
New 3-D Wiring Technique Advances Scalable Quantum Computing
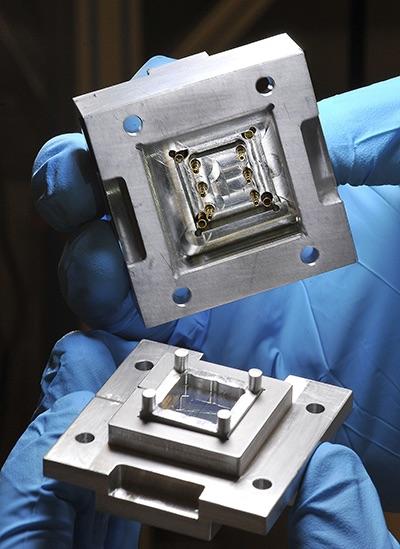
Researchers from the Institute for Quantum Computing at the University of Waterloo led the development of a quantum socket, representing a significant step towards to the realization of a scalable quantum computer.
Credit: University of Waterloo
“The quantum socket is a wiring method that uses three-dimensional wires based on spring-loaded pins to address individual qubits,” said Jeremy Béjanin, a PhD candidate with IQC and the Department of Physics and Astronomy at Waterloo.
He and Thomas McConkey, PhD candidate from IQC and the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Waterloo, are lead authors on the study that appears in the journal Physical Review Applied as an Editors' Suggestion and is featured in Physics. “The technique connects classical electronics with quantum circuits, and is extendable far beyond current limits, from one to possibly a few thousand qubits.”
One promising implementation of a scalable quantum computing architecture uses a superconducting qubit, which is similar to the electronic circuits currently found in a classical computer, and is characterized by two states, 0 and 1.
Quantum mechanics makes it possible to prepare the qubit in superposition states, meaning that the qubit can be in states 0 and 1 at the same time. To initialize the qubit in the 0 state, superconducting qubits are brought down to temperatures close to -273 degrees Celsius inside a cryostat, or dilution refrigerator.
To control and measure superconducting qubits, the researchers use microwave pulses. The pulses are typically sent from dedicated sources and pulse generators through a network of cables connecting the qubits in the cryostat's cold environment to the room-temperature electronics. The network of cables required to access the qubits inside the cryostat is a complex infrastructure and, until recently, has presented a barrier to scaling the quantum computing architecture.
“All wire components in the quantum socket are specifically designed to operate at very low temperatures and perform well in the microwave range required to manipulate the qubits,” said Matteo Mariantoni, a faculty member at IQC and the Department of Physics and Astronomy at Waterloo and senior author on the paper. “We have been able to use it to control superconducting devices, which is one of the many critical steps necessary for the development of extensible quantum computing technologies.”
###
The paper, Three-Dimensional Wiring for Extensible Quantum Computing: The Quantum Socket, is a collaborative effort of researchers at INGUN Prüfmittelbau GmbH, Germany, INGUN USA, and Google in the United States, plus the following researchers from IQC and Waterloo: Jeremy Béjanin, Thomas McConkey, John Rinehart, Carolyn Earnest, Corey Rae McRae, Daryoush Shiri, James Bateman, Yousef Rohanizadegan and Matteo Mariantoni.












