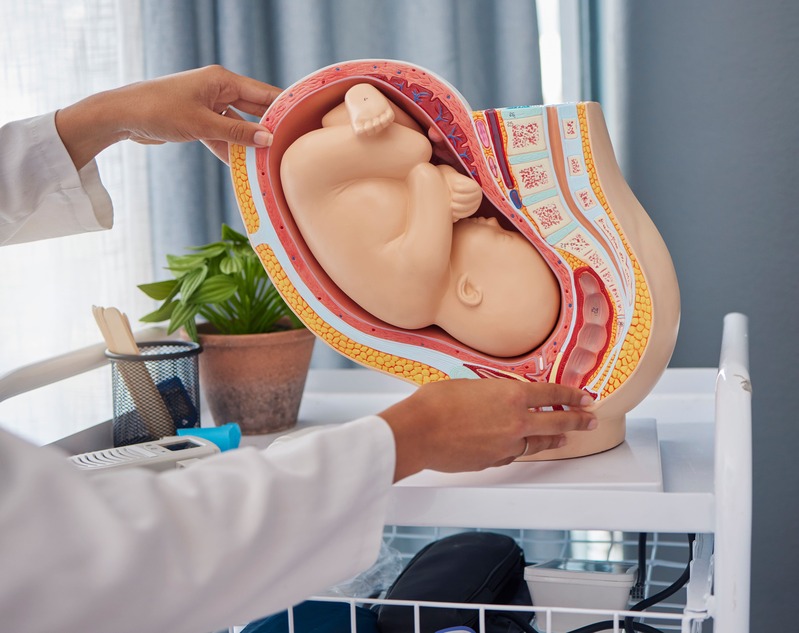
A study involving over 700 pregnant women analyzes for the first time how air pollution may affect fetal brain development Fetuses more exposed to certain air pollutants show changes in the size of specific brain structures, particularly during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. This is the main finding of a new study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a center supported by the ”la Caixa” Foundation, in collaboration with the BCNatal center (Hospital Sant Joan…
A new method improving the accuracy of interpreting blood pressure measurements taken at the ankle could be crucial for people who cannot have their arm blood pressure measured. New research from the University of Exeter Medical School, published in BMJ Open and funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR), analysed data from over 33,000 people to create a personalised predictive model for more accurately estimating arm blood pressure from ankle readings – when compared to previously…
New analysis of the remains of two ‘puppies’ dating back more than 14,000 years ago has shown that they are most likely wolves, and not related to domestic dogs, as previously suggested. The genetic analysis also proved that the cubs were sisters at the age of around two months, and like modern day wolves had a mixed diet of meat and plants. Researchers, however, were surprised to see evidence of a wooly rhinoceros as part of their last meals, as…
Leg amputation caused by arterial disease four times higher in disadvantaged areas Leg amputation rates caused by arterial disease are four times as high in the most disadvantaged areas in England. The new study, from the University of Sheffield, also found patients living in the most socioeconomically disadvantaged areas are more likely to die following leg amputation compared with those living in the least disadvantaged areas. Whilst socioeconomic disadvantage is associated with a higher risk of amputation, this new study…

Study reveals new information about how to prevent chronic inflammation from zombie-like cells that accumulate with age In humans and other multicellular organisms, cells multiply. This defining feature allows embryos to grow into adulthood, and enables the healing of the many bumps, bruises and scrapes along the way. Certain factors can cause cells to abandon this characteristic and enter a zombie-like state known as senescence where they persist but no longer divide to make new cells. Our bodies can remove…

University of Arizona neuroscientists studying the brains of songbirds have found that aging alters the gene expressions that control the birds’ song. The finding could lead to earlier diagnoses and better treatments for human neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease, which are known to hinder vocal production in their early stages. The study, published in the journal Neurobiology of Aging, found that networks of interacting genes, in a region of the bird’s brain involved with singing, dramatically…

