Ions and Rydberg-atoms: a bond between David and Goliath
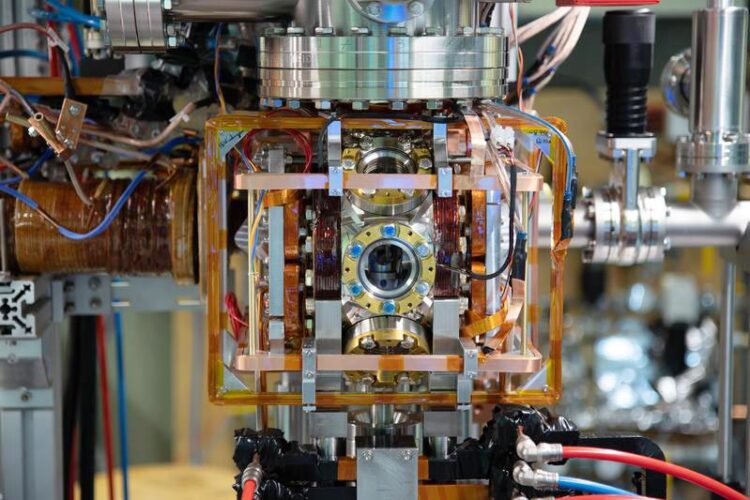
Vacuum chamber. The electric field control and the first lens of the ion microscope are sitting in the center of the chamber.
Credit: Nicolas Zuber / University of Stuttgart
Researchers at the 5th Physical Institute of the University of Stuttgart have verified a novel binding mechanism forming a molecule between a tiny charged particle and in atomic measures gigantic Rydberg atom. The scientists could observe spatially resolved the molecule with the help of a self-build ion microscope. The well-known journal “Nature” published the results on May 18, 2022.
When single particles like atoms and ions bond, molecules emerge. Such bonds between to particles can arise if they have for example opposite electrical charges and hence attract each other. The molecule observed at the University of Stuttgart exhibits a special feature: It consists of a positive electrically charged ion and a neutral atom in a so-called Rydberg state. These Rydberg atoms have grown in size a thousand times compared to typical atoms. As the charge of the ion deforms the Rydberg atom in a very specific way, the bond between the two particles emerges.
Rubidium cloud cooled down close to the absolute zero
To verify and study the molecule, the researchers prepared an ultra-cold rubidium cloud, which was cooled down close to the absolute zero at -273°C. Only at these low temperatures, the force between the particles is strong enough to form a molecule. In these ultra-cold atomic ensembles, the ionization of single atoms with laser fields prepares the first building block of the molecule – the ion. Additional laser beams excite a second atom into the Rydberg state. The electric field of the ion deforms this gigantic atom. Interestingly the deformation can be attractive or repulsive depending on the distance between the two particles, letting the binding partners oscillate around an equilibrium distance and inducing the molecular bond. The distance between the binding partners is unusually large and amounts to about the tenth of the thickness of a human hair.
Microscopy with the aid of electric fields
A special ion microscope made this observation possible. It was developed, build and commissioned by the researches at the 5th Physical Institute in close collaboration with the workshops of the University Stuttgart. In contrast to typical microscopes working with light, the device influences the dynamics of charged particles with the help of electrical fields to magnify and image the particles onto a detector. “We could image the free floating molecule and its constituents with this microscope and directly observe and study the alignment of this molecule in our experiment”, explains Nicolas Zuber, PhD student at the 5th Physical Institute, the results.
In a next step, the researchers want to study dynamical processes within this unusual molecule. With the help of the microscope, it should be possible to study vibrations and rotations of the molecul. Because of its gigantic size and the weak binding of the molecule, the dynamical processes are slower compared to usual molecules. The research group hopes to gain new and more detailed knowledge about the inner structure of the molecule.
Originalpublikation:
Nicolas Zuber, Viraatt S. V. Anasuri, Moritz Berngruber, Yi-Quan Zou, Florian Meinert, Robert Löw, Tilman Pfau: “Observation of a molecular bond between ions and Rydberg atoms”, Nature 2022 05 18, DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-04577-5,
Weitere Informationen:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-04577-5 article in Nature
https://www.uni-stuttgart.de/en/university/news/all/Ions-and-Rydberg-atoms-a-bon… Press Release University of Stuttgart
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Machine learning algorithm reveals long-theorized glass phase in crystal
Scientists have found evidence of an elusive, glassy phase of matter that emerges when a crystal’s perfect internal pattern is disrupted. X-ray technology and machine learning converge to shed light…

Mapping plant functional diversity from space
HKU ecologists revolutionize ecosystem monitoring with novel field-satellite integration. An international team of researchers, led by Professor Jin WU from the School of Biological Sciences at The University of Hong…

Inverters with constant full load capability
…enable an increase in the performance of electric drives. Overheating components significantly limit the performance of drivetrains in electric vehicles. Inverters in particular are subject to a high thermal load,…





















