
Targeting chaperon protein HSP70 as a novel therapeutic strategy for FLT3-ITD-positive acute myeloid leukemia
Credit: HU Chen
A new type of targeting chaperon protein HSP70 inhibitor QL47 was recently discovered by a team led by Prof. LIU Qingsong from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences to treat FLT3-ITD-positive acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Their findings have been published on Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.
“What we are seeking is a new therapeutic strategy which imperative for FLT3-ITD-positive AML,” said HU Chen, lead author of the study.
Approximately, 25% of AMLs carry FLT3-ITD (internal tandem duplication) oncogenic mutations, and FLT3 kinase inhibitors have already achieved great success in the clinic for FLT3-ITD-positive AML. However, after prolonged treatment, drug-acquired resistance is observed in patients treated with FLT3 kinase inhibitor.
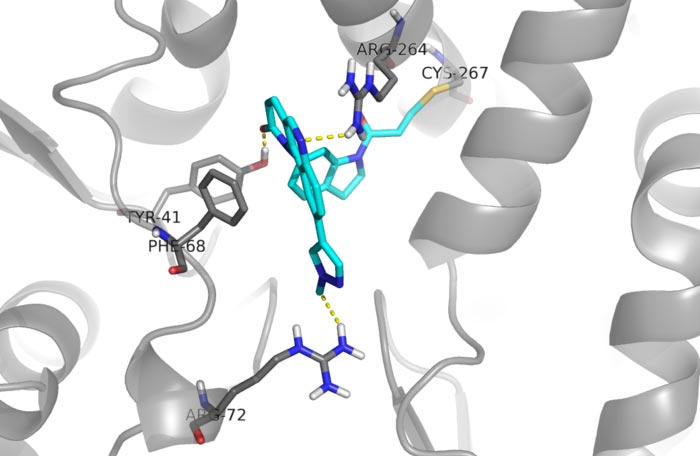
In this research, the researchers found that compound QL47 had potent anti-proliferative activity against FLT3-ITD positive AML cell lines and induces FLT3-ITD protein degradation.
Further study proved that QL47 irreversibly bound to the heat shock protein HSP70 and inhibited its refolding activity, which in turn led to the degradation of FLT3-ITD and inhibited proliferation of the FLT3-ITD positive AML cells.
“It is inducible HSP70 instead of constitutive expressed HSC70 that is important for FLT3 protein stabilization and FLT3-ITD-positive cell viability,” said Dr. HU.
The evaluation of QL47 in primary patient cells and in vivo tumor models showed that QL47 induced the degradation of FLT3-ITD protein and cell apoptosis in primary patient cells. In mice bone marrow engraftment model, QL47 significantly extends the animal survivals.
“Targeting the chaperone protein HSP70 could potentially provide a novel strategy for FLT3-ITD-positive AML treatment,” said HU.
Journal: Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy
DOI: 10.1038/s41392-021-00672-7
Method of Research: Experimental study
Subject of Research: Not applicable
Article Title: Targeting chaperon protein HSP70 as a novel therapeutic strategy for FLT3-ITD-positive acute myeloid leukemia
Article Publication Date: 15-Sep-2021
Media Contact
Weiwei Zhao
Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences
annyzhao@ipp.ac.cn
Office: 86-551-655-91206