A new type of antibody which stimulates the immune system to target cancer cells slows tumor growth, according to new research Antibody treatment which activates the patient’s own immune system against cancer, known as immunotherapy, is increasingly being investigated as an alternative for chemotherapy and radiotherapy. This is because it specifically targets the cancer cells, which reduces the side effects seen with more conventional therapies. Tumours, such as some breast and ovarian cancers, can express the marker HER2. HER2 is…

Gemini North’s MAROON-X instrument finds evidence for four mini-Earth exoplanets around our famous cosmic neighbor Barnard’s Star For a century, astronomers have been studying Barnard’s Star in the hope of finding planets around it. First discovered by E. E. Barnard at Yerkes Observatory in 1916, it is the nearest single star system to Earth [1]. Barnard’s Star is classified as a red dwarf — low-mass stars that often host closely-packed planetary systems, often with multiple rocky planets. Red dwarfs are extremely numerous in the Universe, so scientists…

Study links genetics, vision and neural processing to mating behavior in Heliconius butterflies A simple neural change alters mating preferences in male butterflies, aiding rapid behavioral evolution, Nicholas VanKuren and Nathan Buerkle at the University of Chicago, US, and colleagues, report March 11th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology. Heliconius are a group of tropical butterflies known for their wide variety of wing patterns and colors, which act as a warning to predators. Because wing coloration is crucial for their…

Understanding children’s subjective experiences through color As a child, did it ever occur to you that your perception of color differed from that of others? It’s quite common to have this thought, but it turns out that the human color experience may be more universal than we previously believed. In psychology and neuroscience, the relationship between subjective experience, such as how we perceive color, and physical brain activity has remained an unresolved problem. Furthermore, due to their limited language abilities,…

University of Arizona astronomers have learned more about a surprisingly mature galaxy that existed when the universe was just less than 300 million years old – just 2% of its current age. What Does the James Webb Telescope Tell Us About the Universe? Ever since the launch of the James Webb Telescope, it has sailed across the starry universe, discovering galaxies formed around thirteen billion years ago—almost the inception of time itself! It possesses advanced infrared capabilities, much more evolved…

Physics professor J. Ping Liu helps boost nation’s energy security and advance toward a world-class magnet research hub University of Texas at Arlington physics Professor J. Ping Liu has won the 2025 Hill Prize in Physical Sciences for pioneering new ways to design magnets that power high-tech devices. Awarded by the Texas Academy of Medicine, Engineering, Science and Technology (TAMEST) and Lyda Hill Philanthropies, the prize recognizes groundbreaking innovations with the potential for real-world impact. Dr. Liu shares the award as co-principal…
Tokyo, Japan—The COVID-19 pandemic increased public awareness of the importance of mask use for personal protection. However, when the mesh size of mask fabrics is small enough to capture viruses, which are usually around one hundred nanometers in size, the fabric typically also restricts air flow, resulting in user discomfort. But now, researchers from Japan have found a way to avoid this. In a study published this month in Materials Advances, researchers from the Institute of Industrial Science, The University…

A new quantum random number generator is almost 1000 times faster than other generators and much smaller, promising to change data management and cybersecurity in several industries including health, finance, and defense A joint team of researchers led by scientists at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) and King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (KACST) has reported the fastest quantum random number generator (QRNG) to date based on international benchmarks. The QRNG, which passed the required randomness…

Very secure and highly efficient: encryption and decryption with luminescent perovskites To guarantee high data security, encryption must be unbreakable while the data remains rapidly and easily readable. A novel strategy for optical encryption/decryption of information has now been introduced in the journal Angewandte Chemie by a Chinese research team. It is based on compounds with carefully modulated luminescent properties that change in response to external stimuli. The compounds are hybrid two-dimensional organic-inorganic metal-halide perovskites, whose structure consists of inorganic…

