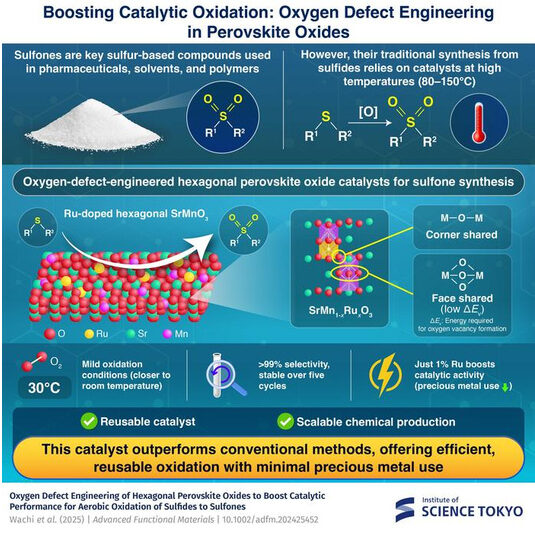
Oxygen defect engineering enables efficient sulfone production using molecular oxygen at low temperature Sulfones, a class of sulfur-containing compounds, are chemically derived from the selective oxidation of sulfides. While these compounds form the core of the pharmaceuticals, solvents and polymer industries, their chemical synthesis is often hindered by high reaction temperatures and extreme reaction conditions. Additionally, these also require costly additives and harsh solvents for production. Against this backdrop, a team of researchers from Japan introduced a new catalyst design,…
Individually, Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) do not make much of an impression. With a maximum body length of six centimetres, a weight of just two grams and its transparent skin, it does not look very spectacular. Yet krill play a central role for life in the Southern Ocean. Billions of these small crustaceans form huge swarms that can extend over several square kilometers and are the most important food source for many predators. A research team from Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg (JMU),…
MAY 9, 2025, NEW YORK – A Ludwig Cancer Research study has identified a key mechanism by which advanced ovarian cancers suppress anti-tumor immune responses and resist immunotherapies. Led by Ludwig Princeton’s Lydia Lynch and reported in the current issue of Science Immunology, the study details how ascites fluid—produced in large quantities as ovarian cancer spreads from the ovaries into the abdomen and its organs—sabotages cytotoxic lymphocytes, a class of immune cells that kill cancer cells. “Although ascites fluid has…
Women who experience significant weight gain after the age of 20 and either have their first child after the age of 30 or don’t have children are almost three times more likely to develop breast cancer than those who give birth earlier and whose weight remains relatively stable, new research from the UK being presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO 2025) has found. Previous research has shown that weight gain in adulthood increases the risk of developing…

Study reveals new information about how to prevent chronic inflammation from zombie-like cells that accumulate with age In humans and other multicellular organisms, cells multiply. This defining feature allows embryos to grow into adulthood, and enables the healing of the many bumps, bruises and scrapes along the way. Certain factors can cause cells to abandon this characteristic and enter a zombie-like state known as senescence where they persist but no longer divide to make new cells. Our bodies can remove…

University of Arizona neuroscientists studying the brains of songbirds have found that aging alters the gene expressions that control the birds’ song. The finding could lead to earlier diagnoses and better treatments for human neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease, which are known to hinder vocal production in their early stages. The study, published in the journal Neurobiology of Aging, found that networks of interacting genes, in a region of the bird’s brain involved with singing, dramatically…

A new type of antibody which stimulates the immune system to target cancer cells slows tumor growth, according to new research Antibody treatment which activates the patient’s own immune system against cancer, known as immunotherapy, is increasingly being investigated as an alternative for chemotherapy and radiotherapy. This is because it specifically targets the cancer cells, which reduces the side effects seen with more conventional therapies. Tumours, such as some breast and ovarian cancers, can express the marker HER2. HER2 is…

Gemini North’s MAROON-X instrument finds evidence for four mini-Earth exoplanets around our famous cosmic neighbor Barnard’s Star For a century, astronomers have been studying Barnard’s Star in the hope of finding planets around it. First discovered by E. E. Barnard at Yerkes Observatory in 1916, it is the nearest single star system to Earth [1]. Barnard’s Star is classified as a red dwarf — low-mass stars that often host closely-packed planetary systems, often with multiple rocky planets. Red dwarfs are extremely numerous in the Universe, so scientists…

Study links genetics, vision and neural processing to mating behavior in Heliconius butterflies A simple neural change alters mating preferences in male butterflies, aiding rapid behavioral evolution, Nicholas VanKuren and Nathan Buerkle at the University of Chicago, US, and colleagues, report March 11th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology. Heliconius are a group of tropical butterflies known for their wide variety of wing patterns and colors, which act as a warning to predators. Because wing coloration is crucial for their…

Understanding children’s subjective experiences through color As a child, did it ever occur to you that your perception of color differed from that of others? It’s quite common to have this thought, but it turns out that the human color experience may be more universal than we previously believed. In psychology and neuroscience, the relationship between subjective experience, such as how we perceive color, and physical brain activity has remained an unresolved problem. Furthermore, due to their limited language abilities,…

