In Alzheimer's mice, memory restored with cancer drug
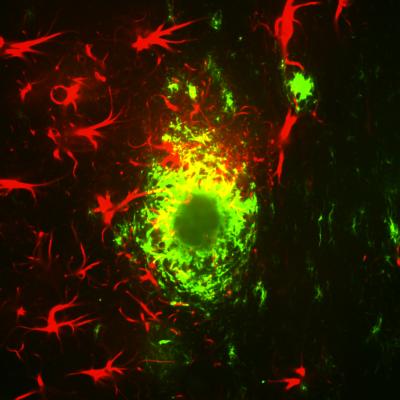
Star-like glial cells in red surround alpha beta plaques in the cortex of a mouse with a model of Alzheimer's Disease. Credit: Strittmatter lab/Yale
The drug, AZD05030, developed by Astra Zeneca proved disappointing in treating solid tumors but appears to block damage triggered during the formation of amyloid-beta plaques, a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease. The new study, funded by an innovative National Institutes of Health (NIH) program to test failed drugs on different diseases, has led to the launch of human trials to test the efficacy of AZD05030 in Alzheimer's patients.
“With this treatment, cells under bombardment by beta amyloid plaques show restored synaptic connections and reduced inflammation, and the animal's memory, which was lost during the course of the disease, comes back,” said Stephen M. Strittmatter, the Vincent Coates Professor of Neurology and senior author of the study.
In the last five years, scientists have developed a more complete understanding of the complex chain of events that leads to Alzheimer's disease. The new drug blocks one of those molecular steps, activation of the enzyme FYN, which leads to the loss of synaptic connections between brain cells. Several other steps in the disease process have the potential to be targets for new drugs, Strittmatter said.
“The speed with which this compound moved to human trials validates our New Therapeutic Uses program model and serves our mission to deliver more treatments to more patients more quickly,” said Christopher P. Austin, M.D., director of NIH's National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS), which funded the work.
###
Yale's Christopher H. van Dyck, a co-author of the paper, and Strittmatter have initiated a multi-site clinical trial to determine whether the drug can also benefit Alzheimer's patients. For more information, visit https:/
The study was funded by the NCATS and the NIH Common Fund, through the Office of Strategic Coordination/Office of the NIH Director
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















