Researchers design solids that control heat with spinning superatoms
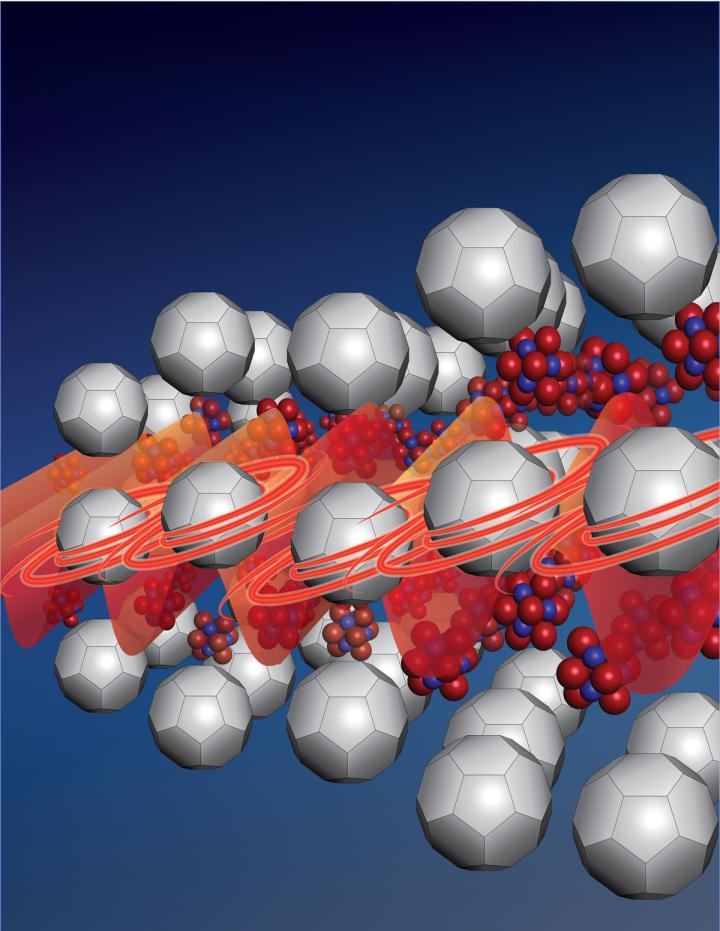
Rotational disorder affects thermal conductivity in superatom crystals. Credit: Ryan Hastie, Department of Chemistry, Columbia University
Researchers found that the thermal conductivity of superatom crystals is directly related to the rotational disorder within those structures. The findings were published in an article in Nature Materials this week.
Carnegie Mellon University's Associate Professor of Mechanical Engineering Jonathan A. Malen was a corresponding author of the paper titled “Orientational Order Controls Crystalline and Amorphous Thermal Transport in Superatomic Crystals.”
Superatom crystals are periodic–or regular–arrangements of C60 fullerenes and similarly sized inorganic molecular clusters. The nanometer sized C60s look like soccer balls with C atoms at the vertices of each hexagon and pentagon.
“There are two nearly identical formations, one that has rotating (i.e. orientationally disordered) C60s and one that has fixed C60s,” said Malen. “We discovered that the formation that contained rotating C60s has low thermal conductivity while the formation with fixed C60s has high thermal conductivity.”
Although rotational disorder is known in bulk C60, this is the first time that the process has been leveraged to create very different thermal conductivities in structurally identical materials.
Imagine a line of people passing sandbags from one end to the other. Now imagine a second line where each person is spinning around–some clockwise, some counter clockwise, some fast, and some slow. It would be very difficult to move a sandbag down that line.
“This is similar to what is happening with thermal conductivity in the superatoms,” explained Malen. “It is easier to transfer heat energy along a fixed pattern than a disordered one.”
Columbia University's Assistant Professor of Chemistry Xavier Roy, the other corresponding author of the study, created the superatom crystals in his laboratory by synthesizing and assembling the building blocks into the hierarchical superstructures.
“Superatom crystals represent a new class of materials with potential for applications in sustainable energy generation, energy storage, and nanoelectronics,” said Roy. “Because we have a vast library of superatoms that can self-assemble, these materials offer a modular approach to create complex yet tunable atomically precise structures.”
The researchers believe that these findings will lead to further investigation into the unique electronic and magnetic properties of superstructured materials. One future application might include a new material that could change from being a thermal conductor to a thermal insulator, opening up the potential for new kinds of thermal switches and transistors.
“If we could actively control rotational disorder, we would create a new paradigm for thermal transport,” said Malen.
For more information, read the Nature Materials article: “Orientational Order Controls Crystalline and Amorphous Thermal Transport in Superatomic Crystals.”
###
Additional Carnegie Mellon investigators included postdoctoral researcher and alumnus Wee-Liat Ong, Patrick S. M. Dougherty, Alan J. H. McGaughey, and C. Fred Higgs. Ong is jointly advised by Malen and Roy as part of a National Science Foundation MRSEC grant led by Columbia University. Other Columbia University researchers included E. O'Brien and D. Paley.
Malen, director of the Malen Laboratory at Carnegie Mellon, received the College of Engineering's Outstanding Research Award in 2016.
About the College of Engineering: The College of Engineering at Carnegie Mellon University is a top-ranked engineering college that is known for our intentional focus on cross-disciplinary collaboration in research. The College is well-known for working on problems of both scientific and practical importance. Our acclaimed faculty have a focus on innovation management and engineering to yield transformative results that will drive the intellectual and economic vitality of our community, nation and world.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Combatting disruptive ‘noise’ in quantum communication
In a significant milestone for quantum communication technology, an experiment has demonstrated how networks can be leveraged to combat disruptive ‘noise’ in quantum communications. The international effort led by researchers…

Stretchable quantum dot display
Intrinsically stretchable quantum dot-based light-emitting diodes achieved record-breaking performance. A team of South Korean scientists led by Professor KIM Dae-Hyeong of the Center for Nanoparticle Research within the Institute for…

Internet can achieve quantum speed with light saved as sound
Researchers at the University of Copenhagen’s Niels Bohr Institute have developed a new way to create quantum memory: A small drum can store data sent with light in its sonic…





















