Atomic Layer Pushes Surface Steps Away
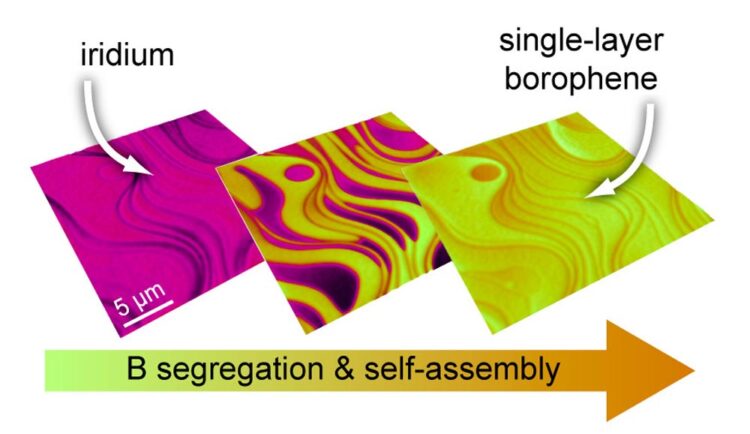
Image sequence showing the evolution from the pure iridium surface (left, pink) to the fully borophen-covered surface of the sample (right, yellow-orange).
© UDE/Petrović
Synthesis of Large-Area 2D Material …
Elbow mentality in a two-dimensional material: This has recently been discovered by an international team led by the Center for Nanointegration (CENIDE) at the University of Duisburg-Essen (UDE): The physicists succeeded in creating boron layers with a height of a single atom. While growing, the material simply pushes interfering steps on the substrate out of the way. The team published its results in the scientific journal ACS Nano.
The team led by UDE’s Prof. Michael Horn-von Hoegen aims at producing the thinnest possible layer of boron, so-called borophene, since it promises properties that could enable the construction of two-dimensional transistors. The molecular beam epitaxy used for this purpose until now results in domains that are far too small. For more precise investigations and for use in technology, however, larger areas are needed.
With their newly developed method of “segregation-enhanced epitaxy”, the team uses borazine gas and an iridium substrate. The essential components of borazine are boron and nitrogen atoms that are arranged in a hexagonal honeycomb structure. By heating the iridium sample in a borazine-containing environment, the boron molecules attach themselves to the surface, followed by the evaporation of the nitrogen.
Above 1100°C, the boron moves into the iridium, because at such high temperatures the iridium can absorb additional boron atoms like a sponge – up to a quarter of its own volume. When the system has cooled down, borophene – the single-atom layer of boron – precipitates on the surface of the iridium crystal. In the process, it does not grow beyond surface steps of the underlying crystal but pushes them away in all directions to form areas as large as possible.
Next Step: Detachment
Experts from the Interdisciplinary Center for Analytics on the Nanoscale (ICAN), led by Professor Frank-J. Meyer zu Heringdorf, were able to prove beyond doubt that the areas are exclusively composed of boron atoms and that the nitrogen has disappeared from the sample.
In a next step, the researchers want to investigate how the borophene can be detached from the iridium substrate.
The publication was a result of a collaboration with physicists from the University of Cologne and the Center of Excellence for Advanced Materials and Sensing Devices in Zagreb (Croatia).
Editor: Birte Vierjahn, +49 203/37 9-8176, birte.vierjahn@uni-due.de
Wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner:
Prof. Dr. Michael Horn- von Hoegen, Experimental Physics, +49 203/37 9-1438, horn-von-hoegen@uni-due.de
Originalpublikation:
K.M. Omambac, M. Petrović, P. Bampoulis, C. Brand, M.A. Kriegel, P. Dreher, D. Janoschka, U. Hagemann, N. Hartmann, P. Valerius, T. Michely, F.J. Meyer zu Heringdorf, M. Horn-von Hoegen
„Segregation-Enhanced Epitaxy of Borophene on Ir(111) by Thermal Decomposition of Borazine“
ACS Nano, published online March 24, 2021
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c00819
https://www.uni-due.de/2021-04-26-synthesis-of-large-area-borophene
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Silicon Carbide Innovation Alliance to drive industrial-scale semiconductor work
Known for its ability to withstand extreme environments and high voltages, silicon carbide (SiC) is a semiconducting material made up of silicon and carbon atoms arranged into crystals that is…

New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification
…offers increased access for prostate cancer patients. A novel SPECT/CT acquisition method can accurately detect radiopharmaceutical biodistribution in a convenient manner for prostate cancer patients, opening the door for more…

How 3D printers can give robots a soft touch
Soft skin coverings and touch sensors have emerged as a promising feature for robots that are both safer and more intuitive for human interaction, but they are expensive and difficult…