
Fruit coated with the material developed by researchers at the University of São Paulo showed 11% less weight loss during storage and took longer to start becoming contaminated by fungi An edible biofilm, obtained from agricultural and fishing waste and developed by researchers at the São Carlos Institute of Chemistry of the University of São Paulo (IQSC-USP) in Brazil, allows the shelf life of strawberries (Fragaria x ananassa Duch.) to be extended. In laboratory tests, the researchers found that over 12…

Nitrate, pesticides, metals, plastic – agricultural soils often contain pollutants. But are there sustainable and climate-friendly ways to restore and promote soil health in agricultural land? Yes, says a research team from the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ). Specific plant species could be used as cover plants for phytoremediation, i.e. to relief agricultural land from adverse pollutant impacts. In their article published in Trends in Plant Sciences, the researchers summarise the results of more than 100 scientific studies and…

Suppression of the CcMCA1 gene has potential in halting invasive plant species The parasitic vine Cuscuta campestris grows by latching onto the stems and leaves of plants and inserting organs called haustorium into the host plant tissues to draw nutrients. The haustorium is formed when ion channels in the cell membrane are stimulated during coiling and induce a reaction within the cell. Further, Cuscuta campestris has many types of ion channels, but which ones were linked to the development of…

With the new system, farmers could significantly cut their use of pesticides and fertilizers, saving money and reducing runoff. Reducing the amount of agricultural sprays used by farmers — including fertilizers, pesticides and herbicides — could cut down the amount of polluting runoff that ends up in the environment while at the same time reducing farmers’ costs and perhaps even enhancing their productivity. A classic win-win-win. A team of researchers at MIT and a spinoff company they launched has developed…

A recent study has unveiled the genetic blueprint behind flowering time in olive trees, a crucial trait for fruit production that is increasingly under threat from climate change. By analyzing 318 olive genotypes from across the Mediterranean, researchers identified key genetic loci governing flowering time, shedding light on the complex polygenic control of this trait. These findings not only deepen our understanding of olive tree adaptation but also offer new genetic insights to guide breeding programs in developing climate-resilient olive…

For decades, scientists believed cool temperate rainforests were fragile ecosystems easily damaged by disturbances like fires or logging. But new research from the University of Melbourne challenges this view, revealing how these ancient forests actually depend on disturbance for their survival. The study focused on Nothofagus moorei, or Antarctic beech, a towering tree that forms the backbone of these ecosystems. The research team analyzed data from silvicultural experiments established in the 1960s across 15 plots in northern New South Wales….

New DNA map could lead to more nutritious, sustainable nuts California produces 99% of the nation’s pistachios, generating nearly $3 billion in economic value in the state. But pistachios have been slightly understudied in part because of the lack of a high-quality map of their DNA. University of California, Davis, researchers have now generated the most comprehensive genome sequence of the pistachio, allowing plant breeders to create better — perhaps more nutritious — varieties. They’ve also detailed how pistachio nuts…

Scientists treat seeds with cold plasma, measure impact on plant growth, insect defense The same substance that paints the sky with the Northern Lights also appears to enhance plant growth and insect defense, according to a new study. Food science and entomology researchers from the Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station teamed up to harness plasma and measure its effects on rice seed. The project began after Mahfuzur Rahman, assistant professor of food science, acquired a machine that produces cold plasma. Known…

Bigger, tastier tomatoes and eggplants could soon grace our dinner plates thanks to Johns Hopkins scientists who have discovered genes that control how large the fruits will grow. The research—led by teams at Johns Hopkins University and Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory—could lead to the development of new varieties of heirloom tomatoes and eggplants, including those that help support agriculture in areas around the world where local varieties are currently too small for large-scale production. Findings were published in the journal Nature. “Once…

