
Brain Organoids Reveal Insights Into Cortical Development Issues
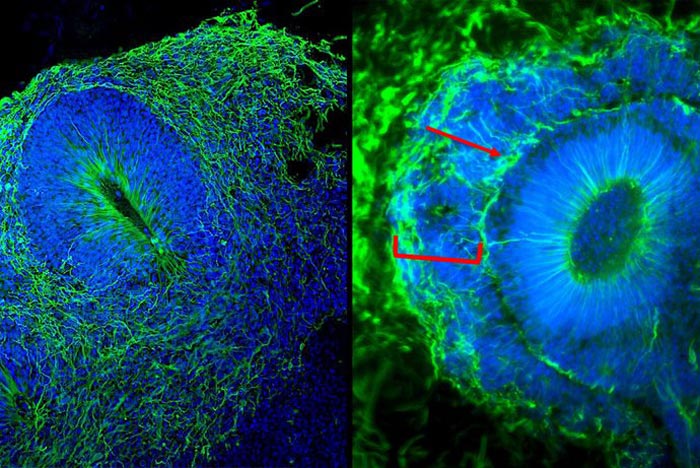
EML1-patient derived brain organoids (right picture) reveal mislocated cells (red bracket; nuclei in blue) as well as a band of mispositioned neurons (in green; red arrowheads) when compared to control brain organoids (left picture) derived from healthy donor cells. Foto: © HITBR
A study at the Hector Institute for Translational Brain Research (HITBR) at the Central Institute of Mental Health (CIMH) in Mannheim shows that cerebral organoids open up new insights into the development of the human brain and associated disorders.
Human pluripotent stem cells cultured as 3D aggregates in a petri dish with nutrient liquid have the capacity to self-organize and develop into so called brain organoids. Under the microscope, these brain organoids display structures that closely resemble the developing brain, making them an attractive new model system to study the development and developmental disorders of the human brain.
In a recent study at the Hector Institute for Translational Brain Research (HITBR) at the Central Institute of Mental Health (CIMH) in Mannheim researchers investigated how mutations in a single gene (the EML1 gene) can lead to a rare congenital malformation of the brain. Patient-derived or genome edited cerebral organoids generated in a petri dish exhibited hallmarks of the human disease (e.g. ectopically located progenitor cells and neurons) and allowed the identification of underlying molecular mechanisms. The work has now been published in the journal EMBO Reports.
Mutation in the EML1 gene leads to severe disorganisation of the cerebral cortex
The human cerebral cortex is a highly organized structure, with layers and folds, which are formed in still little-understood ways. Malformations associated with defects in human cortical development (MCD) can result in disorganization of the cortex with severe consequences including epilepsy and intellectual disability. Using brain organoids as a model of human brain development, scientists at the HITBR investigated how mutations in the Echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 1 (EML1) gene can lead to severe disorganization and increased brain size in patients. “Interestingly, EML1-patient derived cerebral organoids exhibit mislocated progenitor cells and neurons, thereby reminiscing what is observed in patients’ brains” explains Ammar Jabali, PhD student and lead author of the study. “This allowed us to investigate the molecular changes behind this phenomenon”.
Misplaced progenitor cells show altered behaviour and gene expression patterns
The researchers around the HITBR group leader Dr. Julia Ladewig produced cerebral organoids from induced pluripotent (iPSC) stem cells either derived from EML1-patients or from iPSCs in which they knocked out the EML1 gene using so called gene scissors. In cerebral organoids the cells organize themselves – very similar to what they do during embryonic brain development; stem cells divide, a proportion of the daughter cells develop into nerve cells; they migrate to specific locations where they eventually integrate into neuronal circuitries. These are highly organized processes leading to a complex tissue.
In EML1-patients, these processes are disturbed. “We were able to show that the progenitor cells exhibit perturbed primary cilia, an organelle important to anchor the progenitor cells at a certain position. In addition, the progenitor cells show altered dividing patterns. As a consequence, they move to places where they do not belong,” explains Dr. Julia Ladewig. Furthermore, using single cell gene expression analyses the researchers identified that the misplaced progenitor cells also show altered gene expression patterns. “These mislocated cells which exhibit perturbed gene expression signatures cannot be found in healthy control derived cerebral organoids supporting the idea that organoids can contribute to the understanding of normal and abnormal human brain development” says Prof. Dr. Philipp Koch, head of the HITBR.
Hippo signalling pathway as key driver of massive expansion
To understand how the mislocated cells expanded, Ladewig’s group looked into potential signaling pathways affected. “Based on recent scientific literature the Hippo-signaling pathway – a conserved signaling pathway that controls cell proliferation and organ growth – became a promising candidate being a key driver of the massive expansion observed” says Jabali. Indeed, the researchers at the HITBR were able to modulate the Hippo pathway and thereby mitigate the phenotypic changes in the EML1-deficient organoids bringing them closer to healthy development.
The scientists emphasize that this study helps to understand fundamental aspects of human brain development and in particular which pathways are affected in EML1 patients. This might help to identify new treatment options for such diseases in the long term.
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Dr. Julia Ladewig
Hector Institute for Translational Brain Research
Central Institute of Mental Health
Phone +49 0621 1703-6091
julia.ladewig@zi-mannheim.de
Originalpublikation:
Publication: Ammar Jabali, Anne Hoffrichter, Ana Uzquiano, Fabio Marsoner, Ruven Wilkens, Marco Siekmann, Bettina Bohl, Andrea C Rossetti, Sandra Horschitz, Philipp Koch, Fiona Francis & Julia Ladewig: Human cerebral organoids reveal progenitor pathology in EML1-linked cortical malformation, EMBO Reports (2022) e54027 DOI: 10.15252/embr.202154027, https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.202154027












