
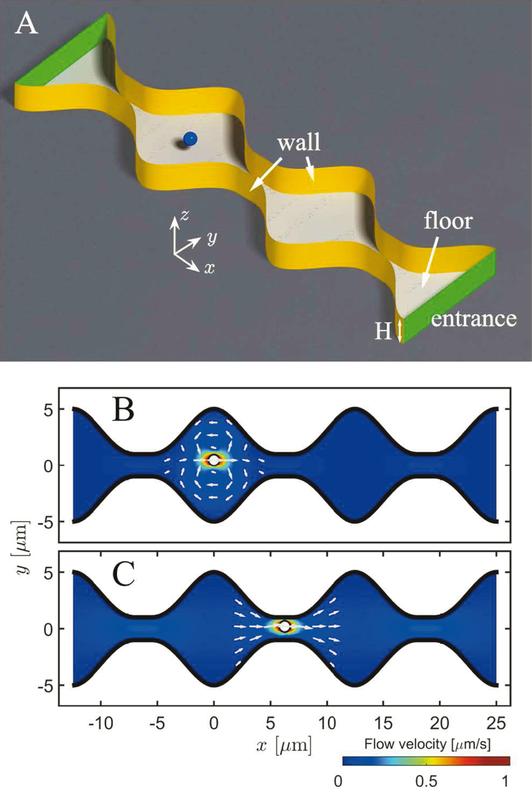
Sketch of the experimental setup for a passive particle diffusing in a corrugated channel.
© Universität Augsburg (IfP)/PNAS
The phenomenon of diffusion is omnipresent and crucial basis of many every-day processes. Diffusion plays a central role for the transport of very small particles. The investigation of Brownian motions by Einstein, Sutherland and Smoluchowski was the foundation of all further research on diffusion processes, also for Prof Peter Hänggi from the University of Augsburg.
Passing the channel
Scientists from various fields such as physics, chemistry and biology are especially interested in the transport through natural and artificial ionic channels and nanopores. Unavoidable component of all channel structures are confining boundaries. The surface of such boundaries are typically not smooth but exhibit rather complex shapes.
Those structural features affect the spontaneous particle zig-zag movements, jittery Brownian motions, on a molecular level. On one hand, there are direct microparticle interactions with the environment, boundaries and surrounding fluid, of attracting and repelling nature altering the transport velocity. On the other hand, the available phase space for motions along the transport direction is limited and determines it, and therefore induces entropic effects.
Hydrodynamic effects were notoriously difficult, if not impossible to explore quantitatively, as the ubiquitous attracting and repelling interactions of corrugated surfaces are hard to model. Solely entropic effects were involved in analytical calculations although they did not mirror the system in its entirety.
Time- and place-dependency of predictions
For the first time, Prof Hänggi and his research group were able to analyze and quantify hydrodynamic effects from theoretical models and experimental set-ups. Their results strongly suggest a reformulation of the existing theories on channel models. In their study, they measured the mean diffusion time and its variances of spherical particles immersed in water inside corrugated channels.
There are three main results representing new milestones for future research on small-scale motion analysis. They could validate the entropic theory in channels that are much wider than the particles radius, and disprove previous simulations of narrow channels. There, hydrodynamic effects can substantially influence the transport velocity of particles.
The mean diffusion time could be 40 % higher than the prediction of the entropic theory tells. Surprisingly, in those narrow channels, the validity of the entropic theory is restored upon using an experimentally determined, spatially dependent effective diffusion coefficient instead of the Stokes-Einstein diffusion coefficient to include the complexity of the hydrodynamic interactions with corrugated confinement.
Publication:
Hydrodynamic and entropic effects on colloidal diffusion in corrugated channels.
Yang X, Liu C, Li Y, Marchesoni F, Hänggi P, Zhang HP.
PNAS 2017 Sep 5;114(36):9564-9569. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1707815114
(Web-Link of the publication: http://www.pnas.org/content/114/36/9564.abstract)
Contact:
Prof. Dr. Dr. h. c. mult. Peter Hänggi
Physics Department
University of Augsburg
86135 Augsburg
Germany
Fon: +49 (0)821-598-3250
Hanggi@physik.uni-augsburg.de
http://www.physik.uni-augsburg.de/theo1/hanggi/












