On the way to robust quantum computers
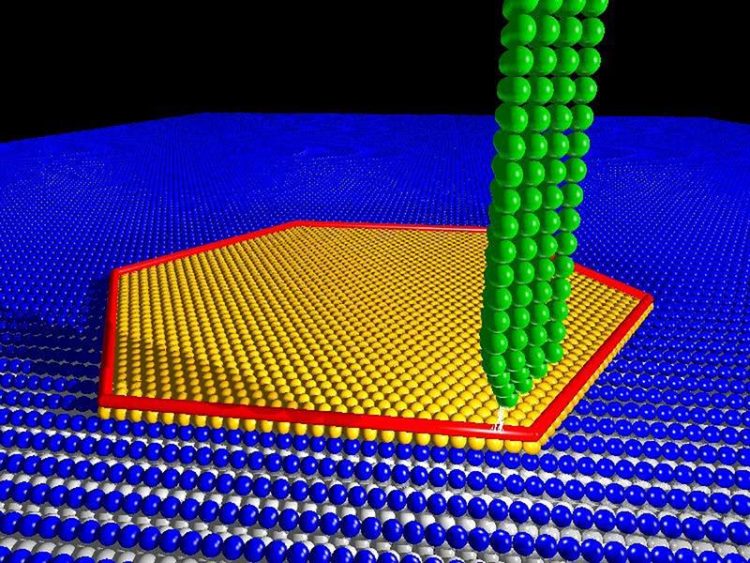
Illustration of an atomically high iron island (yellow) on a superconducting rhenium crystal and with the Majorana edge state (red) at the periphery. UHH/MIN/Kim/Wiesendanger
The development of quantum computers is the major goal of industrial and university research efforts worldwide. The main problem in the realization of a quantum computer is the sensitivity of quantum states to external perturbations.
Majorana quasiparticles have raised great hopes for the future of quantum computers since they are robust against disturbing influences from the environment in contrast to other kinds of quantum bits.
Last year, the Hamburg research group headed by Prof. Dr. Roland Wiesendanger had already observed Majorana states at the ends of magnetic chains of individual iron atoms on a superconducting rhenium crystal.
The same team has now succeeded in directly observing Majorana states at the edges of iron islands – which are only one atomic layer high – on rhenium.
The formation of an exotic superconducting state was observed as a prerequisite for the formation of Majorana states. The experimental results could be explained and interpreted by a theoretical study carried out simultaneously by researchers from Hamburg and Chicago.
The coupling of Majorana edge states on atomic islands and Majorana end states in atomic chains can be used to realize elementary building blocks for memory and logic operations of a quantum computer.
The demonstration of basic computational operations based on Majorana states is now the next major goal of the Hamburg researchers on their way to a robust quantum computer.
Prof. Dr. Roland Wiesendanger
Faculty of Mathematics, Informatics and Natural Sciences
Department of Physics
Phone: +49 40 42838-5244
E-Mail: wiesendanger@physnet.uni-hamburg.de
Heiko Fuchs
Faculty of Mathematics, Informatics and Natural Sciences
Dean's office, science editorial office
Phone: +49 40 42838-7193
E-Mail: heiko.fuchs@uni-hamburg.de
A. Palacio-Morales, E. Mascot, S. Cocklin, H. Kim, S. Rachel, D. K. Morr, and R. Wiesendanger, Atomic-scale interface engineering of Majorana edge modes in a 2D magnet-superconductor hybrid system, Science Advances 5, eaav6600 (2019).
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.uni-hamburg.de/All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