What does it mean if our economy works without fossil raw materials such as oil and gas? The logical answer is that we will have to create value almost exclusively with biological, renewable resources. This so-called bioeconomy presents us with major challenges, both locally and globally. Researchers from Leibniz Institute for Agricultural Engineering and Bioeconomy in Potsdam recently published a concept paper in the scientific Biofuel Research Journal, which combines common bioeconomy models into a comprehensive concept. They describe what…
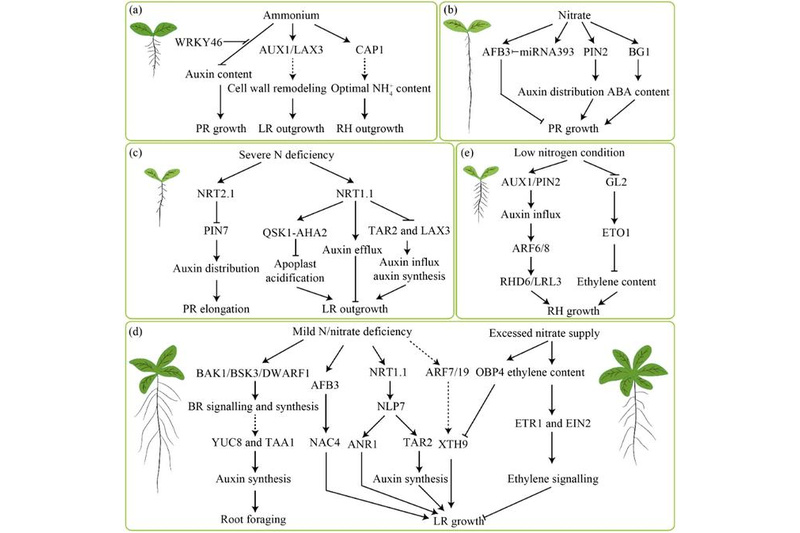
In soil, nitrogen (N), an essential macronutrient for plant growth, exhibits significant spatial heterogeneity. This necessitates plants to grapple with a complex array of environmental conditions in their quest for N sustenance. Roots, as the pivotal organs in N acquisition, manifest a remarkable morphological plasticity, including variations in the length and density of primary roots, lateral roots, and root hairs, in response to the form and content of available N, which is termed N-dependent root system architecture (RSA). For cultivated crops, the…

Famously twisted shrub mainly grows in California A new species of manzanita — a native California shrub famous for its twisted branches and wildfire resilience — has been discovered on the central coast, but its survival is already threatened by urban development that could destroy much of its fragile population. The discovery is detailed in a new study published in PhytoKeys, where researchers used genetic analysis to confirm the plant as a distinct species. Named Arctostaphylos nipumu to honor the…

Researchers in the Department of Entomology found that the secret to the bees’ success in food gathering is all in the “waggle.” As far as animals go, honeybees are world-class dancers. While not as deep and complex as a Super Bowl half-time show, the bees’ moves, known as the “waggle” dance, convey very specific food foraging instructions to their nestmates. The direction the dancer moves explains to other bees which way to go, and the duration of the waggle dance,…

Agricultural fertilizers are critical for feeding the world’s population, restoring soil fertility and sustaining crops. Excessive and inefficient use of those resources can present an environmental threat, contaminating waterways and generating greenhouse gases such as nitrous oxide. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Agricultural Science & Technology have addressed those challenges with glass fertilizer beads. The beads control nutrient release, and the researchers say they’re environmentally compatible. “The results show that glass fertilizers can be tailored to plant needs, slowly and…

Model predicts presence of animal feeding operations with 87 percent accuracy. Understanding where farm animals are raised is crucial for managing their environmental impacts and developing technological solutions, but gaps in data often make it challenging to get the full picture. Becca Muenich, biological and agricultural engineering researcher, set out to fill the gap with a new technique for mapping animal feeding operations. Without proper control strategies, the waste generated by these operations can pose significant ecological harm, Muenich said,…

The National Champion Tree Program to take nominations for next register through August The National Champion Tree Program (NCTP) will take nominations for new Champion Trees on its website starting February 28. The list of eligible tree species for the 2025-2026 register includes more than 1,200 species of trees native and naturalized to the U.S., a steep increase from the 900 species eligible for the 2024 register. It is available online in the Register of Champion Trees. Nominations for potential Champions will stay…