
Eye movements predict speed limits in perception If you quickly move a camera from object to object, the abrupt shift between the two points causes a motion smear that might give you nausea. Our eyes, however, do movements like these two or three times per second. These rapid movements are called saccades, and although the visual stimulus during a saccade shifts abruptly across the retina, our brain seems to keep it under the hood: we never perceive the shift. New…

A more efficient and environmentally friendly approach to extracting rare earth elements that power everything from electric vehicle batteries to smartphones could increase domestic supply and decrease reliance on costly imports. This new method, developed by researchers at The University of Texas at Austin, allows for separating and extracting these in-demand elements where it’s not possible today, opening up new avenues for gathering rare earth elements amid global trade tensions. “Rare earth elements are the backbone of advanced technologies, but their…

Criegee intermediates (CIs)—highly reactive species formed when ozone reacts with alkenes in the atmosphere—play a crucial role in generating hydroxyl radicals (the atmosphere’s “cleansing agents”) and aerosols that impact climate and air quality. The syn-CH3CHOO is particularly important among these intermediates, accounting for 25-79% of all CIs depending on the season. Until now, scientists have believed that syn-CH3CHOO primarily disappeared through self-decomposition. However, in a published in Nature Chemistry, a team led by Profs. YANG Xueming, ZHANG Donghui, DONG Wenrui and FU Bina from the Dalian Institute…

Many bird species are monogamous. However, genetic studies have shown that the social partner is often not the genetic father of all offspring. Some studies found biased sex ratios: more males than females among extra-pair fledglings. This has been interpreted as evidence of adaptive sex allocation by females: if an extra-pair mate is of high quality and this quality has a genetic basis, fitness can be optimized if offspring with the extra-pair mate’s “good” genes are predominantly male. However, there…

Bioinformatics: Publication in Science Bioinformaticians from Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) and the university in Linköping (Sweden) have established that the genes in bacterial genomes are arranged in a meaningful order. In the renowned scientific journal Science, they describe that the genes are arranged by function: If they become increasingly important at faster growth, they are located near the origin of DNA replication. Accordingly, their position influences how their activity changes with the growth rate. Are genes distributed randomly along…

Mechanical compression induces multicellular organization in archaeaIn a discovery that reframes our understanding of life’s fundamental organization, researchers at Brandeis University, the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, and the Max Planck Institute for Biology Tübingen have found that mechanical compression can induce the formation of tissue-like multicellular structures in archaea. This novel finding, focusing on the haloarchaeon Haloferax volcanii, reveals a previously unknown pathway for the emergence of multicellularity within this domain of life, offering new insights into the evolutionary…

Capturing carbon dioxide (CO₂) from industrial emissions is crucial in the fight against climate change. But current methods, like chemical absorption, are expensive and energy-intensive. Scientists have long eyed graphene—an atom-thin, ultra-strong material—as a promising alternative for gas separation, but making large-area, efficient graphene membranes has been a challenge. Now, a team at EPFL, led by Professor Kumar Agrawal, has developed a scalable technique to create porous graphene membranes that selectively filter CO₂ from gas mixtures. Their approach slashes production…

Researchers developed a cell-based reporter assay that can quantify epigenetic changes induced by chemicals and potential carcinogens Chemicals used as food preservatives, flavoring agents, dyes, pesticides, cosmetics, cleaners, and other industrial materials are being increasingly recognized as a health hazard. Their rampant use has led to an increase in the prevalence of various chemical toxicity-induced diseases, including hormonal disruption, cancer, neurological disorders, skin conditions, and occupational poisoning. Numerous chemicals are known to trigger “carcinogenesis” or cancer development by exerting genotoxic…

Researchers explore transition metal-free strategies to reduce environmental impact and enhance efficiency in pharmaceutical and fine chemical industries Coupling reactions are among the most transformative tools in organic chemistry, enabling the formation of crucial chemical bonds in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and advanced materials. Since their introduction, they have been one of the backbones of modern organic synthesis. However, these methods have long relied on environmentally taxing transition metal catalysts, such as palladium, which are often scarce, costly, and generate unwanted byproducts….

