Scientists observe role of cavitation in glass fracturing
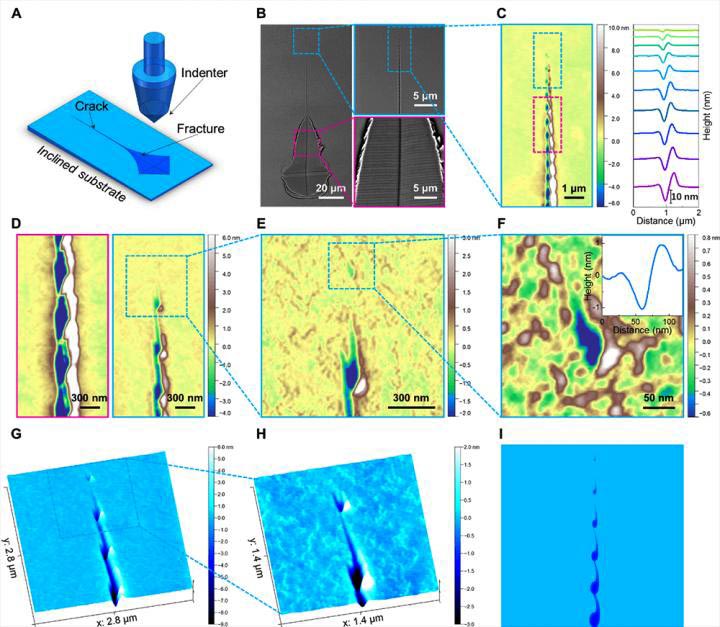
Fig. 1. Observation of the cavitation-dominated crack propagation in a metallic glass.
Credit: Institute of Physics
Glassy materials play an integral role in the modern world, but inherent brittleness has long been the Achilles’ heel that severely limits their usefulness. Due to the disordered amorphous structure of glassy materials, many mysteries remain. These include the fracture mechanisms of traditional glasses, such as silicate glasses, as well as the origin of the intriguing patterned fracture morphologies of metallic glasses.
Cavitation has been widely assumed to be the underlying mechanism governing the fracture of metallic glasses, as well as other glassy systems. Up until now, however, scientists have been unable to directly observe the cavitation behavior of fractures, despite their intensive efforts.
This situation changed with recent work by Dr. SHEN Laiquan, Prof. BAI Haiyang, Prof. SUN Baoan, and others from Prof. WANG Weihua’s group at the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), who have successfully observed the effect of cavitation on fracture behavior in glasses. They revealed that crack propagation is dominated by the self-organized nucleation, growth, and coalescence of nanocavities in metallic glasses.
They showed the evolutionary process of crack morphologies from separated nanocavities to wave-like nanocorrugations, and confirmed that cavitation is the origin of periodic fracture surface patterns.
In addition, they found that cavitation-induced nanopatterns are also prevalent in typical polymer glass (polycarbonate) and silicate glass (silica), indicating that the cavitation mechanism is common in the fracture of glasses. Plastic flow exhibited by the cavitation process thus proves that nanoscale ductility is involved in the breakage of nominally brittle glasses.
The discovery of cavitation behavior in the fracture of glasses challenges the traditional concept of how glasses break. The researchers’ findings have significant implications for the understanding of the fundamental process of failure in disordered systems, and provides incentives for engineering better glasses.
###
This study, entitled “Observation of cavitation governing fracture in glasses,” was published in Science Advances.
The work was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of CAS, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Research and Development Program, and the National Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province.
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















