Latest News

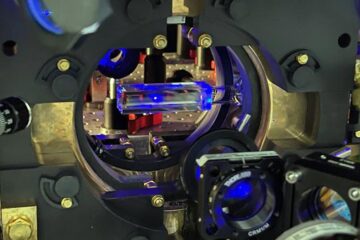
New analysers to unlock mineral value
Scientists are working on a new range of materials characterisation analysers and techniques that could help unlock the value contained in Australia’s mineral…

Heart disease: B vitamin pills have no effect
“There is no evidence to support the use of B-vitamins as supplements for reducing the risk of heart attack, stroke or death associated with cardiovascular…

Area-wide traffic calming improves safety — but will it work in low- and middle-income countries?
Each year, 1.23 million people die in road traffic accidents. Over the next decade, road deaths are expected to rise particularly sharply in low- and…

Genome sequence published for important biofuels yeast
A strain of yeast that thrives on turning sugar cane into ethanol for biofuel has had its genome completely sequenced by researchers at Duke University Medical…

Albatross camera reveals fascinating feeding interaction with killer whale
A miniature digital camera was attached to the backs of four black-browed albatrosses (Thalassarche melanophrys) breeding at colonies on Bird Island, South…

Fewer hikers means less support for conservation
Oliver Pergams, visiting research assistant professor of biological sciences at the University of Illinois at Chicago, and Patricia Zaradic, director of the…