
Terahertz Wireless: Fast Satellite Links Rival Fiber-Optics
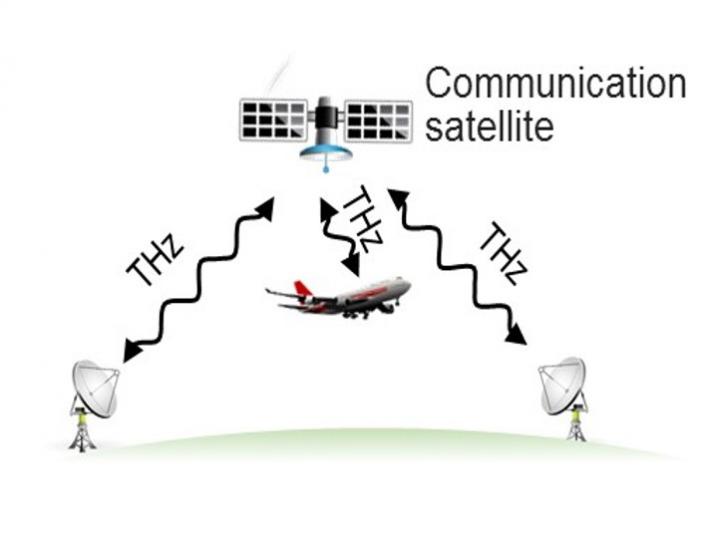
Terahertz wireless links to spaceborne satellites could make gigabit-per-second connection speeds available to anyone anytime, anywhere on the face of the earth, on the ground or in flight.
Credit: Fujishima et al. (Hiroshima University)
The THz band is a new and vast frequency resource expected to be used for future ultrahigh-speed wireless communications. The research group has developed a transmitter that achieves a communication speed of 105 gigabits per second using the frequency range from 290 GHz to 315 GHz.
This range of frequencies are currently unallocated but fall within the frequency range from 275 GHz to 450 GHz, whose usage is to be discussed at the World Radiocommunication Conference (WRC) 2019 under the International Telecommunication Union Radiocommunication Section (ITU-R). Last year, the group demonstrated that the speed of a wireless link in the 300-GHz band could be greatly enhanced by using quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) [2].
This year, they showed six times higher per-channel data rate, exceeding 100 gigabits per second for the first time as an integrated-circuit-based transmitter. At this data rate, the whole content on a DVD (digital versatile disk) can be transferred in a fraction of a second.
“This year, we developed a transmitter with 10 times higher transmission power than the previous version's. This made the per-channel data rate above 100 Gbit/s at 300 GHz possible,” said Prof. Minoru Fujishima, Graduate School of Advanced Sciences of Matter, Hiroshima University. “We usually talk about wireless data rates in megabits per second or gigabits per second. But we are now approaching terabits per second using a plain simple single communication channel. Fiber optics realized ultrahigh-speed wired links, and wireless links have been left far behind.
Terahertz could offer ultrahigh-speed links to satellites as well, which can only be wireless. That could, in turn, significantly boost in-flight network connection speeds, for example. Other possible applications include fast download from contents servers to mobile devices and ultrafast wireless links between base stations,” said Prof. Fujishima.
“Another, completely new possibility offered by terahertz wireless is high-data-rate minimum-latency communications. Optical fibers are made of glass and the speed of light slows down in fibers. That makes fiber optics inadequate for applications requiring real-time responses. Today, you must make a choice between 'high data rate' (fiber optics) and 'minimum latency' (microwave links). You can't have them both. But with terahertz wireless, we could have light-speed minimum-latency links supporting fiber-optic data rates,” he added. The research group plans to further develop 300-GHz ultrahigh-speed wireless circuits.
###
This work was supported by the R&D on Wireless Transceiver Systems with CMOS Technology in 300-GHz Band, as part of an R&D program on Key Technology in Terahertz Frequency Bands of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, Japan.
References [1] K. Takano, S. Amakawa, K. Katayama, S. Hara, R. Dong, A. Kasamatsu, I. Hosako, K. Mizuno, K. Takahashi, T. Yoshida, M. Fujishima, “A 105Gb/s 300GHz CMOS Transmitter,” International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) 2017.
[2] K. Katayama, K. Takano, S. Amakawa, S. Hara, A. Kasamatsu, K. Mizuno, K. Takahashi, T. Yoshida, M. Fujishima, “A 300GHz 40nm CMOS Transmitter with 32-QAM 17.5Gb/s/ch Capability over 6 Channels,” International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) 2016.
Media Contacts: Hiroshima University Public Relations Group Email: koho@office.hiroshima-u.ac.jp
National Institute of Information and Communications Technology Press Office, Public Relations Department Tel: +81-(0)42-327-6923 E-mail: publicity@nict.go.jp
Panasonic Corporation Public Relations Department Tel: +81-(0)3-3574-5664 Fax: +81-(0)3-3574-5699
Media Contact
Norifumi Miyokawa
miyokawa@hiroshima-u.ac.jp
81-824-244-427
http://www.









![[Figure 1] Schematic of next-generation CNT-PANI composite fiber supercapacitor and comparison graph with recent results](https://www.innovations-report.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/KIST_leads_next-generation_energy_storage_technolo_1746783279-e1746784635527-362x245.jpg)