Researchers at the University of Utah’s Department of Psychiatry and Huntsman Mental Health Institute today published a paper introducing RiskPath, an open source software toolkit that uses Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) to predict whether individuals will develop progressive and chronic diseases years before symptoms appear, potentially transforming how preventive healthcare is delivered. XAI is an artificial intelligence system that can explain complex decisions in ways humans can understand. The new technology represents a significant advancement in disease prediction and prevention…

Researchers train AI to predict if and why proteins form sticky clumps, a mechanism linked to 50 human diseases affecting half a billion people An AI tool has made a step forward in translating the language proteins use to dictate whether they form sticky clumps similar to those linked to Alzheimer’s Disease and around fifty other types of human disease. In a departure from typical “black-box” AI models, the new tool, CANYA, was designed to be able to explain its…
Bedtime procrastination in young adults is associated with negative emotions DARIEN, IL – A new study to be presented at the SLEEP 2025 annual meeting found that bedtime procrastination in young adults is associated with specific personality traits, including depressive tendencies. Results show that bedtime procrastination was associated with higher neuroticism and lower conscientiousness and extraversion. These results remained significant after statistically adjusting for chronotype. “Our study demonstrated that individuals who habitually procrastinate their bedtime were actually less likely to…

NASA spacecraft make progress in final commissioning, preliminary science operations SAN ANTONIO — June 10, 2025 — Southwest Research Institute’s Dr. Craig DeForest discussed the latest accomplishments of NASA’s PUNCH (Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere) mission during a media event at the 246th American Astronomical Society meeting in Anchorage, Alaska. As the spacecraft constellation completes commissioning, early PUNCH data showed coronal mass ejections, or CMEs, as they erupted from the Sun and traveled across the inner solar system….

Using advanced computational modelling, a research team led by the University of Oxford, working in partnership with the Instituto Superior Técnico in the University of Lisbon, has achieved the first-ever real-time, three-dimensional simulations of how intense laser beams alter the ‘quantum vacuum’—a state once assumed to be empty, but which quantum physics predicts is full of virtual electron-positron pairs. Excitingly, these simulations recreate a bizarre phenomenon predicted by quantum physics, known as vacuum four-wave mixing. This states that the combined…

An international team of astronomers, including researchers from the University of Liège and collaborators in UK, Chile, the USA, and Europe, has discovered a giant planet orbiting the smallest known star to host such a companion The host star, TOI-6894, is a red dwarf with only 20% the mass of the Sun, typical of the most common stars in our galaxy. Until now, such low-mass stars were not thought capable of forming or retaining giant planets. But as published today…

The detection of atmospheric methane and silicon monoxide suggests that it originated in a region analogous to the Solar System’s domain of gas and ice giants. Observations with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have provided new clues about how the exoplanet WASP-121b has formed and where it might have originated in the disc of gas and dust around its star. These insights stem from the detection of multiple key molecules: water vapour, carbon monoxide, silicon monoxide, and methane. With…

Female earwigs may use their forceps as weapons too—just like males A new study from Toho University reveals that female earwigs exhibit a similar pattern of exaggerated forceps growth as males, suggesting that both sexes may have evolved these traits through sexual selection. Do larger male elk have proportionally larger antlers? The answer is no. In fact, larger individuals tend to have disproportionately larger antlers—a phenomenon known as positive allometry. This pattern, where certain body parts grow disproportionately large relative to body…

Researchers from the University of Adelaide, in collaboration with the University of Melbourne, University of Queensland and Monash University, have discovered that the genetic mechanism that determines sex in monotremes is different from all other mammals. Monotremes, which include echidnas and platypuses, differ in many aspects of their biology to all other mammals. Most distinctly, they lay eggs into a transient pouch rather than giving birth to live young. In almost all mammals, male sex-determination occurs via the SRY gene…

