
Discovering Tiny Tubular Structures: A Serendipitous Find
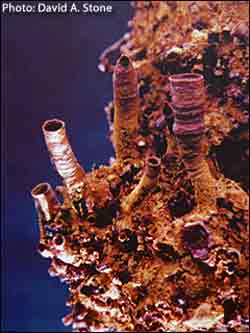
An accidental discovery may provide insights into the creation of tubular structures such as those found in caves and at hydrothermal vents.
While doing some electroplating work for a class project, David Stone stumbled upon a way to grow tiny tubes that look like the cave formations known as soda straws. At the time, Stone, a former sculptor and foundry worker, had just returned to school.
“I botched the experiment. I can still remember being in my carport, picking up the cathode and thinking, ’Oh shoot,’” he said. “And as I held it up to my head to throw it into the garbage, I noticed tubes growing on it. I thought, ’Hmm, tubes.’”
The tubes from the failed experiment intrigued him, so he showed the structures to several faculty members at the University of Arizona in Tucson, including UA physics professor Raymond E. Goldstein. “I was just bowled over when I saw it,” Goldstein said. “It looked like something formed by a living organism.”
So Goldstein and Stone, now a doctoral candidate in UA’s department of soil, water and environmental science, teamed up to figure out how the fascinating tubules formed. Their paper, “Tubular precipitation and redox gradients on a bubbling template,” will be published in the early online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences the week of July 26. The research was funded by the Research Corporation and the National Science Foundation.
Tubular structures in nature span a range of sizes and locations, from giant chimneys at hydrothermal vents deep in the ocean to tiny tubes formed on corroding iron.
But how such things develop is not well understood.
To expand Stone’s carport experiment, he and Goldstein used a setup similar to that used for electroplating. They constructed a rectangular glass chamber about four inches tall with a positively charged iron electrode on the top and a negatively charged iron electrode on the bottom. The researchers filled the container with mixture of water, ammonium, iron and sulfates and turned on the current.
The electric current split water into hydrogen and oxygen. As expected, tiny hydrogen bubbles gathered on the negatively charged electrode, grew larger and then broke away.
To the researchers’ surprise, after tens of minutes the electrode was covered with a forest of small tubes, which the scientists dubbed “ferrotubes.”
To study the growth of ferrotubes, the researchers filmed their experiments.
Stone said, “We used a camera with this incredible microscope of a lens that would allow us to peer into this solution better than any human eye. It’s dark in there, there’s stuff swirling around. With just a little light we could see for the first time, that, Ah! There’s this obvious film forming around the bubble.”
The bubbles are tiny, about one-eighth inch in diameter. As a bubble grows, a thin film forms on the bubble and then breaks apart as the bubble detaches. A bit of the film is left as a circular residue on the electrode.
That film, a special type of iron oxide known as green rust, forms when ammonia gas inside the bubble meets the iron dissolved in the surrounding fluid, say the scientists.
Each time a bubble forms and breaks, a bit of the film, or precipitate, is left. That ring of precipitate guides subsequent tube formation. As the precipitate builds up, a tiny tube of iron oxides — rust — develops.
Goldstein said, “The tube is a guide for the bubble, and the bubble is the template for the tube.”
In nature, such formations as soda straws in caves take hundreds or thousands of years to form. But in the laboratory, Stone and Goldstein can grow a miniature forest of one-inch-long, one-eighth-inch-diameter tubules in one to two hours.
“It’s a controllable system that can be studied in the laboratory on human time scales instead of just coming upon it after the fact,” said Goldstein.
That control has allowed the team to figure out exactly how the tubes are formed. A better understanding of the process will let the researchers model how natural structures, such as cave formations, are made.
Tubular structures found on a Martian meteorite had been suggested as evidence of life, he said.
Goldstein pointed out that finding a chemical means to grow such self-organizing systems highlights the fact that living organisms are not needed to create such structures.
“Such tubes can be generated and yet have nothing to do with life,” he said.












