
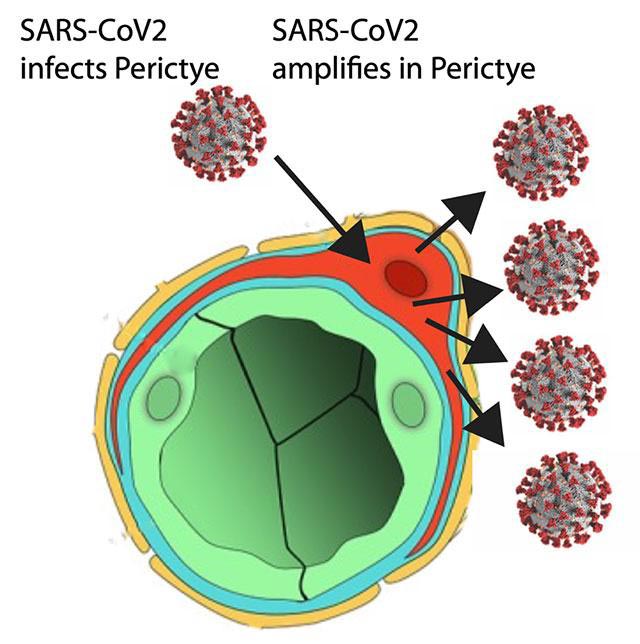
Figure depicts SARS-CoV-2 spreading through blood vessels (green) to infect pericytes (red), which amplify infection and can spread infection to other cell types in the brain.
Credit: UC San Diego Health Sciences
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Rady Children’s Institute for Genomic Medicine have produced a stem cell model that demonstrates a potential route of entry of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, into the human brain.
The findings are published in the July 9, 2021 online issue of Nature Medicine.
“Clinical and epidemiological observations suggest that the brain can become involved in SARS-CoV-2 infection,” said senior author Joseph Gleeson, MD, Rady Professor of Neuroscience at UC San Diego School of Medicine and director of neuroscience research at the Rady Children’s Institute for Genomic Medicine.
“The prospect of COVID19-induced brain damage has become a primary concern in cases of ‘long COVID,’ but human neurons in culture are not susceptible to infection. Prior publications suggest that the cells that make the spinal fluid could become infected with SARS-CoV-2, but other routes of entry seemed likely.”
Gleeson and colleagues, who included both neuroscientists and infectious disease specialists, confirmed that human neural cells are resistant to SARS-CoV-2 infection. However, recent studies hinted that other types of brain cells might serve as a ‘Trojan horse.’
Pericytes are specialized cells that wrap around blood vessels — and carry the SARS-CoV2 receptor. The researchers introduced pericytes into three-dimensional neural cell cultures — brain organoids — to create “assembloids,” a more sophisticated stem cell model of the human body. These assembloids contained many types of brain cells in addition to pericytes, and showed robust infection by SARS-CoV-2.
The coronavirus was able to infect the pericytes, which served as localized factories for production of SARS-CoV-2. These locally produced SARS-CoV-2 could then spread to other cell types, leading to widespread damage. With this improved model system, they found that the supporting cells known as astrocytes were the main target of this secondary infection.
The results, said Gleeson, indicate that one potential route of SARS-CoV-2 into the brain is through the blood vessels, where SARS-CoV-2 can infect pericytes, and then SARS-CoV-2 can spread to other types of brain cells.
“Alternatively, the infected pericytes could lead to inflammation of the blood vessels, followed by clotting, stroke or hemorrhages, complications that are observed in many patients with SARS-CoV-2 who are hospitalized in intensive care units.”
Researchers now plan to focus on developing improved assembloids that contain not just pericytes, but also blood vessels capable of pumping blood to better model the intact human brain. Through these models, Gleeson said, greater insight into infectious disease and other human brain disease could emerge.
###
Co-authors include: Lu Wang, David Sievert and Sangmoon Lee, UC San Diego and Rady Children’s Institute for Genomic Medicine; Alex E. Clark and Aaron F. Carlin, UC San Diego; Hannah Federman, UC San Diego, Rady Children’s Institute for Genomic Medicine and Rutgers University; and Benjamin D. Gastfriend, Eric V. Shusta and Sean P. Palecek, University of Wisconsin-Madison.












