Researchers design superhydrophobic 'nanoflower' for biomedical applications
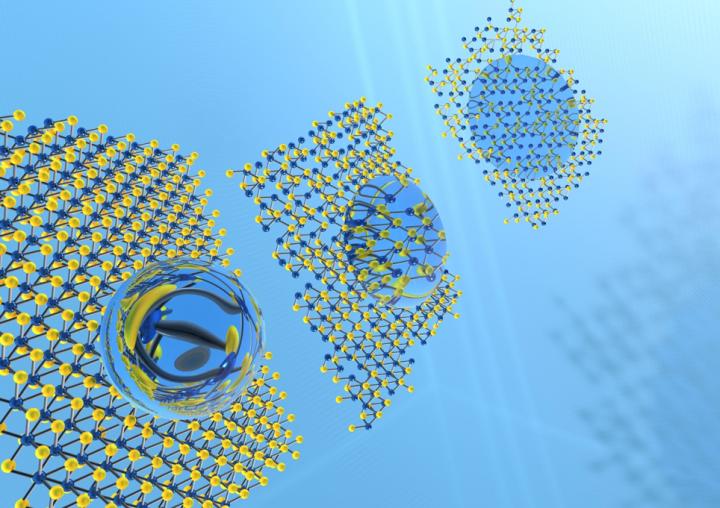
Dr. Akhilesh K. Gaharwar, assistant professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering, introduces a new concept to control the wetting characteristics by modulating atomic defects in 2D nanomaterials. This work sheds new light on the role of atomic vacancies on wetting characteristic that can be leveraged to develop superhydrophobic surfaces for biomedical applications. Credit: Texas A&M University
Plant leaves have a natural superpower — they're designed with water repelling characteristics. Called a superhydrophobic surface, this trait allows leaves to cleanse themselves from dust particles. Inspired by such natural designs, a team of researchers at Texas A&M University has developed an innovative way to control the hydrophobicity of a surface to benefit to the biomedical field.
Researchers in Dr. Akhilesh K. Gaharwar's lab in the Department of Biomedical Engineering have developed a “lotus effect” by incorporating atomic defects in nanomaterials, which could have widespread applications in the biomedical field including biosensing, lab-on-a-chip, blood-repellent, anti-fouling and self-cleaning applications.
Superhydrophobic materials are used extensively for self-cleaning characteristic of devices. However, current materials require alteration to the chemistry or topography of the surface to work. This limits the use of superhydrophobic materials.
“Designing hydrophobic surfaces and controlling the wetting behavior has long been of great interest, as it plays crucial role in accomplishing self-cleaning ability,” Gaharwar said. “However, there are limited biocompatible approach to control the wetting behavior of the surface as desired in several biomedical and biotechnological applications.”
The Texas A&M design adopts a 'nanoflower-like' assembly of two-dimensional (2D) atomic layers to protect the surface from wetting. The team recently released a study published in Chemical Communications. 2D nanomaterials are an ultrathin class of nanomaterials and have received considerable attention in research. Gaharwar's lab used 2D molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), a new class of 2D nanomaterials that has shown enormous potential in nanoelectronics, optical sensors, renewable energy sources, catalysis and lubrication, but has not been investigated for biomedical applications. This innovative approach demonstrates applications of this unique class of materials to the biomedical industry.
“These 2D nanomaterials with their hexagonal packed layer repel water adherence, however, a missing atom from the top layer can allow easy access to water molecules by the next layer of atoms underneath making it transit from hydrophobic to hydrophilic,” said lead author of the study, Dr. Manish Jaiswal, a senior research associate in Gaharwar's lab.
This innovative technique opens many doors for expanded applications in several scientific and technological areas. The superhydrophobic coating can be easily applied over various substrates such as glass, tissue paper, rubber or silica using the solvent evaporation method. These superhydrophobic coatings have wide-spread applications, not only in developing self-cleaning surfaces in nanoelectronics devices, but also for biomedical applications. Specifically, the study demonstrated that blood and cell culture media containing proteins do not adhere to the surface, which is very promising. In addition, the team is currently exploring the potential applications of controlled hydrophobicity in stem cell fate.
###
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health Director's New Innovator Award by the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Superradiant atoms could push the boundaries of how precisely time can be measured
Superradiant atoms can help us measure time more precisely than ever. In a new study, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval,…

Ion thermoelectric conversion devices for near room temperature
The electrode sheet of the thermoelectric device consists of ionic hydrogel, which is sandwiched between the electrodes to form, and the Prussian blue on the electrode undergoes a redox reaction…

Zap Energy achieves 37-million-degree temperatures in a compact device
New publication reports record electron temperatures for a small-scale, sheared-flow-stabilized Z-pinch fusion device. In the nine decades since humans first produced fusion reactions, only a few fusion technologies have demonstrated…





