University of Arizona astronomers have learned more about a surprisingly mature galaxy that existed when the universe was just less than 300 million years old – just 2% of its current age. Observed by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, the galaxy – designated JADES-GS-z14-0 – is unexpectedly bright and chemically complex for an object from this primordial era, the researchers said. This provides a rare glimpse into the universe’s earliest chapter. The findings, published in the journal Nature Astronomy, build…

Physics professor J. Ping Liu helps boost nation’s energy security and advance toward a world-class magnet research hub University of Texas at Arlington physics Professor J. Ping Liu has won the 2025 Hill Prize in Physical Sciences for pioneering new ways to design magnets that power high-tech devices. Awarded by the Texas Academy of Medicine, Engineering, Science and Technology (TAMEST) and Lyda Hill Philanthropies, the prize recognizes groundbreaking innovations with the potential for real-world impact. Dr. Liu shares the award as co-principal…
Oxygen defect engineering enables efficient sulfone production using molecular oxygen at low temperature Sulfones, a class of sulfur-containing compounds, are chemically derived from the selective oxidation of sulfides. While these compounds form the core of the pharmaceuticals, solvents and polymer industries, their chemical synthesis is often hindered by high reaction temperatures and extreme reaction conditions. Additionally, these also require costly additives and harsh solvents for production. Against this backdrop, a team of researchers from Japan introduced a new catalyst design,…

Researchers at the University of Utah’s Department of Psychiatry and Huntsman Mental Health Institute today published a paper introducing RiskPath, an open source software toolkit that uses Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) to predict whether individuals will develop progressive and chronic diseases years before symptoms appear, potentially transforming how preventive healthcare is delivered. XAI is an artificial intelligence system that can explain complex decisions in ways humans can understand. The new technology represents a significant advancement in disease prediction and prevention…

Researchers train AI to predict if and why proteins form sticky clumps, a mechanism linked to 50 human diseases affecting half a billion people An AI tool has made a step forward in translating the language proteins use to dictate whether they form sticky clumps similar to those linked to Alzheimer’s Disease and around fifty other types of human disease. In a departure from typical “black-box” AI models, the new tool, CANYA, was designed to be able to explain its…

Jairo Sinova of Mainz University to coordinate a new Priority Program for fundamental and applied research into information technology based on altermagnetism Professor Jairo Sinova of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) will be coordinating a new Priority Program in the field of condensed matter physics that will be dealing with unconventional magnetism. The Priority Program will involve fundamental and applied research in the field of unconventional magnetic systems to develop IT components or devices that will reach the technical limits…

Researchers developed a novel annealing processing system that scales both the number of spins and interaction bit width simultaneously Combinatorial optimization problems (COPs) arise in various fields such as shift scheduling, traffic routing, and drug development. However, they are challenging to solve using traditional computers in a practical timeframe. Alternatively, annealing processors (APs), which are specialized hardware for solving COPs, have gained significant attention. They are based on the Ising model, in which COP variables are presented as magnetic spins…
How social networks shape the vocal diversity of monk parakeets In the urban parks of Barcelona, Spain, the calls of a tropical parrot fill the air. The bright green monk parakeet, native to South America, has found a new home in European cities. Monk parakeets thrive in huge colonies where they communicate with each other using many distinct sounds—offering scientists a unique window into understanding the interplay of individual social relationships with vocal variety. For social animals, communication is a…

An international team of researchers, including the Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (Kavli IPMU, WPI), has used a mismatch between elementary particles and gamma rays from NGC 1068 to propose a new route by which neutrinos can be produced. Antarctic ice has eyes that can see elementary particles called neutrinos, and what they’ve observed is puzzling scientists: a remarkably strong neutrino signal accompanied by a surprisingly weak gamma ray emission in the galaxy NGC 1068,…

Can we do away with the troublesome singularity at the heart of black holes? A new paper in JCAP reimagines these extreme objects in light of current knowledge. “Hic sunt leones,” remarks Stefano Liberati, one of the authors of the paper and director of IFPU. The phrase refers to the hypothetical singularity predicted at the center of standard black holes — those described by solutions to Einstein’s field equations. To understand what this means, a brief historical recap is helpful….

The XRISM science team, including members of Nagoya University, has explained how galaxy clusters maintain their heat despite emitting X-rays, which typically have a cooling effect on the hot gas. By observation of the Centaurus cluster of galaxies, the XRISM team discovered the existence of a fast-moving, high-temperature gas flow in the center of the cluster. Their findings, published by Nature, may solve the ‘cooling flow problem’, explaining why clusters of galaxies look like they do. Galaxy clusters are made…

First Light! The spectro-polarimeter of the world’s largest solar telescope in Hawaii looks at the Sun for the first time. The instrument was developed in Germany With a primary mirror diameter of four meters, the Inouye Solar Telescope is the largest in the world. Thanks to the optimal observational conditions on the Hawaiian volcano Haleakala and the use of sophisticated methods of image stabilization and reconstruction, the Inouye Solar Telescope has been providing breathtakingly detailed views of our star since…

