High-Quality Perovskite Materials Developed Capable of Utilizing Long-Wavelength Sunlight
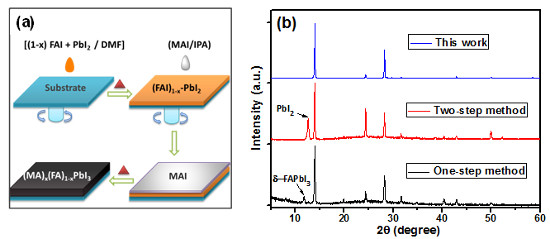
Figure: (a) Fabrication method for a high-quality perovskite material; (b) X-ray diffraction patterns of perovskite materials prepared with different methods. The x-axis represents the intensity of X-ray diffraction while the y-axis denotes the X-ray diffraction angle. Copyright : NIMS
Moving toward the Realization of Low-Cost, High-Efficiency Solar Cells
A NIMS research team led by Liyuan Han, director of the Photovoltaic Materials Unit, has developed the world’s first method to fabricate high-quality perovskite materials capable of utilizing long-wavelength sunlight of 800 nm or longer.
Compared to conventional methods, this method enables the creation of perovskite materials that have a 40-nm wider optical absorption spectrum, a high short-circuit current and high open-circuit voltage. Thus, this method is regarded as a new approach to enhance the efficiency of perovskite solar cells.
The currently available perovskite solar cells possess optical absorption spectra skewed toward shorter wavelengths. To improve the energy conversion efficiency of these cells, it is vital to develop perovskite materials with optical absorption spectra expanded to include longer wavelengths.
Accordingly, several research institutes are developing perovskite materials, (MA)xFA1—xPbI3, which include two types of cations, MA and FA, capable of absorbing light in the longer wavelength region. However, these cations have demerits: their mixing ratio and crystallization temperature are difficult to control. Moreover, due to their tendency to form a mixed crystal phase, there had been no effective method established to fabricate high-purity, single-crystalline perovskite materials.
To resolve these issues, we developed a new method to fabricate a new type of mixed cation-based perovskite material. We first fabricated a pure, single-crystalline precursor material, (FAI)1—xPbI2, under altering temperatures. Then, we performed a reaction between the precursor and MAI (methylammonium iodide).
The resulting perovskite material, (MA)xFA1—xPbI3, was a single crystalline phase and had a long fluorescence lifetime. These observations indicated that electrons in the material rarely recombine and they have long lifetimes. The optical absorption spectrum of the solar cells employing this material covered up to 840 nm, which was 40 nm wider than the spectrum of conventional perovskite material (MA3PbI3). As a result, the solar cells we developed obtained 1.4 mA/cm2 higher short-circuit current than the MAPbI3 solar cells that were manufactured under the same conditions.
In future studies, we intend to develop high-quality perovskite solar cells capable of utilizing a broader spectrum of sunlight by adjusting the ratio of the two cations.
A part of these results were obtained through research activities under the research topic “Device physics of dye-sensitized solar cells” in the research area “Creative research for clean energy generation using solar energy” (Research Supervisor: Masafumi Yamaguchi, Principal Professor, Toyota Technological Institute) specified in the Core Research of Evolutional Science and Technology (CREST) program sponsored by the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST).
Associated links
Original article from NIMS
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.researchsea.comAll latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Bringing bio-inspired robots to life
Nebraska researcher Eric Markvicka gets NSF CAREER Award to pursue manufacture of novel materials for soft robotics and stretchable electronics. Engineers are increasingly eager to develop robots that mimic the…

Bella moths use poison to attract mates
Scientists are closer to finding out how. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids are as bitter and toxic as they are hard to pronounce. They’re produced by several different types of plants and are…

AI tool creates ‘synthetic’ images of cells
…for enhanced microscopy analysis. Observing individual cells through microscopes can reveal a range of important cell biological phenomena that frequently play a role in human diseases, but the process of…





















