World-first discovery of cornea T cells
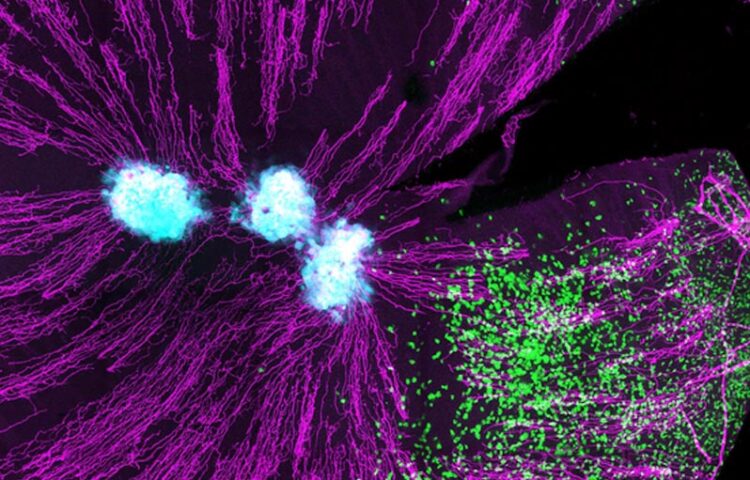
Immune cells (T cells, green) can be see entering the cornea of the eye, towards the Herpes Simplex virus infected cells (light blue). The eye is rich in nerves (purple).
Credit: Doherty Institute
… protecting eyes from viral infections.
The cornea – the transparent protective outer layer of the eye critical to helping us see – produces a delicate and limited immune response to fight infections without damaging our vision, according to a ground-breaking new study from the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute).
Published today in Cell Reports, the study has shown long-living memory T cells that patrol and fight viral infections are present in the cornea, upending current thought that T cells are not found in healthy corneas – expanding our understanding of the eye’s immune response to infections.
The team used a multiphoton microscope that provides live images of living, intact biological tissues to study cornea cells in mice infected with Herpes Simplex Virus.
Their images revealed long-living memory T cells produced in the mice’s eyes to fight the infection. The memory T cells remained in the cornea after the virus was eliminated to ward off any future reinfection.
Advanced imaging of the eye in healthy people also revealed immune cells patrolling the cornea – the first time that cells have been imaged moving in human eyes.
For humans to see, the cornea must remain transparent to ensure focused light is received by the retina through the iris.
The presence of T cells in the corneas was previously not considered, given the eyes produce only a dampened immune response to avoid inflammation that would obstruct our vision.
Lead author University of Melbourne Professor Scott Mueller, laboratory head at the Doherty Institute said that these discoveries have important implications for understanding how eyes ward off dangerous infections.
“Current understanding that T cells are not found in healthy corneas needs to be reconsidered, as our discovery shows tissue-resident memory T cells entering the cornea and remaining there for long periods,” Professor Mueller said.
“Our findings will improve the understanding of how to protect our eyes from infections that cause permanent blindness, such as Herpes Simplex Virus.
“This also has implications for understanding chronic conditions such as dry eye disease and common eye allergies where unwanted T cells might also cause disease.”
This study was conducted in collaboration with the University of Melbourne’s Department of Optometry and Vision Sciences and Department of Anatomy and Neuroscience, and Monash University’s Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences.
Journal: Cell Reports
Method of Research: Experimental study
Subject of Research: Animals
Article Title: Corneal tissue resident memory T cells form a unique immune compartment at the ocular surface
Article Publication Date: 25-May-2022
Media Contact
Thomas Fraser
The Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity
thomas.fraser1@unimelb.edu.au
Cell: +61 (0) 401 312 634
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Properties of new materials for microchips
… can now be measured well. Reseachers of Delft University of Technology demonstrated measuring performance properties of ultrathin silicon membranes. Making ever smaller and more powerful chips requires new ultrathin…

Floating solar’s potential
… to support sustainable development by addressing climate, water, and energy goals holistically. A new study published this week in Nature Energy raises the potential for floating solar photovoltaics (FPV)…

Skyrmions move at record speeds
… a step towards the computing of the future. An international research team led by scientists from the CNRS1 has discovered that the magnetic nanobubbles2 known as skyrmions can be…





