The elucidation of the biosynthetic pathway of ipecacuanha alkaloids shows how two distantly related plant species could develop the same substance independently Plants produce an enormous abundance of natural products. Many plant natural products are ancestry-specific and occur only in certain plant families, sometimes only in a single species. Interestingly, however, the same substances can sometimes be found in distantly related species. In most cases, however, only the end product is known and it is largely unclear how these substances…

Uncovering the genetic basis of purring in cats Kyoto, Japan — Whether you are lucky enough to have a cat companion or must merely live this experience vicariously through cat videos, Felis catus is a familiar and comforting presence in our daily lives. Unlike most other feline species, cats exhibit sociality, can live in groups, and communicate both with other cats and humans, which is why they have been humans’ trusted accomplices for millennia. Despite this intimacy, there is still…

Tokyo, Japan—The COVID-19 pandemic increased public awareness of the importance of mask use for personal protection. However, when the mesh size of mask fabrics is small enough to capture viruses, which are usually around one hundred nanometers in size, the fabric typically also restricts air flow, resulting in user discomfort. But now, researchers from Japan have found a way to avoid this. In a study published this month in Materials Advances, researchers from the Institute of Industrial Science, The University…

CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Millions of years of evolution have enabled some marine animals to grow complex protective shells composed of multiple layers that work together to dissipate physical stress. In a new study, engineers have found a way to mimic the behavior of this type of layered material, such as seashell nacre, by programming individual layers of synthetic material to work collaboratively under stress. The new material design is poised to enhance energy-absorbing systems such as wearable bandages and car…

Triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) are a transformative class of next-generation devices for energy conversion and self-powered sensing. Selecting appropriate triboelectric and conductive materials is crucial for optimizing TENG performance. In recent years, MXenes, especially Ti3C2 MXene, have become highly promising candidates for both triboelectric and conductive materials in TENGs. Although many studies (including research and review articles) have focused on TENG construction and performance, there is a significant gap in the literature: a comprehensive summary of MXene applications from a materials…

Oxygen defect engineering enables efficient sulfone production using molecular oxygen at low temperature Sulfones, a class of sulfur-containing compounds, are chemically derived from the selective oxidation of sulfides. While these compounds form the core of the pharmaceuticals, solvents and polymer industries, their chemical synthesis is often hindered by high reaction temperatures and extreme reaction conditions. Additionally, these also require costly additives and harsh solvents for production. Against this backdrop, a team of researchers from Japan introduced a new catalyst design,…

New analysis of the remains of two ‘puppies’ dating back more than 14,000 years ago has shown that they are most likely wolves, and not related to domestic dogs, as previously suggested. The genetic analysis also proved that the cubs were sisters at the age of around two months, and like modern day wolves had a mixed diet of meat and plants. Researchers, however, were surprised to see evidence of a wooly rhinoceros as part of their last meals, as…
Plant fossils found in the abdomen of a sauropod support the long-standing hypothesis that these dinosaurs were herbivores, finds a study publishing June 9 in the Cell Press journal Current Biology. The dinosaur, which was alive an estimated 94 to 101 million years ago, ate a variety of plants and relied almost entirely on its gut microbes for digestion. “No genuine sauropod gut contents had ever been found anywhere before, despite sauropods being known from fossils found on every continent…

Tiny, hardworking cleaner fish play a role in reef microbial diversity Where do you go when you’re a fish and you need a skincare treatment? Coral reefs contain natural “beauty salons,” lively social hubs of activity where fish “clients” swim up and wait to be serviced by smaller fish cleaners. The little cleaners dart under and around their much bigger clients — even entering their mouths — cleaning their scales of bacteria and parasites like a team of car washers…

A new study published in Nature Ecology & Evolution has found a simple rule that seems to govern how life is organised on Earth. The researchers believe this rule helps explain why species are spread the way they are across the planet. The discovery will help to understand life on Earth – including how ecosystems respond to global environmental changes. At first glance, Earth seems like a collection of wildly different worlds. Each region has its own species and environmental conditions. Yet,…