
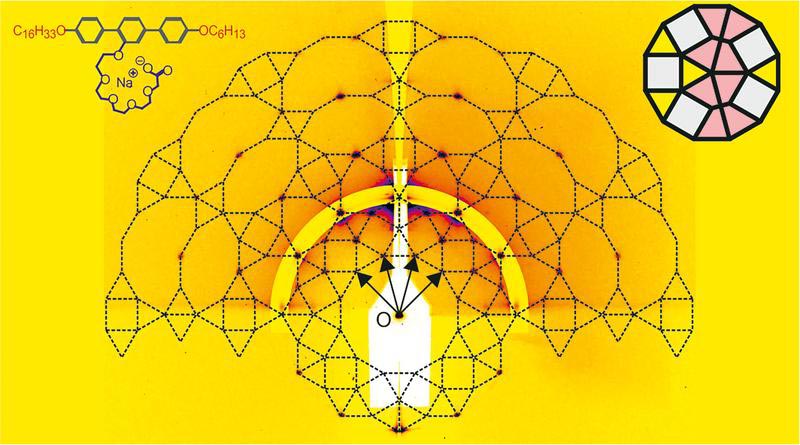
Illustration of liquid quasicrystals consisting of dodecagons
(c) Zeng et al / Nature Chemistry
An unusual quasicrystal has been discovered by a team from the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU), the University of Sheffield and Xi’an Jiaotong University. It has a dodecagonal honeycomb structure that has never been seen before. Until now, similar quasicrystals were only known to come in a solid – not liquid – form. The team presents its results in the scientific journal “Nature Chemistry”.
Quasicrystals have a special structure. They have a regular pattern similar to normal crystals, however, in normal crystals, the arrangement of the individual components is repeated over and over at regular intervals. In the case of quasicrystals, the components do not fit together in such a periodic pattern. This special structure gives them special properties that normal crystals do not have.
The newly discovered quasicrystal consists of dodecagons, which in turn are made up of a mixture of triangular, square and, for the first time, trapezoidal shaped cells. These are generated from the self-assembly of “T-shaped” molecules. “We have discovered a perfectly ordered liquid quasicrystal. Such a material has never been seen before,” says chemist Professor Carsten Tschierske at MLU. The team’s latest study also provides new insights into the formation of these special structures. “Until now, it was assumed that the stability of quasicrystals was based on an entropy gain resulting from the breaking of strict periodic tessellation rules. However, our results suggest that, in this case, the stability may be due to energy minimisation in the perfect quasicrystalline order,” Tschierske adds.
According to the researcher, the potential applications for these new liquid quasicrystals are promising. For example, they could be used in the future to produce functional self-assembling and self-healing materials which could be applied in optics and electronics, as they have the potential to create new ways to manipulate light and charge carriers.
Parts of the work were funded by the German Research Foundation within the framework of the Research Training Group 2670 “Beyond Amphiphilicity: Self-Organization of Soft Matter via Multiple Noncovalent Interactions”.
Originalpublikation:
Study: X. Zeng et al. A columnar liquid quasicrystal with a honeycomb structure that consists of triangular, square and trapezoidal cells. Nature Chemistry (2023). doi: 10.1038/s41557-023-01166-5
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-023-01166-5












