
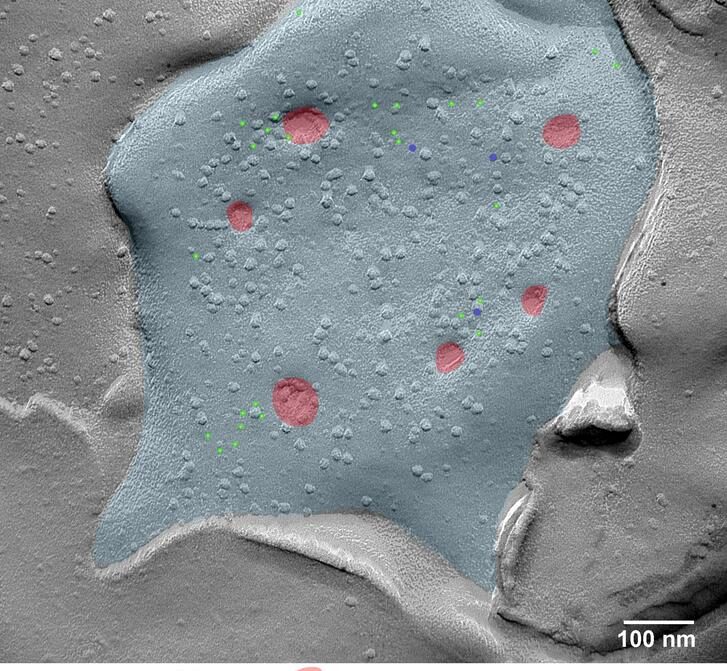
A lunar surface-like electron microscopic image of an activated medial habenula neuron. SPO (light green), CAPS2 (dark blue), vesicles on the verge of releasing neurotransmitters (red), and the delimiting membrane (light blue).
© Koppensteiner et al./PNAS
ISTA researchers analyze brain region using new method.
Fear and addiction exert significant influence within society. Managing them is often challenging, as they are driven by intricate neuronal circuits in our brains. Understanding the underlying molecular mechanisms is crucial to intervene when these processes malfunction. Pioneered by scientists at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA), the novel “Flash and Freeze-fracture” technique provides a unique glimpse into the respective brain region. The results were recently published in the journal PNAS.
A bird encounters a fox while looking for food. It gets away just in time, but the sight and the sound of the predator lingers. The negative experience will form a memory in its brain and will be associated with fear and stress from now on. Whenever it meets a fox again, the fear memory is revived. The bird’s attention spikes, its heart rate goes up, and it changes its behavior to reduce the risk of predation. Such memory is mediated by a specific brain region called the medial habenula, one of the epicenters for emotional processing.
Peter Koppensteiner, together with Pradeep Bhandari, Cihan Önal and other members of Ryuichi Shigemoto’s research group at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) investigated this particular part of the brain to understand how its neurons (nerve cells) communicate with each other. Published in the journal PNAS, the results give an unprecedented look into this subject, utilizing a novel visualization technique called “Flash and Freeze-fracture”.
Counter-intuitive brain cells
Nerve cells in the medial habenula exhibit unusual behavior, contradicting the general understanding of how neurons transmit signals to each other. “Typically, communication between neurons is shut down, as soon as a specific molecule on the surface of the cells, known as the ‘GABAB’-receptor, is activated,” explains Peter Koppensteiner, previously a postdoc in the Shigemoto group and now a staff scientist at one of ISTA’s Scientific Service Units (SSUs). In neurons of the medial habenula, the exact opposite happens. “With the activation of GABAB, communication is elevated, to the extent that it shows the strongest synaptic facilitation throughout the entire brain,” he continues. The underlying mechanism, however, was still unknown.

Flash and Freeze-fracture. Schematics of the method. Stimulated neurons in a brain sample are frozen. The frozen brain tissue is broken/fractured and proteins in the brain tissue are labeled and visualized with gold particles, using an electron microscope. © Koppensteiner et al./PNAS
New method to uncover the inside of neurons
Driven by curiosity, the ISTA scientists embarked on a journey to decipher this phenomenon. The goal was to thoroughly examine medial habenula neurons in mice after they had been activated with a light flash. “It’s a very challenging task,” says Ryuichi Shigemoto. “The processes inside neurons occur in milliseconds, and classical electron microscope methods lack the temporal resolution to capture them.”
A method formulated within the past decade, significantly influenced by Peter Jonas’ research group at ISTA called “Flash and Freeze”, proved to be a great starting point. It is a powerful tool, where neurons are frozen after being stimulated with light, to analyze the structure of neurons. The scientists now elevated it to the next level. Their new “Flash and Freeze-fracture” technique introduces the possibility of also depicting proteins and molecules. This advancement allows researchers to track their trajectories, i.e., where proteins are going after neuronal activation, and reveal why they occupy distinct positions.
The latter is of particular importance. “The communication at the synapse varies depending on the localization of specific proteins. Our new method reveals that rapid position changes of some proteins strengthen the synapses,” explains Koppensteiner. Two proteins with previously unknown functions in particular, SPO and CAPS2, localize near the synapse, where CAPS2 anchors vesicles—tiny bubbles carrying neurotransmitters—to this region. A crucial event that enables a strong release of their messenger signals to the next nerve cell, thus facilitating communication between nerve cells.
Understanding these details could potentially open new doors to actively strengthen synapses in neurodegenerative diseases, where they are not functioning properly anymore.
Shigemoto adds, “I’m beyond excited about this remarkable publication that elucidates the mechanism of this peculiar phenomenon in the brain.”
Funding information
This project was supported by funding from the European Research Council (ERC) and European Commission, under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program (ERC grant agreement no. 694539 to Ryuichi Shigemoto and the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement no. 665385 to Cihan Önal).
Information on animal studies
In order to better understand fundamental processes, for example, in the fields of neuroscience, immunology, or genetics, the use of animals in research is indispensable. No other methods, such as in silico models, can serve as alternative. The animals are raised, kept, and treated according to the strict regulations of Austrian law. All animal procedures are approved by the Federal Ministry of Education, Science and Research.
Originalpublikation:
P. Koppensteiner, P. Bhandari, C. Önal, C. Borges-Merjane, E. Le Monnier, U. Roy, Y. Nakamura, T. Sadakata, M. Sanbo, M. Hirabayashi, J. Rhee, N. Brose, P. Jonas, R. Shigemoto. 2024. GABAB receptors induce phasic release from medial habenula terminals through activity-dependent recruitment of release-ready vesicles. PNAS. DOI: https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2301449121
Weitere Informationen:
https://ista.ac.at/en/research/shigemoto-group/ Shigemoto Group at ISTA
https://ista.ac.at/en/research/jonas-group/ Jonas Group at ISTA
https://ista.ac.at/en/news/flash-and-freeze-reveals-dynamics-of-nerve-connection… Article about Flash and Freeze method
https://ista.ac.at/en/research/scientific-service-units/ SSUs at ISTA












