Latest News

Computer predicts reactions between molecules and surfaces, with 'chemical precision'
An international team of researchers, headed by Leiden theoretical chemist Geert-Jan Kroes, published on this subject this week in the journal Science. Hydrogen on copper…

DNA molecules in moss open door to new biotechnology
Researchers from Uppsala University in Sweden have now demonstrated that plasmid-based methods, which had been limited to single-cell organisms such as…
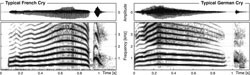
Babies with an accent
In the first days of their lives, French infants already cry in a different way to German babies. This was the result of a study by researchers from the Max…

Nitrogen loss threatens desert plant life
“This is a way that nitrogen is lost from an ecosystem that people have never accounted for before,” said Jed Sparks, associate professor of ecology and…

Researchers find new way to attack inflammation in Graves' eye disease
A small group of patients with severe Graves' eye disease experienced rapid improvement of their symptoms — and improved vision — following treatment with the…

Ants are friendly to some trees, but not others
The research, published in the November issue of the American Naturalist, is the first to document that ants bore into live trees, and it reopens a…