NASA Sees System 05B Fizzle in Bay of Bengal
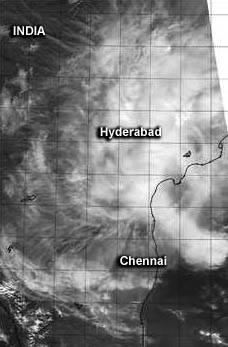
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Cyclone 05B's remnants on Nov. 9 when the center of circulation was still over open waters and the western-most clouds extended north of Chennai. Image Credit: NASA/NRL
The tropical cyclone's western edge spread over land on Sunday, Nov. 9 while the center of the low-level circulation remained over open waters of the Bay of Bengal.
On that day, 05B's remnants were centered near 14.0 north latitude and 83.8 east longitude, about 215 miles east-northeast of Chennai, India.
Infrared imagery from satellites on Nov. 9 indicated that the low-level circulation center of the storm was exposed to outside winds. There was some disorganized deep flaring convection (rising air that forms the thunderstorms that make up a tropical cyclone) and thunderstorm development over the western quadrant, but that didn't last the day.
The storm's circulation center had also become elongated, which is an indication the storm was weakening. Tropical cyclones need to maintain a circular rotation in order to strengthen. When a storm elongates, its rotation can be likened to an automobile tire that is low on air, no longer circular and cannot spin as fast.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Cyclone 05B's remnants on Nov. 9. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument aboard captured a visible image that showed the center of circulation still over open waters of the Northern Indian Ocean/Bay of Bengal, with the western-most clouds north of Chennai.
On Nov. 9, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center noted that Tropical Cyclone 05B had a low chance for regenerating. By Monday, Nov. 10, the remnants of Tropical Cyclone 05B dissipated near 14.0 north longitude and 83.8 east latitude and there is no longer a chance for regeneration.
Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/05b-northern-indian-ocean/All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Machine learning algorithm reveals long-theorized glass phase in crystal
Scientists have found evidence of an elusive, glassy phase of matter that emerges when a crystal’s perfect internal pattern is disrupted. X-ray technology and machine learning converge to shed light…

Mapping plant functional diversity from space
HKU ecologists revolutionize ecosystem monitoring with novel field-satellite integration. An international team of researchers, led by Professor Jin WU from the School of Biological Sciences at The University of Hong…

Inverters with constant full load capability
…enable an increase in the performance of electric drives. Overheating components significantly limit the performance of drivetrains in electric vehicles. Inverters in particular are subject to a high thermal load,…





















