Latest News

Ohio University alumnus receives Nobel Prize in Chemistry
Ramakrishnan attended Ohio University's graduate physics program starting in 1971, earning his Ph.D. in 1976. After completing his doctorate Ramakrishnan…

Alfalfa sprouts key to discovering how meandering rivers form and maintain
Sinuous, meandering streams produce diverse and wildlife-rich habitats and are the aim of many river restoration efforts, but until now, the bank, water flow…

Homebound termites answer 150-year-old evolution question
Staying at home may have given the very first termite youngsters the best opportunity to rule the colony when their parents were killed by their neighbors….

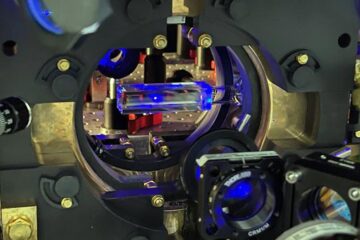
For future superconductors, a little bit of lithium may do hydrogen a lot of good
Scientists have a long and unsuccessful history of attempting to convert hydrogen to a metal by squeezing it under incredibly high and steady pressures.Metallic hydrogen is predicted to be a high-temperature superconductor. A superconductor is a state of matter where electrons, and thus electricity, can flow indefinitely and without resistance….

New analysers to unlock mineral value
Scientists are working on a new range of materials characterisation analysers and techniques that could help unlock the value contained in Australia’s mineral…

Heart disease: B vitamin pills have no effect
“There is no evidence to support the use of B-vitamins as supplements for reducing the risk of heart attack, stroke or death associated with cardiovascular…