Magnetic quantum crystals
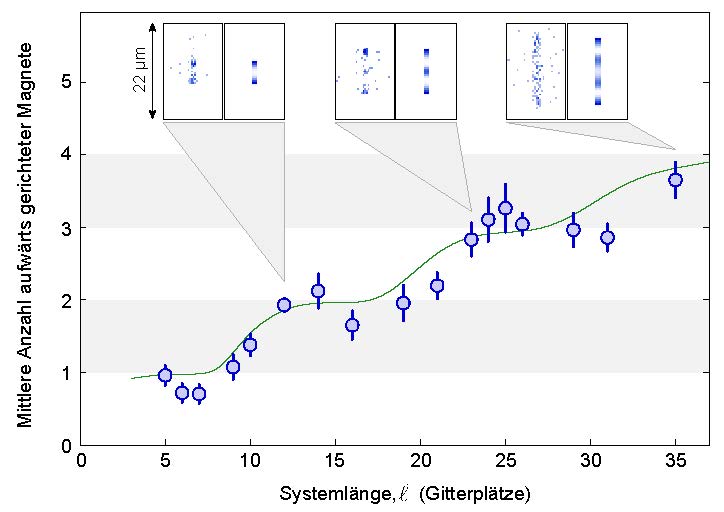
With growing system length the number of upwards oriented magnets rises in steps. The green curve displays the numerical calculations of a group of theoretical physicists around Thomas Pohl. MPQ, Quantum Many-Body Systems Division
Materials with a defined crystal structure are a familiar phenomenon in condensed matter physics. A crystal exhibits a regular structure, due to a periodic repetition of its building blocks. The resulting geometry depends on external parameters such as pressure and temperature, and even more strongly on the type of interaction between the building blocks, for example the Coulomb force or the van der Waals force.
For the first time a team of scientists around Prof. Immanuel Bloch (Director at MPQ und Chair of Experimental Physics at the LMU), in cooperation with theorists from Dresden, have succeeded in generating incompressible magnetic quantum crystals containing several hundred rubidium atoms.
Depending on the shape of the crystal and the strength of the magnetization different geometries are formed. In these experiments the scientists exploit the extremely enhanced interactions between highly excited gigantic Rydberg atoms that have a diameter a thousand times larger than ground state atoms (Science, 27 March 2015).
In their experiment the scientists prepare an ensemble of about 250 to 700 rubidium atoms in an optical lattice – a checkerboard-like pattern of dark and bright spots generated by crosswise superposition of standing laser waves. The number of atoms and the intensity of the laser beam are chosen such that each lattice site is occupied with exactly one atom. For a first series of measurements the scientists cut out a line-shaped segment, for a second series a disc-shaped one.
This procedure resembles the cutting out of cookies from flat dough – but with atomic precision! In the next step the sample gets exposed to laser light that excites single atoms to a so-called Rydberg state. Here the outermost shell electron is located at such a large distance from the atomic nucleus that the radius of the atom is blown up by a factor of about 1000. These huge Rydberg atoms repel each other very strongly even when they are separated by a large distance.
An intriguing question is how the number of Rydberg atoms evolves over time when the laser radiation is changed, and what kind of structures emerge due to the repulsive interactions between them. “The influence of laser light on the state of the atoms can be compared to the magnetization of solid crystals by an external magnetic field in classical physics”, Dr. Christian Groß, leader of the project, explains. “The rubidium atoms play the role of little elementary magnets that have two orientations with respect to the external field. Atoms in the ground state correspond to magnets pointing down, i.e. being aligned with the field, whereas the excited Rydberg atoms are the pendant to magnets pointing upwards.”
In order to flip single magnets classically one would start to rotate the direction of the external field. In the quantum physics experiment, the scientists shift the frequency of the pump laser across the resonance frequency, simultaneously changing the laser power. At different times the radiation is switched off, and the “status quo” of the system is registered. With the technique of fluorescence microscopy single Rydberg atoms can be directly imaged. That way it is possible to trace the formation of the crystal on the microscopic scale.
In addition the scientists investigated how the behaviour changed with the size of the system. This measurement showed a stepwise rise of the magnetization, revealing plateaus with a constant number of Rydberg atoms up to a critical system size – the onset of a new crystal structure (see figure 1). In the plateau regions the system is incompressible as expected for a crystal. For the elongated system the emergence of crystalline states at different steps of magnetization is directly apparent.
“At the beginning of the pulse we observe delocalized Rydberg atoms throughout the cloud characteristic for the magnetically disordered phase in this parameter regime.” Peter Schauß says, doctoral candidate at the experiment. “After a while the upwards oriented magnets gather at the two ends of the elongated cloud. The next steps are characterized by the ordering of further Rydberg atoms in between in regular distances. That way we were able to generate one-dimensional crystals of up to four Rydberg atoms. The measured dynamics of this process agree very well with the theoretical expectation.”
A similar behaviour was observed for the two-dimensional disc-shaped ensemble. As before the geometric structure of the emerging crystal was clearly dependent on the number of Rydberg atoms (figure 2). “In fact, we find a distinct geometry for each magnetization step”, Christian Groß emphasizes. “The spatial orientation of the resulting quantum crystals is not fixed, instead, all possible orientations are superimposed. It is the measurement that determines the orientation that we observe.”
The fragile quantum crystals are interesting not only for their geometry but also for their magnetic properties. Because the interaction between two Rydberg atoms (the upwards oriented magnets) is extremely strong and extends over several lattice sites there are always a couple of ground state atoms in between. This resembles the structure of antiferromagnetic materials (example: manganese-oxide MnO), where, however, every second elementary magnet is oriented opposite to its neighbour.
Considering the short lifetime of Rydberg atoms – they decay after a couple of ten microseconds – the generation of distinct crystal phases made of a few atoms is an amazing experimental success made possible only by the sophisticated methods of high precision steering of atoms developed in the Bloch group. In the future, this technique might be used to explore quantum phase transitions and long-range quantum magnets. The demonstrated level of control over Rydberg many-body systems also is an important step towards the quantum simulation of dynamical gauge theories in high enery physics.
Olivia Meyer-Streng
Original publication:
P. Schauß, J. Zeiher, T. Fukuhara, S. Hild, M. Cheneau, T. Macrì, T. Pohl, I. Bloch, C. Gross
Crystallization in Ising quantum magnets
Science, 27 March 2015
Kontakt:
Prof. Dr. Immanuel Bloch
Lehrstuhl für Quantenoptik, LMU München
Schellingstr. 4, 80799 München
Direktor am Max-Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik
Hans-Kopfermann-Straße 1
85748 Garching b. München
Telefon: +49 (0)89 / 32 905 -138
E-Mail: immanuel.bloch@mpq.mpg.de
Dr. Christian Groß
Max-Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik
Telefon: +49 (0) 89 / 32 905 -713
E-Mail: christian.gross@mpq.mpg.de
Peter Schauß
Max-Planck-Institut für Quantenoptik
Telefon: +49 (0)89 / 32 905 -218
E-Mail: peter.schauss@mpq.mpg.de
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…





