From seat cushions to mattresses to insulation, foam is everywhere — even if we don’t always see it. Now, researchers at The University of Texas at Dallas have fused chemistry with technology to create a 3D-printed foam that is more durable and more recyclable than the polymer foam found in many everyday products. The research, which appears in the March 1 print edition of RSC Applied Polymers, a journal of the Royal Society of Chemistry, focused on creating a sturdy but lightweight foam…
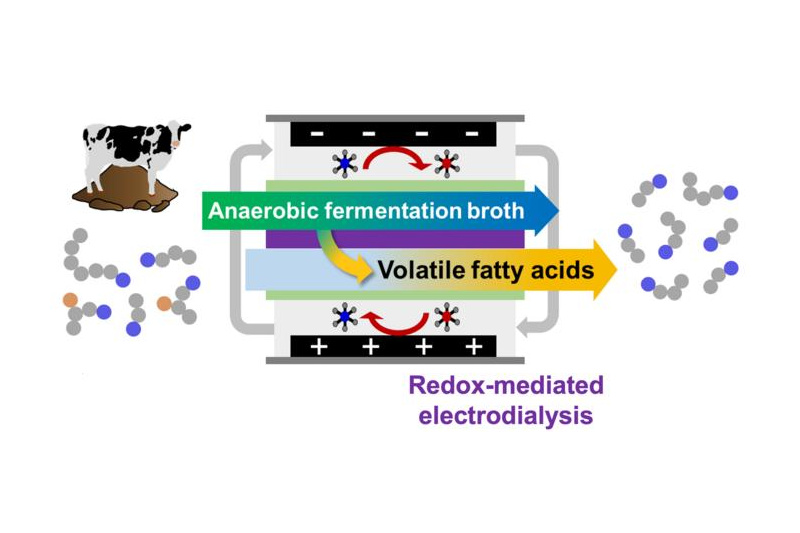
A collaboration between chemical engineers and animal scientists has created a system for recovering valuable industrial chemicals from animal waste, representing a major step towards circularity and environmental sustainability. Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed a nanofiltration system for separating volatile fatty acids (VFAs) – organic molecules that are critical in fine chemical production across many sectors – from cattle manure fermented in bioreactors. Thanks to the incorporation of selective ion-exchange membranes into an electrochemical separation system,…

Findings show that radiation-induced chemistry may mitigate metal alloy corrosion in nuclear reactors cooled by molten salts High temperatures and ionizing radiation create extremely corrosive environments inside a nuclear reactor. To design long-lasting reactors, scientists must understand how radiation-induced chemical reactions impact structural materials. Chemists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and Idaho National Laboratory recently performed experiments showing that radiation-induced reactions may help mitigate the corrosion of reactor metals in a new type of reactor…

Research hints at calcium’s potential role in enforcing a specific molecular handedness among primitive polyesters and early biomolecules A new study led by researchers at the Earth-Life Science Institute (ELSI) at Institute of Science Tokyo has uncovered a surprising role for calcium in shaping life’s earliest molecular structures. Their findings suggest that calcium ions can selectively influence how primitive polymers form, shedding light on a long-standing mystery: how life’s molecules came to prefer a single “handedness” (chirality). Like our left…

Scientists have for the first time filmed the real-time growth and contraction of Palladium nanoparticles, opening new avenues for utilising and recycling precious metal catalysts. Researchers at the University of Nottingham’s School of Chemistry used transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to observe the complete lifecycle of palladium nanoparticles in a liquid environment, from nucleation through growth to dissolution, with the entire cycle repeating multiple times. This study has been published today in Nanoscale. One of the most important applications of metal nanoparticles is…

Sugar coatings aren’t only for candies; they also help viruses, like the ones that cause COVID-19, hide from their hosts’ immune system. Now, researchers have developed a universal vaccine that targets coronaviruses and the sugars that they use as cover. As demonstrated in animal studies, the vaccine removed sugar molecules from an area of a coronavirus spike protein that rarely mutates and created effective and plentiful antibodies to inactivate the virus. Chi-Huey Wong, a chemistry professor at Scripps Research, will…

Traditionally, chemists have relied on well-established but limiting methods to synthesize these molecules. This new research presents a fundamentally different approach. Researchers at Indiana University and Wuhan University in China have unveiled a groundbreaking chemical process that could streamline the development of pharmaceutical compounds, chemical building blocks that influence how drugs interact with the body. Their study, published in Chem, describes a novel light-driven reaction that efficiently produces tetrahydroisoquinolines, a group of chemicals that play a crucial role in medicinal chemistry. Tetrahydroisoquinolines serve…