Red Giant Betelgeuse was yellow some 2,000 years ago
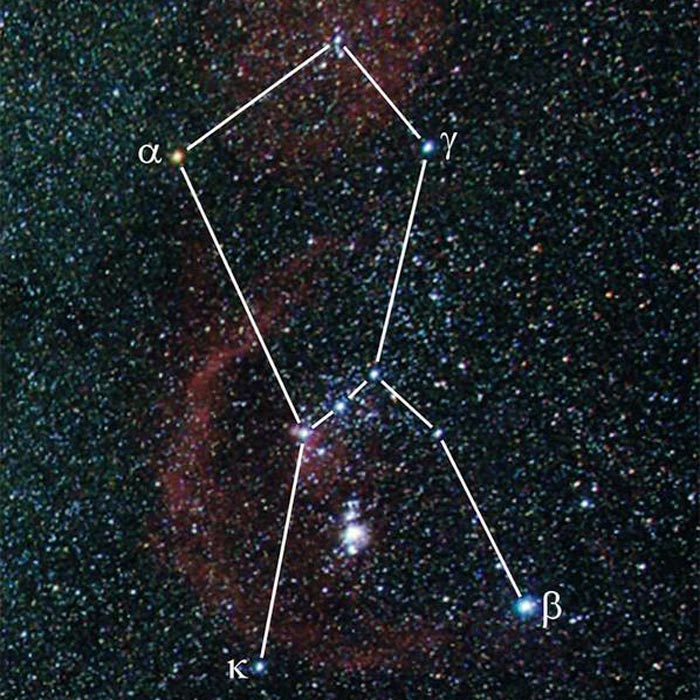
The constellation Orion, Betelgeuse is marked with Alpha.
Image: Markus Mugrauer / University of Jena
Interdisciplinary team around Jena astrophysicist utilized observations from antiquity to prove, that Betelgeuse – the bright red giant star in the upper left of the constellation Orion – was yellow-orange some 2,000 years ago.
With progressing nuclear fusion in the center of a star, brightness, size, and color also change. Astrophysicists can derive from such properties important information on age and mass of a star. Those stars with significantly more mass than our Sun are blue-white or red – the transition from red via yellow and orange is relative rapid for astronomical time-scales. Astrophysicists of Friedrich Schiller University Jena, Germany, together with colleagues of other subjects from the USA and Italy, have now been successful to detect and date such a color change in a bright star. With several historical sources, they found that Betelgeuse – the bright red giant star in the upper left of the constellation Orion – was yellow-orange some 2,000 years ago. They report about their results in the current issue of „Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society“.
Sources from antiquity from around the world
The Chinese court astronomer Sima Qian wrote around 100 BC about star colors: white is like Sirius, red like Antares, yellow like Betelgeuse, blue like Bellatrix. “From these specifications, one can conclude that Betelgeuse at that time was in color between the blue-white Sirius and Bellatrix and the red Antares”, says Prof. Ralph Neuhäuser from the University of Jena. Independent from the above, the Roman scholar Hyginus described some 100 years later that Betelgeuse was in color like the yellow-orange Saturn – thus, one can quantify the former color of Betelgeuse with even more precision. Further authors from antiquity like Ptolemy bring further indications that Betelgeuse at their time did not belong to the group of bright red stars like Antares (in the constellation Scorpion) and Aldebaran (in Taurus, the Bull). The Greek name Antares means „like Mars“ in color, it was indeed reported as red and compared to Mars since millennia from cultures around the world. “From a statement by the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe, one can conclude that, in the 16th century, Betelgeuse was more red than Aldebaran”, as Neuhäuser notes. Today, Betelgeuse is comparable in brightness and color to Antares.
Still 1.5 million years to go until Betelgeuse explodes as supernova
Astronomer Ralph Neuhäuser from Jena includes historical celestial observations in his astrophysical research since some ten years – this field is called „Terra-Astronomy“. He closely collaborates with colleagues from languages, history, and natural philosophy – including his wife Dagmar. “The view back in time delivers strong impulses and important results“, Neuhäuser adds. “There are quite a number of astrophysical problems which can hardly be solved without historical observations.”
What do those historical transmissions tell us about Betelgeuse? “The very fact that it changed in color within two millennia from yellow-orange to red tells us, together with theoretical calculations, that it has 14 times the mass of our Sun – and the mass is the main parameter defining the evolution of stars”, Neuhäuser explains. “Betelgeuse is now 14 million years old and in its late evolutionary phases. In about 1.5 million years, it will finally explode as supernova.”
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Prof. Dr Ralph Neuhäuser
Astrophysical Institute and University Observatory
Friedrich Schiller University Jena
Schillergaesschen 2, 07743 Jena, Germany
Tel.: +49 (0)3641 947500
E-mail: ralph.neuhaeuser@uni-jena.de
www.astro.uni-jena.de
Originalpublikation:
R. Neuhäuser, G. Torres, M. Mugrauer, D. L. Neuhäuser, J. Chapman, D. Luge, M. Cosci: Colour evolution of Betelgeuse and Antares over two millennia, derived from historical records, as a new constraint on mass and age, MNRAS, 2022. DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stac1969
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















