston, because the stresses and residence times are smaller and shorter.
“The results extracted from this simple prototype have deepened insights into the disintegration process that takes place in the stomach,” co-author Damien Dufour said. “Drops near the wall will break up as they are transported toward the pylorus. The drops in the center return toward the corpus, without major size reduction, to disintegrate later. One may perceive this combined action of the ACWs as a classifying effect.”
The article “Investigation of the dispersing characteristics of antral contraction wave flow in a simplified model of the distal stomach” is authored by Damien Dufour, Franz X. Tanner, Kathleen Feigl, and Erich J. Windhab. The article will appear in Physics of Fluids on Aug. 3, 2021 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0053996). After that date, it can be accessed at https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/5.0053996.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex fluids. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/phf.
DOI 10.1063/5.0053996
Article Title: Investigation of the dispersing characteristics of antral contraction wave flow in a simplified model of the distal stomach
Article Publication Date: 3-Aug-2021
Media Contact
Larry Frum
media@aip.org
Office: 301-209-3090












