
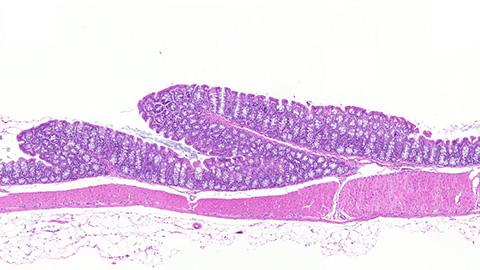
This is a histological image of colon sections from mice that received T cells from CD4-creERafl/fl mice.
Credit: University of Turku
The incidence of autoimmune diseases such as MS, RA, and SLE is higher in women than in men. The estrogen hormone secreted in women may contribute to the pathogenesis of these diseases.
A research team led by Docent Zhi Chen from Turku Center for Biotechnology of the University of Turku has collaborated with researchers from the University of Georgia, United States to address the long-standing issue of hormonal effect on autoimmune diseases.
Estrogen hormone shows its action on cells mostly through estrogen receptor alpha (ERα). Researchers from Turku generated mice with ERα protein specifically deleted in T cells.
– The eureka moment of our research is that in a mouse model of human inflammatory bowel disease, transfer of naive T helper cells from ERα deficient mice did not succumb to colitis, unlike transfer from their counterparts, Docent Zhi Chen tells.
– Furthermore, using cutting-edge technique RNA sequencing approach combined with in vitro and in vivo experiments, we discovered that ERα regulates multiple aspects of T cell function, including T cell activation, proliferation and survival, Chen adds.
Regulatory T cells are group of T cells that help in preventing autoimmune diseases. The researchers found that ERα influences the function and differentiation of regulatory T cells.
###
The research is funded by grants from the Academy of Finland to Zhi Chen as postdoctoral fellow and later as Academy Research Fellow and National Institutes of Health R01 to Wendy Watford at the University of Georgia.
The study is published in the journal Science Signaling. The F1000 prime, the faculty that recommends the best articles has adjudged this study as new finding and also potential to develop a novel drug target.
More information: Docent Zhi Chen, +358294503775, zhi.chen@utu.fi
Original publication:
Estrogen receptor α contributes to T cell-mediated autoimmune inflammation by promoting T cell activation and proliferation. Imran Mohammad, Inna Starskaia, Tamas Nagy, Jitao Guo, Emrah Yatkin, Kalervo Väänänen, Wendy T. Watford, and Zhi Chen. Sci. Signal. 17 Apr 2018: Vol. 11, Issue 526, eaap9415. DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.aap9415.












