
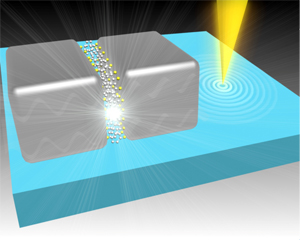
An electron nanoprobe (yellow) placed near the functionalized silver nanoparticles measured plasmon-assisted quantum tunneling at terahertz frequencies.
© 2014 Shu Fen Tan, National University of Singapore
Plasmonic devices combine the ‘super speed’ of optics with the ‘super small’ of microelectronics. These devices exhibit quantum effects and show promise as possible ultrafast circuit elements, but current material processing limits this potential. Now, a team of Singapore-based researchers has used a new physical process, known as quantum plasmonic tunneling, to demonstrate the possibility of practical quantum plasmonic devices(1).
Tunneling is an intriguing aspect of quantum mechanics whereby a particle is able to pass through a classically insurmountable barrier. Theoretically, quantum plasmonic tunneling is only noticeable when plasmonic components are very closely spaced — within half a nanometer or less. However, researchers from the A*STAR Institute of Materials Research and Engineering, the A*STAR Institute of High Performance Computing and the National University of Singapore were able to observe quantum effects between materials spaced more than one nanometer apart.
They investigated the tunneling of electrons across a gap between two nanoscale cubes of silver coated with a monolayer of molecules. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy showed that these nanocubes self-assembled into pairs. The separation, and hence the tunneling distance, between the nanoparticles could be controlled by the choice of surface molecule — between 0.5 and 1.3 nanometers in the cases tested.
The monolayer of molecules had an another function — to provide molecular electronic control over the frequency of the oscillating tunnel current, which could be tuned between 140 and 245 terahertz (1 terahertz = 1012 hertz), as was shown by monochromated electron energy-loss spectroscopy.
Theoretical predictions, supported by experimental results, confirmed the nature of the plasmon-assisted tunnel currents between the silver cubes. “We show that it is possible to shine light onto a small system of two closely spaced silver cubes and generate a tunnel current that oscillates very rapidly between these silver electrodes,” explains A*STAR researcher Michel Bosman. “The oscillation is several orders of magnitude faster than typical clock speeds in microprocessors, which currently operate in the gigahertz (= 109 hertz) regime.” At the same time, the results also demonstrate the possibility of terahertz molecular electronics.
Two factors contributed to the success of the experiments. First, the nanocubes had atomically flat surfaces, maximizing the tunneling surface area between the two nanoparticles. Second, the molecule-filled gap increased the rate of tunneling, making it possible to measure plasmon-assisted quantum tunneling.
“We will now use different molecules in the tunnel gap to find out how far the tunnel currents can be carried, and in what range we can tune the oscillation frequency,” says Bosman.
Reference
(1) Tan, S. F., Wu, L., Yang, J. K. W., Bai, P., Bosman, M. & Nijhuis, C. A. Quantum plasmon resonances controlled by molecular tunnel junctions. Science 343, 1496–1499 (2014).
Associated links












