
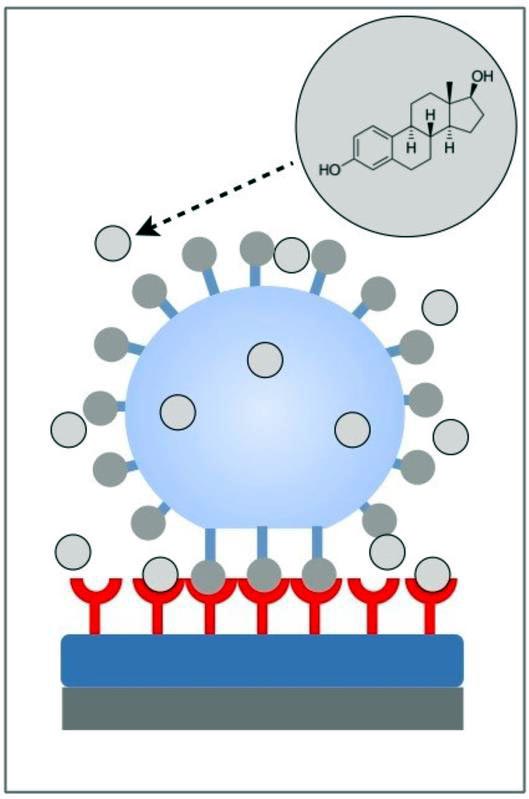
Scheme of the new detection principle.
(c) Rettke et al.
Scientists from the Universities of Dresden and Leipzig have presented a new method for detecting hormonally active substances in food, cosmetics and water in the journal “Biosensors & Bioelectronics”.
Scientists from the Universities of Dresden and Leipzig have presented a new method for detecting hormonally active substances in food, cosmetics and water in the journal “Biosensors & Bioelectronics”. Hormonally active substances can cause serious health problems, including breast and prostate cancer, thyroid disorders, and neurological and mental illnesses. A fast and simple analytical method for risk assessment of products and food is therefore an important tool for health and consumer protection.
They are almost everywhere – in food, washing powder, dishwashing detergent, cosmetic products, in medicines as well as in drinking and waste water: hormonally active compounds such as synthetic estrogen derivatives, which are the main ingredient in hormonal contraceptives, or the “bulk chemical” bisphenol A (BPA), which is used for example in beverage bottles or food cans. Its harmful effects on humans and the environment have long been proven.
However, simple detection of endocrine disruptors for effective monitoring and reliable risk assessment of products and waters is a challenge due to the structural diversity of the substances. Previous analytical methods are usually based on complex laboratory-diagnostic procedures or do not reach the required detection limits. The new method developed by scientists at the Universities of Dresden and Leipzig could now remedy this situation, which is why a patent application has been filed.
“Our method detects hormonally active compounds using immobilized sulfotransferases and microparticles and includes a kit for detecting the compounds in food, cosmetics, water samples and much more. To this end, we have implemented this enzyme of estrogen metabolism into a biosensor that serves as a “capture probe” for estrogen-like compounds. Depending on the concentration of estrogen-like compounds in the detection solution, the binding of microparticles to a biochip is impaired and thus even low concentrations of hormonally active substances can be detected quickly and easily,” explains Prof. Tilo Pompe from the University of Leipzig.
“In particular, I would like to point out the modularity of implementing an estrogen-metabolizing enzyme, as the approach is not limited to this specific enzyme, but also allows the use of other hormone-metabolizing or hormone-binding proteins in a multiplex assay. This could open new approaches to cover the whole complexity of evaluating hormonally active substances without animal testing,” adds Dr. Kai Ostermann from Technische Universität Dresden.
Caption:
Scheme of the new detection principle. A functionalized hydrogel microparticle (blue sphere) binds to the directionally immobilized enzyme (red) on a chip surface. Depending on the presence of estrogen-like compounds (gray spheres) in the detection solution, these bonds are blocked and the hydrogel microparticles become less deformed, which can be read out by optical methods. Copyright: Rettke et al.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Dr. Kai Ostermann
Institute of Genetics
TU Dresden
Email: kai.ostermann@tu-dresden.de
Prof. Dr. Tilo Pompe
Biophysical Chemistry
Universität Leipzig
Email: tilo.pompe@uni-leipzig.de
Originalpublikation:
David Rettke, Florian Seufert, Julia Döring, Kai Ostermann, Dimitri Wilms, Stephan Schmidt, Tilo Pompe. Biomimetic estrogen sensor based on soft colloidal probes, Biosensors and Bioelectronics, Volume 192, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113506












