Alcohol-free zone
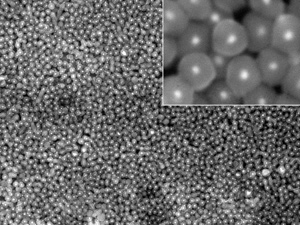
Scanning electron microscopy image showing silica-coated silver nanoparticles produced by a simple and effective alcohol-free process (inset shows high-magnification image). Reproduced, with permission, from Ref. 1 © 2014 Royal Society of Chemistry
Silica-coated noble metal nanoparticles have attracted great interest because they can be used as catalysts as well as in calorimetric and optical applications. They are typically produced using silane precursors, but these are generally insoluble in water. Consequently, alcohol has to be added to water to facilitate the hydrolysis of these precursors, increasing the cost of production and making the process less green.
Now, a team led by Ming-Yong Han and Shah Kwok Wei at the A*STAR Institute of Materials Research and Engineering has devised an alcohol-free method for producing silica-coated noble metal nanoparticles.
To do this, the team took a commonly used precursor, tetramethoxysilane (Si(OCH₃)₄), and substituted a polar group (mercaptopropyl) for a methoxy group (O–CH3), which resulted in a water-soluble precursor. Then, to enable this precursor to bind directly with the metal nanoparticle surfaces, they functionalized it with a thiol group (–SH).
This process has many advantages. It is straightforward to implement, efficient, universal and easily scalable. Furthermore, since the thickness of the silica shell increases with coating time, shell thickness can be readily controlled up to several tens of nanometers.
By slightly modifying the process, Han and colleagues could also produce nanoparticles that have a high activity for an extremely sensitive spectroscopic technique known as surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) and are promising for highly sensitive detection in analytical and biological applications. SERS is based on the hugely enhanced Raman signal generated when a Raman-active compound is adsorbed on a metal surface. The researchers prepared the fluorescence-free SERS-active nanoparticles by sandwiching Raman-active molecules between the noble metal nanoparticle and the silica shell.
“The simplicity of the silica coating process means it has great potential for coating and protecting the surfaces of various kinds of metal nanoparticles,” explains Han. “Furthermore, the resulting highly negatively charged and SERS-active metal nanoparticles with thiol-functionalized silica shells and surface-protective features are very promising for various applications involving aqueous solutions.”
In particular, Han notes, this water-based route to facile, efficient and functional silica coating of metal nanoparticles at room temperature could be extended to coat metal oxide nanoparticles for green building applications.
Reference
[1] Shah, K. W., Sreethawong, T., Liu, S.-H., Zhang, S.-Y., Tan, L. S. & Han, M.-Y. Aqueous route to facile, efficient and functional silica coating of metal nanoparticles at room temperature. Nanoscale 6, 11273–11281 (2014).
Associated links
A*STAR article
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…