
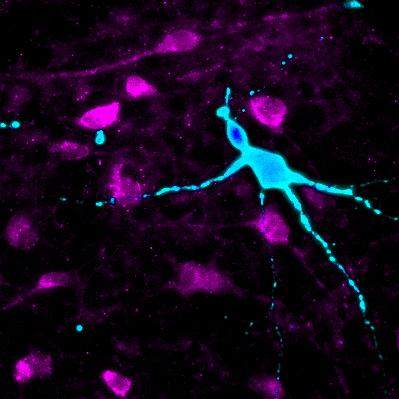
Image shows two types of hypothalamic neurons (in magenta and cyan) that were derived from induced pluripotent stem cells as part of a Cedars-Sinai-led study of the brain and obesity.
Credit: Cedars-Sinai Board of Governors Regenerative Medicine Institute
Scientists have re-created brain neurons of obese patients using “disease in a dish” technology, offering a new method to study the brain's role in obesity and possibly help tailor treatments to specific individuals.
“We have taken the first step in developing a great platform that potentially could be used to evaluate the effects of experimental therapeutics on specific patients,” said Dhruv Sareen, PhD, assistant professor of Biomedical Sciences at Cedars-Sinai. “Ultimately, we are paving the way for personalized medicine, in which drugs could be customized for obese patients with different genetic backgrounds and disease statuses.”
Sareen is senior author of a study about the findings, which was led by Cedars-Sinai investigators and published today in the journal Cell Stem Cell.
More than one-third of U.S. adults are obese, a condition that puts them at higher risk for heart disease, stroke, diabetes and certain cancers, according to federal statistics. “We wanted to do this study because obesity and related metabolic diseases are global epidemics that are increasing alarmingly each year,” Sareen said. “Even more worrying is the increase in childhood obesity, which could have lasting effects on future generations.”
The new study focused on the brain's hypothalamus area, which regulates hunger, thirst, body temperature and other functions requiring hormonal control. Some studies have suggested that obesity may result, in part, from genetic mutations in certain hypothalamic neurons. These neurons produce and respond to chemicals that influence metabolism and help the brain and gastrointestinal tract communicate with each other. When these neurons malfunction, an individual may have trouble sensing when they are full and should stop eating, leading to weight gain.
“Understanding how this signaling process works at the cellular level is important in providing much-needed clues for future treatment strategies for obesity,” Sareen said. “But the process is difficult to investigate because hypothalamus tissues from living patients are not readily accessible for direct examination.”
The new study demonstrates a way around this barrier by using stem-cell technology to reproduce hypothalamic neurons outside the body.
For their study, investigators sampled blood and skin cells from five super-obese individuals and seven individuals of normal weight. Super-obesity was defined as having a body mass index of 50 or higher versus a normal score under 25. The investigators genetically reprogrammed these cells into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which can create any type of cell in the body. The iPSCs were coaxed to generate the special hypothalamic neurons. Because of the way they were produced, these “neurons in a dish” matched the genetics of the individual patient who donated the original cells.
When the investigators compared the iPSC-generated neurons of super-obese individuals to those of normal-weight individuals, they found significant differences. The super-obese neurons contained multiple genetic mutations and responded abnormally to several hormones that regulate hunger, satiety and metabolism.
“These findings showed that iPSC technology is a powerful method for studying obesity and how interactions between genes and the environment may influence its development,” said Sareen, who directs the Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Core Facility at the Cedars-Sinai Board of Governors Regenerative Medicine Institute. “We reliably and efficiently differentiated multiple iPSCs into hypothalamic neurons and, using sophisticated gene expression and statistical techniques, showed these neurons are similar to human hypothalamic tissues.”
He added there are several intermediate steps before the full potential of the method can be realized.
Uthra Rajamani, PhD, a Cedars-Sinai research scientist and the study's first author, said one limitation of the study's findings is that in the body the special hypothalamic neurons communicate with other centers of the brain, as well as the gut, liver, pancreas and other organs. This integration is difficult to reproduce in a dish using only one type of cell.
“In future studies, we would like to show functional communication between iPSC-generated hypothalamic neurons and other relevant cell types, and also create relevant human circuitry in a dish–where these neurons can communicate with other organs as they do in a human body,” Rajamani said.
###
Besides Sareen and Rajamani, the study team included Cedars-Sinai investigators from the Genomics Core, the Metabolism and Mitochondrial Research Core and the Smidt Heart Institute; and from University of California, Irvine.
The Cell Stem Cell study is part of the Cedars-Sinai Precision Health initiative, whose goal is to drive the development of the newest technology and best research, coupled with the finest clinical practice, to rapidly enable a new era of personalized health.
Funding: Research reported in this publication was supported by Cedars-Sinai institutional programmatic funds and the National Center for Advancing Translational Science of the National Institutes of Health under UCLA CTSI award number UL1TR000124.