Eye movements predict speed limits in perception If you quickly move a camera from object to object, the abrupt shift between the two points causes a motion smear that might give you nausea. Our eyes, however, do movements like these two or three times per second. These rapid movements are called saccades, and although the visual stimulus during a saccade shifts abruptly across the retina, our brain seems to keep it under the hood: we never perceive the shift. New…

A more efficient and environmentally friendly approach to extracting rare earth elements that power everything from electric vehicle batteries to smartphones could increase domestic supply and decrease reliance on costly imports. This new method, developed by researchers at The University of Texas at Austin, allows for separating and extracting these in-demand elements where it’s not possible today, opening up new avenues for gathering rare earth elements amid global trade tensions. “Rare earth elements are the backbone of advanced technologies, but their…

Criegee intermediates (CIs)—highly reactive species formed when ozone reacts with alkenes in the atmosphere—play a crucial role in generating hydroxyl radicals (the atmosphere’s “cleansing agents”) and aerosols that impact climate and air quality. The syn-CH3CHOO is particularly important among these intermediates, accounting for 25-79% of all CIs depending on the season. Until now, scientists have believed that syn-CH3CHOO primarily disappeared through self-decomposition. However, in a published in Nature Chemistry, a team led by Profs. YANG Xueming, ZHANG Donghui, DONG Wenrui and FU Bina from the Dalian Institute…

Many bird species are monogamous. However, genetic studies have shown that the social partner is often not the genetic father of all offspring. Some studies found biased sex ratios: more males than females among extra-pair fledglings. This has been interpreted as evidence of adaptive sex allocation by females: if an extra-pair mate is of high quality and this quality has a genetic basis, fitness can be optimized if offspring with the extra-pair mate’s “good” genes are predominantly male. However, there…

Oxygen defect engineering enables efficient sulfone production using molecular oxygen at low temperature Sulfones, a class of sulfur-containing compounds, are chemically derived from the selective oxidation of sulfides. While these compounds form the core of the pharmaceuticals, solvents and polymer industries, their chemical synthesis is often hindered by high reaction temperatures and extreme reaction conditions. Additionally, these also require costly additives and harsh solvents for production. Against this backdrop, a team of researchers from Japan introduced a new catalyst design,…

TUM researchers develop new material for solid-state batteries The team led by Prof. Thomas F. Fässler from the Chair of Inorganic Chemistry with a Focus on Novel Materials partially replaced lithium in a lithium antimonide compound with the metal scandium. This creates specific gaps, so-called vacancies, in the crystal lattice of the conductor material. These gaps help the lithium ions to move more easily and faster, resulting in a new world record for ion conductivity. Since the measured conductivity far…

Iron-based magnetic nanomaterials have emerged as candidates in biomedicine due to their unique physicochemical properties. Beyond their established role as clinical MRI contrast agents, they have shown potential in drug delivery, magnetic hyperthermia, and the treatment of iron deficiency. Macrophages are also primary targets for these nanomaterials in vivo. The biological effects of iron-based nanomaterials are closely linked to the plasticity and phenotypic shifts of macrophages. However, the underlying mechanisms by which these materials influence macrophage-mediated immune regulation remain unclear….

Iron-rich hematite, commonly found in rocks and soil, turns out to have magnetic properties that make it a promising material for ultrafast next-generation computing In 2023, EPFL researchers succeeded in sending and storing data using charge-free magnetic waves called spin waves, rather than traditional electron flows. The team from the Lab of Nanoscale Magnetic Materials and Magnonics, led by Dirk Grundler, in the School of Engineering used radiofrequency signals to excite spin waves enough to reverse the magnetization state of…

Individually, Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) do not make much of an impression. With a maximum body length of six centimetres, a weight of just two grams and its transparent skin, it does not look very spectacular. Yet krill play a central role for life in the Southern Ocean. Billions of these small crustaceans form huge swarms that can extend over several square kilometers and are the most important food source for many predators. A research team from Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg (JMU),…

Tyrannosaurus rex evolved in North America, but its direct ancestor came from Asia, crossing a land bridge connecting the continents more than 70 million years ago, according to a new study led by UCL researchers. The study, published in Royal Society Open Science, also found that the rapid growth in size of tyrannosaurids (the group that included the T. rex) as well as a closely related group called megaraptors coincided with a cooling of the global climate following a peak…

Study models spatial patterns of “grazing halos” around reefs. In coral reefs throughout the world, visually striking bands of bare sand surrounding reefs are often visible in satellite imagery but their cause remains a mystery. One theory is fear. Parrotfish and other herbivores will leave a reef’s shelter to eat algae or the surrounding seagrass, but their fear of being gobbled up by predators may keep them from roving too far or eating too much, creating, what’s known as “grazing…

Many of the fish we eat play a key role in maintaining the seabed – and therefore our climate, new research shows. Convex Seascape Survey scientists assessed the role of fish in bioturbation (churning and reworking sediments) in shallow UK seas. The Atlantic cod – a staple in chip shops – jointly topped the list of these important “ecosystem engineers” (along with Atlantic hagfish and European eel). In total, 185 fish species were found to play a role in bioturbation…