
Faster LEDs Enhance Wireless Communication Using Invisible Light
Researchers aimed to improve LEDs that specifically communicate via deep ultraviolet light, which isn't visible to the human eye.
Credit: Kazunobu Kojima, Tohoku University
Now, a team of researchers based in Japan has married the two options into the ideal combination of long lasting and fast LEDs. They published their results on July 22 in Applied Physics Letters.
“A key technology for faster modulation is to decrease the device si earch for Advanced Materials at Tohoku University. “However, this tactic creates a dilemma: although smaller LEDs can be modulated faster, they have lower power.”
Another issue is that both visible and infrared optical wireless communications can have significant solar interference, according to Kojima. To avoid confusion with visible and infrared solar light, the researchers aimed to improve LEDs that specifically communicate via deep ultraviolet light, which can be detected without solar interference.
“Deep ultraviolet LEDs are currently mass produced in factories for applications related to COVID-19,” Kojima said, noting that deep ultraviolet light is used for sterilization processes as well as in solar-blind optical wireless communications. “So, they're cheap and practical to use.”
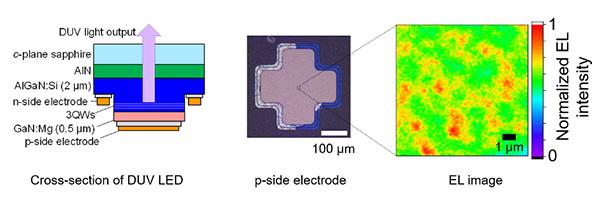
The researchers fabricated the deep ultraviolet LEDs on sapphire templates, which are considered an inexpensive substrate, and measured their transmission speed. They found that the deep ultraviolet LEDs were smaller and much quicker in their communications than traditional LEDs at that speed.
“The mechanism underlying this speed is in how a lot of tiny LEDs self-organize in a single deep ultraviolet LED,” Kojima said. “The tiny LED ensemble helps with both power and speed.”
The researchers want to use the deep ultraviolet LEDs in 5G wireless networks. Many technologies are currently under testing to contribute 5G, and Li-Fi, or light fidelity, is one of the candidate technologies.
“Li-Fi's critical weakness is its solar dependency,” Kojima said. “Our deep ultraviolet LED-based optical wireless technology can compensate for this problem and contribute to society, I hope.”
###
This work was supported in part by Five-Star Alliance and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.












