
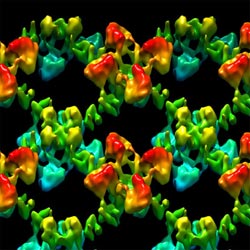
The scientists working with Prof. Henning Stahlberg at the Biozentrum of the University of Basel have now identified the complete 3D structure of a particular potassium channel, a HCN channel.
This enabled them to draw conclusions about its mechanism of action, which they describe in the current issue of “Nature Communications”.
Neurons conduct information by way of electrical impulses through our body. Potassium channels are a key component of this electrical circuit and are controlled either by an electrical impulse or through signaling molecules. In man, the dysfunction of the so-called HCN potassium channels is associated with neurological disorders such as epilepsy and depression. Prof. Henning Stahlberg’s team at the Biozentrum of the University of Basel has now elucidated the full structure of a bacterial counterpart of this type of potassium channel, which has provided new insights into its functioning.
New operating principle thanks to the 3D structure
Potassium channels are embedded in the membrane of cells. They form a pore with a filter that selectively allows the passage of potassium ions, and which is controlled by the signaling molecule cAMP. It was previously assumed that the pore could open and close, thus regulating the flow of potassium ions. Stahlberg’s team has now, however, found indications for another mode of action. Employing crystallization technology and electron microscopy, the scientists have reconstructed the intact three dimensional structure of the bacterial channel in its natural environment in both the presence and absence of cAMP.
Based on the analysis of these structures, they discovered, contrary to popular belief, that the pore always remains open. “When the signaling molecule cAMP docks onto the potassium channel, it causes a rearrangement and shift in the protein scaffold,” explains Julia Kowal, first author of this study. “We think that cAMP in fact widens the filter somewhat, thereby controlling the flow of potassium ions.” The newly uncovered structural details have made it possible for the researchers to consider the mode of functioning of these channels from a new perspective.
Mechanism relevant for new drugs
Stahlberg would like to investigate the filter region more closely with an extremely high resolution camera, in order to resolve the last remaining questions about this mechanism. These signal-driven potassium channels are also referred to as “pacemaker channels”. They help to generate the rhythm of the heart as well as the rhythmic excitability of neurons. The precise understanding of the mode of action is thus the basis for developing specific drugs for the treatment of epilepsy and cardiac arrhythmias.
Original Citation
Julia Kowal, Mohamed Chami, Paul Baumgartner, Marcel Arheit, Po-Lin Chiu, Martina Rangl, Simon Scheuring, Gunnar F. Schröder, Crina M. Nimigean, and Henning Stahlberg
Ligand-induced structural changes in the cyclic nucleotide-modulated potassium channel MloK1.
Nature Communications, Published Online 28 January 2014
DOI: 10.1038/ncomms4106
Further Information
Prof. Henning Stahlberg, Biozentrum, University of Basel at the Department for Biosystems Science and Engineering (D-BSSE), Tel.: +41 61 387 32 62, E-mail: henning.stahlberg@unibas.ch












