
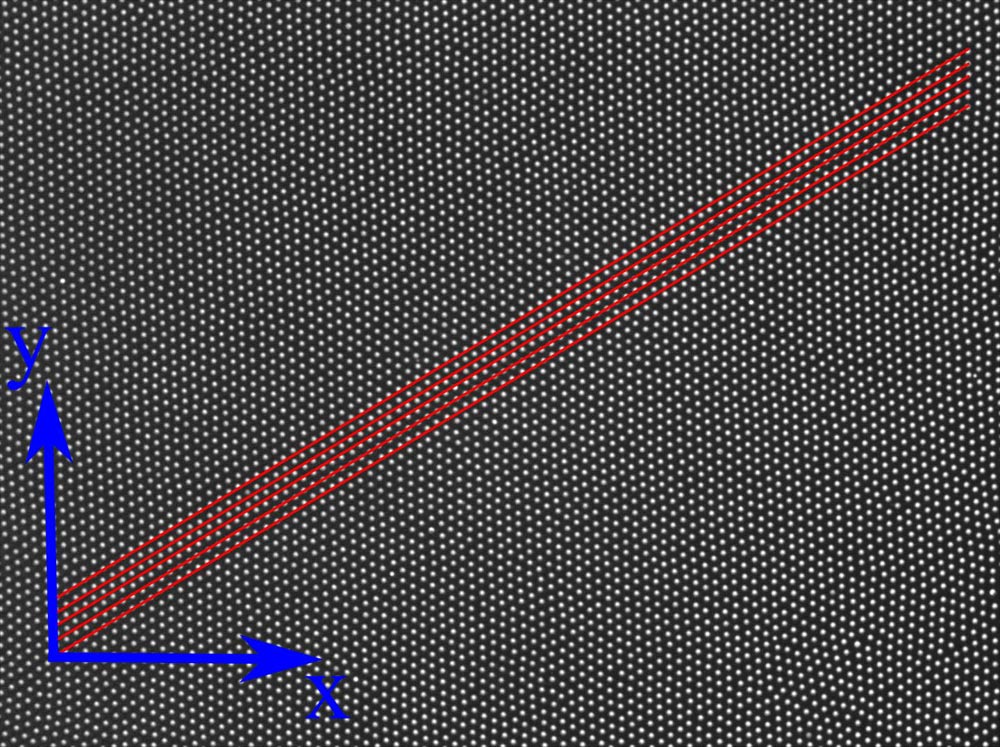
Microscopic image of lattice vibrations in a two-dimensional crystal consisting of a monolayer of approx. 6,500 colloids. Deviations of particle positions from ideal lattice sites can be observed. If these deviations grow (logarithmically) with the system size beyond all limits, they are due to Mermin-Wagner fluctuations. In a three-dimensional crystal, particle distances are fixed and deviations are limited, irrespective of the size of the crystal.
Credit: University of Konstanz
Now, 50 years later, a group of physicists from Konstanz headed by Dr Peter Keim, were able to prove the Mermin-Wagner theorem by experiments and computer simulations – at the same time as two international working groups from Japan and the USA. The research results were published in the 21 February 2017 edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) scientific journal.
Based on a model system of colloids, Peter Keim was able to prove that in low-dimensional systems slow but steadily growing fluctuations occur in the distance between particles: the positions deviate from perfect lattice sites, distances frequently increase or decrease. Crystal formation over long ranges is therefore not possible in low-dimensional materials.
“Often the Mermin-Wagner theorem has been interpreted to mean that no crystals at all exist in two-dimensional systems. This is wrong: in fact long-wave density fluctuations grow logarithmically in two-dimensional systems and only destroy the order over long ranges,” explains Peter Keim. In small systems of only a few hundred particles, crystal formation can indeed occur.
But the larger the systems, the more the irregularities in particle position grow, ultimately preventing crystal formation over long ranges. Peter Keim was also able to measure the growth rate of these fluctuations: he observed the predicted logarithmic growth, the slowest possible form of a monotonic increase. “However, the perturbation of the order not only has a structural impact, but also leaves traces in the dynamics of the particles,” continues Keim.
The Mermin-Wagner theorem is one of the standard topics of interest in statistical physics and recently became a subject of discussion again in the context of the Nobel Prize for Physics: Michael Kosterlitz, the 2016 Nobel Prize winner published in a commentary how he and David Thouless got motivated to investigate so-called topological phase transitions in low-dimensional materials: it was the contradiction between the Mermin-Wagner theorem that prohibits the existence of perfect low-dimensional crystals, on the one hand and the first computer simulations that nevertheless indicated crystallization in two dimensions on the other hand. The proof from Peter Keim and his research team has now resolved this apparent contradiction: over short scales crystal formation is indeed possible, but impossible over long ranges.
The Konstanz-based project analyses data from four generations of doctoral theses. The Mermin-Wagner fluctuations were successfully proven by investigating the dynamics in unordered, amorphous, that means glassy, two-dimensional solids – just as in the work from Japan and the USA which appeared almost at the same time – while the existence of Mermin-Wagner fluctuations in two-dimensional crystals still has not been proven directly. The Konstanz research was sponsored by the German Research Foundation (DFG) and the Young Scholar Fund of the University of Konstanz.
###
Factual overview:
- Model system of the experiment: Colloids confined at a flat water-air-interface.
- Project sponsored by: German Research Foundation(DFG) and the Young Scholar Fund of the University of Konstanz
- Proved almost simultaneously by: H. Shiba, Y. Yamada, T. Kawasaki, K. Kim: Phys. Rev.Lett., 117, 245701 (2016) S. Vivek, C. Kelleher, P. Chaikin, E. Weeks: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, 114, 1850 (2017)
- Comment from Michael Kosterlitz about his early work that led to the Nobel Prize:
Journal of Physics Condensed Matter, 28, 481001 (2016)
Note to editors:
Photos can be downloaded from here:
https:/
Caption: Microscopic image of lattice vibrations in a two-dimensional crystal consisting of a monolayer of approx. 6,500 colloids. Deviations of particle positions from ideal lattice sites can be observed. If these deviations grow (logarithmically) with the system size beyond all limits, they are due to Mermin-Wagner fluctuations. In a three-dimensional crystal, particle distances are fixed and deviations are limited, irrespective of the size of the crystal.
https:/
Caption: Dr Peter Keim, University of Konstanz
Original publication:
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) 114, 1861 (2017)
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1612964114
Comments highlighting the original publication:
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 114, 2440 (2017)
Nature Physics 13, 205 (2017)
Contact:
University of Konstanz
Communication and Marketing
Phone: +49 753188-3603
E-mail: kum@uni-konstanz.de












