
New Advances in DNA Microcapsules for Artificial Molecular Systems
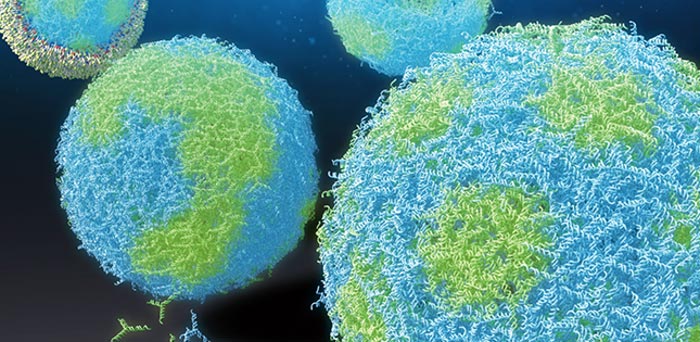
The DNA microcapsules with patterns made of sequence-designed DNA nanostructures.
Credit: Yusuke Sato
Biophysicists in Japan have found ways to make and manipulate capsule-like DNA structures that could be used in the development of artificial molecular systems. Such systems could function, for example, inside the human body. The study was a collaboration between Yusuke Sato of Tohoku University and Masahiro Takinoue of the Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), and the findings were published in the JACS Au.
To make the capsules, the researchers first created two different types of DNA nanostructures. Each type was made using three single-stranded DNA molecules with sticky bits at their ends. Due to differences in their DNA sequences, only similar nanostructures stuck together when the two types were mixed.
Sato and Takinoue then combined the nanostructures in solution with an oily mixture of charged and non-charged molecules. The mixture was first heated and then cooled, and finally examined under a microscope.
The researchers found that water-in-oil droplets had formed, with the DNA nanostructures accumulating at the water-oil interface. The nanostructures came together in different kinds of patch-like patterns, depending on the concentration of each type relative to the other.
The scientists also found that the DNA nanostructures agglomerated in a more homogeneous way when an extra X-shaped DNA nanostructure was added to the mix to connect the two types together.
This worked just as well inside lipid vesicles as in water-in-oil droplets. Sato and Takinoue were also able to separate the DNA capsules from the droplets and vesicles without losing their capsule-like shapes. Finally, they were able to open the capsules and degrade them using specific enzymes.
The findings demonstrate an approach for constructing and modifying DNA capsules that could have a variety of different functions and purposes. For example, they could be used to carry substances to specific target organs, releasing their cargo when exposed to certain enzymes. They could also be made mobile by using DNA nanostructures that can be manipulated to alter the shapes of the capsules. Or they could be modified with proteins or DNA-based molecular devices to make functional compartmental structures, like cellular membranes.
“We believe that functional capsules made from DNA, like the ones we have designed, could provide a new approach for developing capsular structures for artificial cell studies and molecular robotics,” say Sato and Takinoue.
The team will next work on inserting different types of cargo into the capsules, including DNA information processors, and releasing them in response to specific stimuli.
Journal: Journal of the American Chemical Society
DOI: 10.1021/jacsau.1c00450
Article Title: Capsule-like DNA Hydrogels with Patterns Formed by Lateral Phase Separation of DNA Nanostructures
Article Publication Date: 9-Dec-2021
Media Contact
Public Relations
Tohoku University
public_relations@grp.tohoku.ac.jp












