Superconductors with ‘zeitgeist’ – when materials differentiate between the past and the future
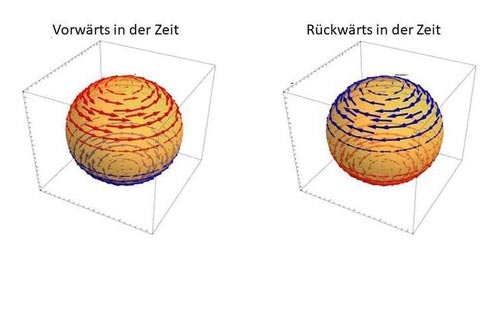
Magnetic fields inside a superconductor with broken time-reversal symmetry: Red and blue arrows illustrate the direction and strength of the internal magnetic fields for forward and backward time development. © Hans-Henning Klauss
What happened yesterday and what will happen tomorrow are usually two different and quite independent matters. The past and the future of human life are not symmetric and therefore not reversible. In physics, this is different.
The fundamental forces of nature in elementary particles, atoms and molecules are symmetric with respect to their development in time: Forwards or backwards makes no difference, scientists call this a time-reversal symmetry.
For decades this symmetry was also found in all superconductors. Superconductors are materials which can conduct electrical currents at low temperatures without energy dissipation.
One of their major applications is the efficient generation of strong magnetic fields, for example in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) diagnosis. Approximately 99% of all known superconducting materials are time-reversal symmetric.
However, for some years, physicists have been discovering new superconductors which brake time-reversal symmetry. To explain these observations, the basic mechanism of superconductivity, which has been known for more than 75 years, had to be modified considerably.
Only these novel superconductors are able to spontaneously generate constant internal magnetic fields. This can lead to new applications, for example in quantum computing devices.
An international research team led by Dr. Vadim Grinenko und Prof. Hans-Henning Klauss from the Institute of Solid State and Materials Physics at TU Dresden discovered this new magnetic state with broken time-reversal symmetry in iron-based superconductors. The synthesis of this versatile class of intermetallic compounds is comparatively simple.
Therefore, these iron-based superconductors have an enormous potential for applications.
“In our study, we show that the iron-based superconductors discovered more than twelve years ago continue to reveal new quests for fundamental research as well as chances for new applications,” states Prof. Hans-Henning Klauss.
Hans-Henning Klauss
Chair of Solid State Physics/Electronic Properties
Email: henning.klauss@tu-dresden.de
Dr. Vadim Grinenko
Institut für Festkörper- und Materialphysik
Email: v.grinenko@ifw-dresden.de
V. Grinenko , R. Sarkar, K. Kihou, C. H. Lee, I. Morozov, S. Aswartham, B. Büchner, P. Chekhonin, W. Skrotzki, K. Nenkov, R. Hühne, K. Nielsch, S. -L. Drechsler, V. L. Vadimov, M. A. Silaev, P. A. Volkov, I. Eremin, H. Luetkens, and H.-H. Klauss, ‘Superconductivity with broken time-reversal symmetry inside a superconducting s-wave state’ Nature Physics, 10.1038/s41567-020-0886-9. URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41567-020-0886-9
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…





















