
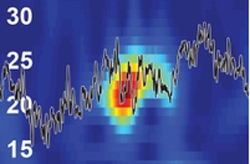
A representation of the neuronal oscillations during a pulse of beta waves.
Image: AG Diester
In cooperation with her working group, Prof. Dr. Ilka Diester of the University of Freiburg's Institute of Biology III and excellence cluster BrainLinks-BrainTools has developed a new method for analyzing data in the brain.
They are using their method to detect short beta wave bursts in real time within neural frequency bands of around 20 Hertz and to show how rats can increase the occurrence of these bursts. The researchers have published their results in the scientific journal “Nature Communication Biology.”
In humans, monkeys, and rodents, it is possible to detect short bursts of up to 150 milliseconds of beta waves – a specific section of the brainwave spectrum – within a frequency range of 15 hertz to 30 hertz. Researchers up to now connected these events with memory, motion, and perception.
During what is known as neuro-feedback training, rats always receive a reward when their brain produces a burst in the beta frequency range. This increases not only the recurrence of beta frequency bursts, but the total amplitude of this frequency range as well.
Through their work, Diester and her team have been able to predict beta range bursts in rats based on the rats movements – particularly in the front half of the rats' bodies. This new method paves the way for investigating the role of beta bursts in specific behaviors.
Because beta frequencies play a significant role in motion control, the method also opens new approaches in neuroprosthetics – the development and application of electronic implants for the restoration of damaged nerve function.
At the Institute of Biology III and BrainLinks-BrainTools, Diester leads a working group that is using optophysiology – or new types of optical tools – to investigate the functioning of neural circuitry.
The researchers are probing the neural underpinnings of motor and cognitive control as well as interactions between the prefrontal and motor cortex, which are both parts of the cerebral cortex.
Original publication
Karvat, G., Schneider, A., Alyahyay, M., Steenbergen, F., Tangermann, M., & Diester, I. (2020): Real-time detection of neural oscillation bursts allows behaviourally relevant neurofeedback. In: “Nature Communications Biology”. DOI: 10.1038/s42003-020-0801-z
Article about Ilka Diester's research in the University of Freiburg's online magazine
http://www.pr.uni-freiburg.de/pm/online-magazin/forschen-und-entdecken/licht-in-…
Contact:
Prof. Dr. Ilka Diester
Institute of Biology III
University of Freiburg
Tel.: 0761/203-8440
ilka.diester@biologie.uni-freiburg.de
https://www.pr.uni-freiburg.de/pm-en/press-releases-2020/brief-bursts-big-insigh…












