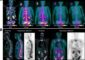
MR angiography highly accurate in detecting blocked arteries

“Contrast-enhanced MR angiography provided highly accurate information about the supra-aortic arteries,” said Kambiz Nael, M.D., research fellow and radiology resident at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA in Los Angeles. “MR angiography produced results comparable to the gold standard of digital subtraction angiography (DSA) and multidetector computed tomography (CT) angiography. In addition, this technology produced images with higher resolution over a larger field of view in a shorter amount of time than previous contrast-enhanced MR angiography techniques,” he said.
Arterial occlusive disease consists of narrowed or blocked arteries. It commonly affects the supra-aortic arteries, which supply blood to the brain, and is a leading cause of stroke. Currently DSA is the reference standard for evaluating these arteries. However, in 2.5 percent of cases DSA can cause a mini-stroke, and, in rare instances, permanent neurological damage. Therefore, CT and MR angiography are increasingly being used to diagnose arterial occlusive disease. As technology has improved, MR angiography offers advantages over CT, particularly because it delivers no ionizing radiation to the patient.
“MR angiography, using a small quantity of MRI dye injected into a vein in the arm, can produce detailed images of the arteries supplying the brain and can detect even minor degrees of narrowing or blockage. It does not involve exposure to x-rays and is widely regarded as a very safe, painless test,” Dr. Nael said.
The researchers studied 80 patients (44 men and 36 women) with suspected arterial occlusive disease to compare the performance of contrast-enhanced MR angiography to DSA and CT angiography. Two independent readers evaluated the images. Blockages were detected with MR angiography in 208 (reader 1) and 218 (reader 2) segments of artery, which correlated significantly to the DSA and CT findings. In addition, MR angiography proved highly accurate (94 to 100 percent) for detecting blockages of over 50 percent, and image quality was rated sufficient to excellent for 97 percent of the arterial segments evaluated.
“This procedure should be highly cost effective for clinical use, because of the speed and modest dose of contrast required,” Dr. Nael said. “In the absence of contraindications to MRI, I would recommend MR angiography over DSA and CTA for routine use—avoiding increased risk of mini-stroke and radiation exposure.”
Dr. Nael predicts that in most cases, contrast-enhanced MR angiography could replace other diagnostic techniques for evaluation of all the arteries that supply blood to the brain.
“As the technology evolves, MR angiography will likely become even faster and more powerful,” he said.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.rsna.orgAll latest news from the category: Medical Engineering
The development of medical equipment, products and technical procedures is characterized by high research and development costs in a variety of fields related to the study of human medicine.
innovations-report provides informative and stimulating reports and articles on topics ranging from imaging processes, cell and tissue techniques, optical techniques, implants, orthopedic aids, clinical and medical office equipment, dialysis systems and x-ray/radiation monitoring devices to endoscopy, ultrasound, surgical techniques, and dental materials.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…