
New Pathway for Cellular Garbage Control in Neurodegenerative Diseases
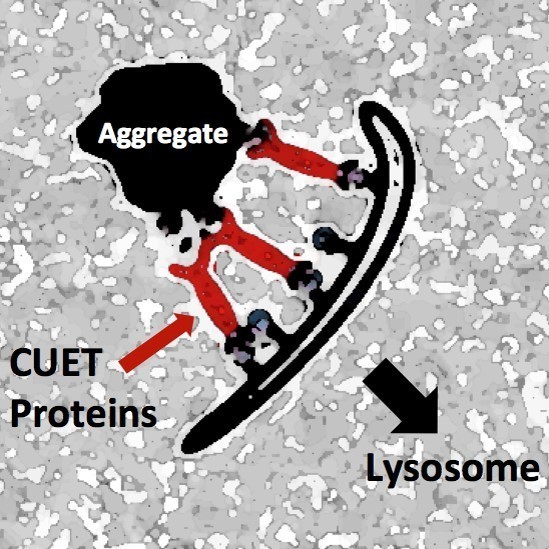
The newly identified proteins, termed CUET proteins (shown in red), recognize toxic protein aggregates and target the whole complex to the cellular waste disposal and recycling station, the lysosome.
Illustration: Stefan Jentsch / Copyright: MPI of Biochemistry
Cellular “garbage” can be removed from cells by sweeping them to a cellular recycling station known as the lysosome. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry in Martinsried, Germany, now discovered a new family of helper proteins that recognize labeled cellular protein waste and guide them efficiently to the lysosome for destruction and subsequent recycling into their reusable compounds.
Proteins, the components of our body that execute, control and organize basically all functions in our cells, are made out of strings of amino acids, which – like an origami – are folded into specific and complex three-dimensional structures according to their desired functions.
However, since folding and maintaining of such structures is highly sensitive to cellular or environmental stress, proteins can potentially misfold or form clumps (aggregates). Such undesired protein waste can be toxic for cells and may even lead to cell death. Because several human neurodegenerative diseases are known to be linked to an accumulation of abnormal protein aggregates, basic science aimed to understand how cells remove cellular garbage is elementary for designing strategies for a potential prevention or cure of such disorders.
Scientists in the laboratory of Stefan Jentsch at the MPIB now successfully used baker’s yeast for screening for new cellular waste disposal pathways. Kefeng Lu, a postdoctoral researcher from China, discovered a new class of helper proteins (termed CUET proteins) present both in yeast and humans that recognize cellular garbage earmarked for disposal by an attached label in the form of the ubiquitously existing protein known as “ubiquitin”.
Importantly, these newly identified helper proteins channel the cellular garbage by a “self-eating” pathway (autophagy) to the lysosome, a compartment of cells dedicated for destruction and recycling. The Max Planck scientists could also show that a toxic protein related to the abnormal, aggregate-forming protein “huntingtin” of patients with the neurodegenerative Huntington’s disease is efficiently destroyed by the newly identified pathway. Remarkably, this pathway seems specific for aggregated proteins like huntingtin and appears to be more potent than previously discovered cellular garbage disposal mechanisms.
Because the identified cellular disposal mechanism operates in yeast as well, the researches will now take full advantage of its powerful experimental possibilities to investigate this pathway further.
A detailed analysis of this mechanism will be crucial to understand how aggregate-forming proteins lead to human diseases and may help to develop concepts for possible disease preventions.
Original Publication:
K. Lu, I. Psakhye and S. Jentsch: Autophagic clearance of polyQ proteins mediated by the conserved CUET protein family. Cell, July 17, 2014.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.048
Contact:
Prof. Dr. Stefan Jentsch
Molecular Cell Biology
Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry
Am Klopferspitz 18
82152 Martinsried
Germany
E-Mail: jentsch@biochem.mpg.de
http://www.biochem.mpg.de/jentsch
Anja Konschak
Public Relations
Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry
Am Klopferspitz 18
82152 Martinsried
Germany
Tel. +49 89 8578-2824
E-Mail: konschak@biochem.mpg.de
http://www.biochem.mpg.de/news
http://www.biochem.mpg.de/jentsch – Website of the Research Departement “Molecular Cell Biology” (Stefan Jentsch)
http://www.biochem.mpg.de/news/ueber_das_institut/forschungsbereiche/zellbiologi… – More press releases about the research of Stefan Jentsch












