
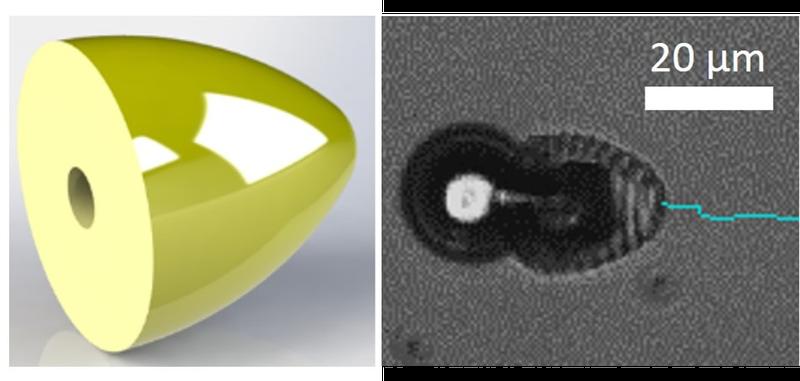
Figures 1 and 2. Microswimmer CAD and microswimmer micrograph
© MPI IS
A tiny robot that gets into the human body through the simple medical injection and, passing healthy organs, finds and treats directly the goal – a non-operable tumor… Doesn’t it sound at least like science-fiction?
To make it real, a growing number of researchers are now working towards this direction with the prospect of transforming many aspects of healthcare and bioengineering in the nearest future. What makes it not so easy are unique challenges pertaining to design, fabrication and encoding functionality in producing functional microdevices.
To make design work
Conventional microfabrication techniques can provide relatively simple geometric structures with limited design flexibility and function. These are so called “passive” systems, limited to a certain structure, such as tube or sphere, which plain fabric allows only restricted chemical functionality.
To overcome these, Prof. Sitti and his coworkers of the Physical Intelligence Department at the Max-Planck-Institute for Intelligent Systems in Stuttgart have recently developed a new two-step approach to provide the devices with desirable functions.
The first step – creation of design entitled to make further elaboration of the microdevice – is realized by crosslinking light-responsive polymers. It is based on the 3D laser lithography technique and allows chemically homogenous base structures to be fabricated with high versatility (see Figure 1).
The second step is linking of functionalities to the produced 3D-sample at its specific sites: the already fabricated structure is being modified with chemically compatible small molecules that are able to introduce new chemical groups on the desired parts of the material (see Figure 2). It is being achieved by selective illumination in 3D: an unreacted polymer precursor is removed and a new precursor, bearing the desired chemical functionality, is performed.
“Size scale of such microdevices strongly determines what type of tools can be used in order to be capable to provide them with definite functionalities. And that’s most challenging: not only to create the convenient design, but to find a way to make it work. “Our research is the first study that translates information from computer design into functional structure in the microscale”, explains Dr. Hakan Ceylan, postdoctoral researcher at the Max-Planck-Institute for Intelligent Systems.
To prove the concept, the authors first prepared a bullet-shaped microswimmer, in which the inner cavity was selectively modified with catalytic platinum nanoparticles over several steps. To further underline the importance of this method for biomaterials development, the researchers designed a microflower bearing orthogonal biotin, thiol and alkyne groups at precisely defined positions (see Figure 3 and Figure 4).
Bigger intelligence at smaller dimensions
In nature, organisms without brains, such as slime molds, bacteria and plants, use physical intelligence as the main route of making decisions and adaptations to complex and evolving conditions. In the same vein, Physical Intelligence Department of Max-Planck-Institute for Intelligent Systems exploits the physical and chemical properties of materials to program active tasks at the micron size.
“Our key objective is to develop new methods of making miniaturized materials that are performing intelligently in complex and unstable environment. An important question concerning this is how intelligence is going to be achieved at the smaller dimensions, where no conventional computational capabilities exist”, Ceylan says. “Our newly developed two-step platform is a significant achievement in this direction”.
Mobile devices at micron scale afford particular advantages to pursue novel bioengineering strategies. The method further unveils computer-aided design to make functional microdevices, potentially opening large avenues for making highly complex new designs that was not conceivable before. Functional soft materials under one-millimeter promise myriad of applications in various fields, including bioengineering, targeted delivery, tissue engineering, programmable matter, self-organizing systems, soft microactuators and mobile microrobots.
A device that has a comparable size of a single cell with on-board motility and sensing capabilities could provide an unprecedented direct access to deep and delicate body sites, such as brain, spinal cord and eye. Therefore it should be perfectly used for minimally invasive medical surgeries, as it potentially opens up new ways of medical interventions with minimal tissue damage compared with the tethered catheters and endoscopes and incision-based procedures.
Although all these new possibilities, which a tiny robot is going to bring, are not yet available, it is not so long to wait till the day it will become our present, scientists are convinced. “In the near future – probably in around 10 years – this could have tremendous applications in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine”, Ceylan assumes, “while, in the longer term, it could revolutionize the treatment of genetic diseases by single cell-level protein or nucleic acid delivery. Such untethered active materials are particularly attractive for microrobotics and medical cargo carrier applications”.












