Magic number colloidal clusters
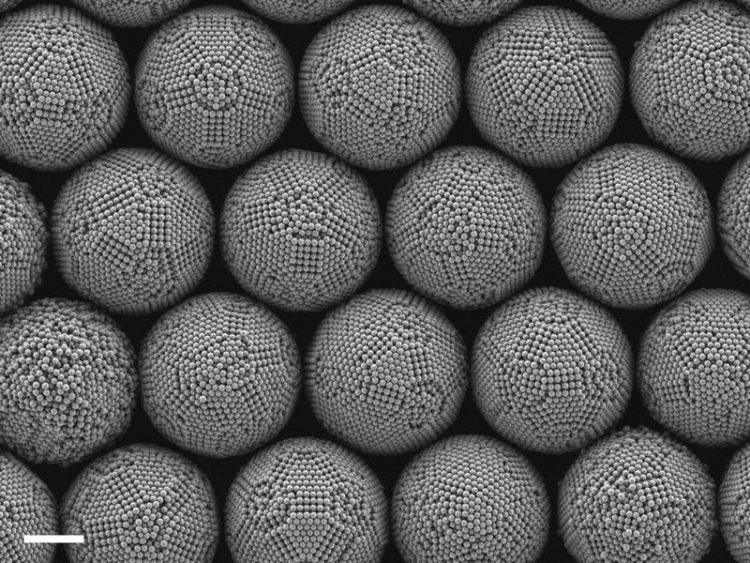
Electron microscopic images of magic number colloidal clusters. Each cluster consists of tiny microscopic polymer balls which come together to form a drying water droplet (scale bar: 2 micrometres). FAU/Junwei Wang
In physics, a cluster is defined as an independent material form at the transition area between isolated atoms and more extensive solid objects or liquids. Magic number clusters can be traced back to the work of Eugene Wigner, Maria Göppert-Mayer and Hans Jensen, who used this theory to explain the stability of atomic nuclei and won the Nobel prize for physics for their research in 1963.
‘Until now, scientists have assumed that the effect is caused purely as a result of the attraction between atoms,’ says Prof. Dr. Nicolas Vogel, Professor for Particle Synthesis. Our research now proves that particles which don’t attract each other also form structures such as these. Our publication contributes to a greater understanding of how structures are formed in clusters in general.’
The research is based on an interdisciplinary collaboration: Prof. Dr. Nicolas Vogel, researcher at the Chair of Particle Technology, and Prof. Dr. Michael Engel, researcher at the Chair of Multi-scale Simulation – both from the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering – have worked closely together with the materials science expert Prof. Dr. Erdmann Spiecker from the Chair of Materials Science (research into micro and nanostructures), pooling their expertise from the various areas. Vogel was responsible for synthesis, Spiecker for structure analysis and Engel for modelling clusters from colloidal polymer balls.
The term colloidal is derived from the ancient Greek word for glue and refers to particles or droplets which are finely distributed in a dispersion medium, either a solid object, a gas, or a liquid. ‘Our three approaches are particularly closely linked in this project,’ underlines Prof. Engel, ‘they complement each other and allow us to gain a deep understanding of the fundamental processes behind the forming of structures for the first time.’
Structures assemble themselves
The first step for the researchers in a process which covers several steps was to synthesise minute colloidal clusters, no larger than a tenth of the diameter of a single hair in total. ‘First of all, water evaporates from an emulsion droplet and the polymer balls are pushed together.
Over time, they assemble increasingly smoother sphere-shaped clusters and begin to crystallise. It is remarkable how several thousand individual particles independently find their ideal position in a precise and highly symmetrical structure in which all particles are placed in predictable positions,’ explains Prof. Vogel.
The researchers discovered more than 25 different magic number colloidal clusters of various shapes and sizes and were able to define four different cluster morphologies: where evaporation was fastest, buckled clusters were formed, as the droplet interface moved faster than the colloidal particles could consolidate. If the evaporation rate was lowered, the clusters were predominantly spherical.
Spherical clusters have a uniformly curved surface with only a weak pattern of crystals. Clusters with icosahedral symmetry were formed as the rate of evaporation decreased further. These clusters have a particularly high degree of symmetry and have numerous two, three or five fold symmetry axes.
Using high resolution microscopy to show the surface of the cluster does not provide sufficient proof of these symmetries. Even if the surface of a cluster appears highly ordered, that is no guarantee that the particles inside the cluster are arranged as expected. To verify this, the researchers used electron tomography, available at the Erlangen Centre for Nanoanalysis and Electron Microscopy (CENEM).
Individual clusters are bombarded with highly energised electrons from all directions and the images recorded. From more than 100 projections, researchers were able to reconstruct the three dimensional structure of the clusters and therefore the pattern of the particles within the clusters in a method reminiscent of computer tomography as used in medicine.
In the next step, the researchers conducted simulations and highly accurate numerical calculations. The analyses proved that clusters consisting of numbers of particles corresponding to a magic number are indeed more stable, as predicted on the basis of the theory. It is well known that the observed icosahedral symmetry can be found in viruses and ultra-small metal clusters, but it has never been investigated directly.
Now, with these results, a detailed and systematic understanding of how such magic number clusters are formed in the investigated model system is possible for the first time, allowing conclusions to be drawn for other natural systems where clusters tend to be formed.
Further information:
Prof. Dr. Nicolas Vogel
Phone: +49 9131 8520357
nicolas.vogel@fau.de
Prof. Dr. Michael Engel
Phone: +49 9131 8520857
michael.engel@fau.de
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















